nutritional and functional properties of whey and lactose
nutritional and functional properties of whey and lactose
nutritional and functional properties of whey and lactose
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
NUTRITIONAL PROPERTIES OF WHEY PRODUCTS<br />
The composition <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>whey</strong> products varies<br />
considerably, depending<br />
on milk source <strong>and</strong> the<br />
manufacturing process<br />
involved. In general, <strong>whey</strong><br />
is rich in proteins, <strong>lactose</strong>,<br />
minerals <strong>and</strong> vitamins.<br />
The proteins in milk <strong>and</strong><br />
<strong>whey</strong> are complete <strong>and</strong><br />
<strong>of</strong> exceptional quality.<br />
They contain, in varying<br />
amounts <strong>and</strong> in the<br />
right proportion, all the<br />
amino acids required by<br />
humans. They are also<br />
readily digestible <strong>and</strong><br />
completely bio-available.<br />
Clearly, <strong>whey</strong> proteins<br />
are among the most<br />
valuable component <strong>of</strong><br />
<strong>whey</strong>. In many cases,<br />
<strong>whey</strong> products are used<br />
for their <strong>nutritional</strong><br />
benefits as they are<br />
a very cost-efficient<br />
source <strong>of</strong> protein,<br />
carbohydrate<br />
<strong>and</strong> minerals<br />
such as<br />
calcium.<br />
PROTEINS<br />
The proteins in <strong>whey</strong> are easily digested<br />
<strong>and</strong> contain all the essential amino acids<br />
in the proper proportions, <strong>and</strong> they rate<br />
as an excellent <strong>nutritional</strong> source.<br />
Using the Protein Digestibility-Corrected<br />
Amino Acid Scoring (PDCAAS) method,<br />
<strong>whey</strong> protein rates a value <strong>of</strong> 1.0 because<br />
it is highly digestible <strong>and</strong> it meets or<br />
exceeds the recommended amount<br />
<strong>of</strong> each essential amino acid.<br />
Using another method to measure<br />
protein quality—the Protein Efficiency<br />
Ratio (PER) value—<strong>whey</strong> also ranks high<br />
on the scale. The higher the PER value,<br />
the better the protein. Casein, the reference<br />
protein, has a PER value <strong>of</strong> 2.5.<br />
Proteins with a PER greater than 2.5<br />
are considered to be quality proteins.<br />
Whey protein, with a PER greater than<br />
3.0, is considered to be a <strong>nutritional</strong>ly<br />
excellent protein.<br />
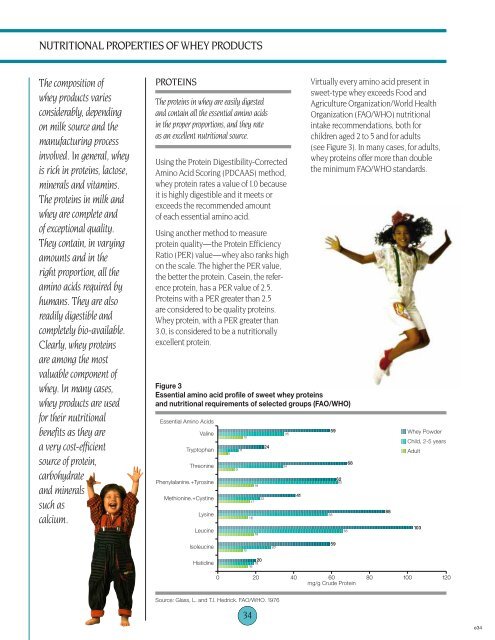
Figure 3<br />
Essential amino acid pr<strong>of</strong>ile <strong>of</strong> sweet <strong>whey</strong> proteins<br />
<strong>and</strong> <strong>nutritional</strong> requirements <strong>of</strong> selected groups (FAO/WHO)<br />
Essential Amino Acids<br />
Valine<br />
Tryptophan<br />
Threonine<br />
Phenylalanine.+Tyrosine<br />
Methionine.+Cystine<br />
Lysine<br />
Leucine<br />
5<br />
9<br />
11<br />
13<br />
17<br />
16<br />
19<br />
19<br />
22<br />
24<br />
35<br />
34<br />
41<br />
Virtually every amino acid present in<br />
sweet-type <strong>whey</strong> exceeds Food <strong>and</strong><br />
Agriculture Organization/World Health<br />
Organization (FAO/WHO) <strong>nutritional</strong><br />
intake recommendations, both for<br />
children aged 2 to 5 <strong>and</strong> for adults<br />
(see Figure 3). In many cases, for adults,<br />
<strong>whey</strong> proteins <strong>of</strong>fer more than double<br />
the minimum FAO/WHO st<strong>and</strong>ards.<br />
59<br />
58<br />
62<br />
63<br />
66<br />
68<br />
88<br />
Whey Powder<br />
Child, 2-5 years<br />
Adult<br />
103<br />
Isoleucine<br />
13<br />
28<br />
59<br />
Histidine<br />
20<br />
19<br />
16<br />
0<br />
20<br />
40<br />
60<br />
mg/g Crude Protein<br />
80<br />
100<br />
120<br />
Source: Glass, L. <strong>and</strong> T.I. Hedrick. FAO/WHO. 1976<br />
34<br />
e34