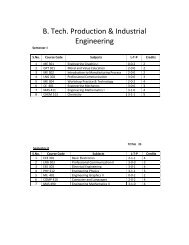
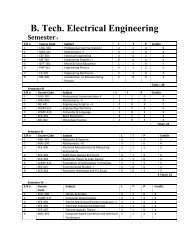
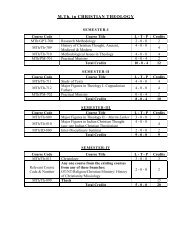
M. Sc. BIOCHEMISTRY - Shiats.edu.in
M. Sc. BIOCHEMISTRY - Shiats.edu.in
M. Sc. BIOCHEMISTRY - Shiats.edu.in
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Unit I: Chromatography: Adsorption, partition, exclusion, ion exchange, aff<strong>in</strong>ity, H.P.L.C., G.L.C.,column.Unit II: Biosensors: Types and uses.Unit III: Centrifugation Techniques: Differential, zonal and density gradient, ultra, types ofcentrifuges and applications.Unit IV: Electrophoresis: Pr<strong>in</strong>ciples and applications, paper, gel, S.D.S., P.A.G.E., P.F.G.E.,Isoelectric hosphor.Unit V: Molecular Biology Techniques: Isolation and purification of DNA, RNA, plasmid DNA,sequenc<strong>in</strong>g of prote<strong>in</strong>s and nucleic acids, chemical synthesis of nucleotides, competent cellpreparation and transformation, DNA foot pr<strong>in</strong>t<strong>in</strong>g, DNA f<strong>in</strong>gerpr<strong>in</strong>t<strong>in</strong>g, PCR.Unit VI: Immunological Techniques: RIA, ELISA, flow cytometry.Unit VII: Radio isotopic and tracer techniques: Detection and measurement of isotopes (GM andsc<strong>in</strong>tillation counters), autoradiography.Practicals:1. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of pH us<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>dicators.2. The separation of am<strong>in</strong>o acids by paper electrophoresis.3. The validity of Beer’s law for the colorimetric estimation of creat<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>.4. Total chlorophyll estimation from the plant sample.5. Prote<strong>in</strong> estimation- A. Biuret method, B. Lowry’s method.6. Estimation of nucleic acid by electrophoresis.BCBT 813 Enzyme Technology 3(2-0-1)Unit1: Introduction of enzymes:General properties and significance, classification andnomenclature.Terms and def<strong>in</strong>ition <strong>in</strong> enzymology, co-factors, coenzymes, active site concept,isoenzymes, allosteric enzymes, marker enzymes, multienzyme complex, ribozyme, abzyme,synzyme, extremozyme, therapeutic enzymes and immobilized enzymes etc.Unit 2: Enzyme k<strong>in</strong>etics:steady rate k<strong>in</strong>etics, Derivation of Michaelis-menten equation us<strong>in</strong>g steadystate/equilibrium k<strong>in</strong>etics, plots of l<strong>in</strong>eweaver- Bruke, Hanes, Eadie- Hofster etc. Mechanism ofbisubstrate and multisubstrate enzyme catalyzed reaction, Enzyme <strong>in</strong>hibitors, mechanism of enzymeaction-lysozyme, chymotryps<strong>in</strong>, alcohol DH.Unit 3: Regulation of enzyme activity: Covalent modification, allosteric model concerted andsequential, cooperativity. Feedback <strong>in</strong>hibition.Unit 4:Enzyme Technology: Commercial production of enzymes, immobilization of enzymes,example of enzyme eng<strong>in</strong>eer<strong>in</strong>g, application of enzyme(therapeutic uses, analytical uses,manipulated uses etc.), uses of enzyme reactors.Unit 5: Isolation, purification and localization of enzymes. Various methods to estimate the enzymeactivity.Practical:1. Effect of temperature, pH, substrate concentration and enzyme concentration and enzymeconcentration on enzyme activity.2. Action of salivary amylase on starch.3. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of acid posphatase activity <strong>in</strong> sample.4. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of alkal<strong>in</strong>e phosphatase activity <strong>in</strong> sample.5. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of SGOT<strong>in</strong> serum.6. Determ<strong>in</strong>ation of SGPT <strong>in</strong> serum.