Stromwandler - 3-K-Elektrik
Stromwandler - 3-K-Elektrik
Stromwandler - 3-K-Elektrik
Erfolgreiche ePaper selbst erstellen
Machen Sie aus Ihren PDF Publikationen ein blätterbares Flipbook mit unserer einzigartigen Google optimierten e-Paper Software.
Technische Information <strong>Stromwandler</strong><br />
Technical Information Current Transformers<br />
Offenbetrieb von <strong>Stromwandler</strong>n<br />
Open-Circuit-Operation of Current Transformers<br />
Der Ausgang von <strong>Stromwandler</strong>n entspricht prinzipiell einer Konstantstromquelle.<br />
Bei zunehmender BŸrde erhšht sich daher die Ausgangsspannung<br />
entsprechend der Beziehung U=R . I, bis SŠttigung<br />
erreicht wird. (Hierin ist auch enthalten, dass sich die Ausgangsspannung<br />
ebenso mit dem PrimŠrstrom entsprechend seinem †bersetzungsverhalten<br />
erhšht!) Diese SŠttigung findet Ihre Ursache in der<br />
SŠttigungsinduktion, also dem Verlauf der B-H-Kennlinie des als<br />
Kernmaterial verwendeten Eisens.<br />
Oberhalb der SŠttigung steigt die Spannung an den SekundŠranschlŸssen<br />
des <strong>Stromwandler</strong>s bei zunehmender Verzerrung weiter<br />
an und erreicht ihren Maximalwert bei unendlich gro§er BŸrde, also<br />
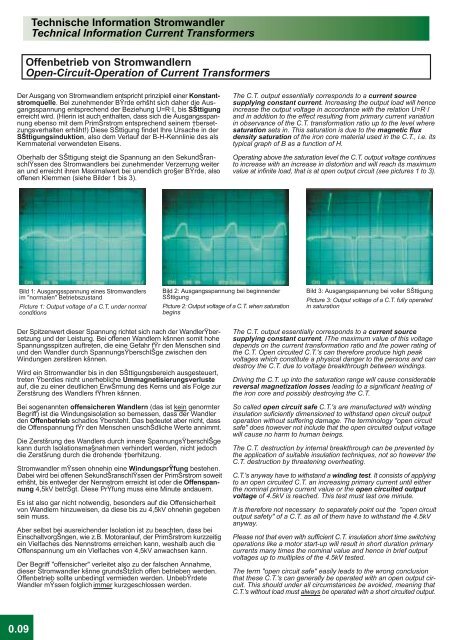
offenen Klemmen (siehe Bilder 1 bis 3).<br />
Bild 1: Ausgangsspannung eines <strong>Stromwandler</strong>s<br />
im "normalen" Betriebszustand<br />
Picture 1: Output voltage of a C.T. under normal<br />
conditions<br />
Der Spitzenwert dieser Spannung richtet sich nach der WandlerŸbersetzung<br />
und der Leistung. Bei offenen Wandlern kšnnen somit hohe<br />
Spannungsspitzen auftreten, die eine Gefahr fŸr den Menschen sind<br />
und den Wandler durch SpannungsŸberschlŠge zwischen den<br />
Windungen zerstšren kšnnen.<br />
Wird ein <strong>Stromwandler</strong> bis in den SŠttigungsbereich ausgesteuert,<br />
treten Ÿberdies nicht unerhebliche Ummagnetisierungsverluste<br />
auf, die zu einer deutlichen ErwŠrmung des Kerns und als Folge zur<br />
Zerstšrung des Wandlers fŸhren kšnnen.<br />
Bei sogenannten offensicheren Wandlern (das ist kein genormter<br />
Begriff) ist die Windungsisolation so bemessen, dass der Wandler<br />
den Offenbetrieb schadlos Ÿbersteht. Das bedeutet aber nicht, dass<br />
die Offenspannung fŸr den Menschen unschŠdliche Werte annimmt.<br />
Die Zerstšrung des Wandlers durch innere SpannungsŸberschlŠge<br />
kann durch Isolationsma§nahmen verhindert werden, nicht jedoch<br />
die Zerstšrung durch die drohende †berhitzung.<br />
<strong>Stromwandler</strong> mŸssen ohnehin eine WindungsprŸfung bestehen.<br />
Dabei wird bei offenen SekundŠranschlŸssen der PrimŠrstrom soweit<br />
erhšht, bis entweder der Nennstrom erreicht ist oder die Offenspannung<br />
4,5kV betrŠgt. Diese PrŸfung muss eine Minute andauern.<br />
Es ist also gar nicht notwendig, besonders auf die Offensicherheit<br />
von Wandlern hinzuweisen, da diese bis zu 4,5kV ohnehin gegeben<br />
sein muss.<br />
Aber selbst bei ausreichender Isolation ist zu beachten, dass bei<br />
EinschaltvorgŠngen, wie z.B. Motoranlauf, der PrimŠrstrom kurzzeitig<br />
ein Vielfaches des Nennstroms erreichen kann, weshalb auch die<br />
Offenspannung um ein Vielfaches von 4,5kV anwachsen kann.<br />
Der Begriff "offensicher" verleitet also zu der falschen Annahme,<br />
dieser <strong>Stromwandler</strong> kšnne grundsŠtzlich offen betrieben werden.<br />
Offenbetrieb sollte unbedingt vermieden werden. UnbebŸrdete<br />
Wandler mŸssen folglich immer kurzgeschlossen werden.<br />
0.09<br />
Bild 2: Ausgangsspannung bei beginnender<br />
SŠttigung<br />
Picture 2: Output voltage of a C.T. when saturation<br />
begins<br />
The C.T. output essentially corresponds to a current source<br />
supplying constant current. Increasing the output load will hence<br />
increase the output voltage in accordance with the relation U=R . I<br />
and in addition to the effect resulting from primary current variation<br />
in observance of the C.T. transformation ratio up to the level where<br />
saturation sets in. This saturation is due to the magnetic flux<br />
density saturation of the iron core material used in the C.T., i.e. its<br />
typical graph of B as a function of H.<br />
Operating above the saturation level the C.T. output voltage continues<br />
to increase with an increase in distortion and will reach its maximum<br />
value at infinite load, that is at open output circuit (see pictures 1 to 3).<br />
Bild 3: Ausgangsspannung bei voller SŠttigung<br />
Picture 3: Output voltage of a C.T. fully operated<br />
in saturation<br />
The C.T. output essentially corresponds to a current source<br />
supplying constant current. IThe maximum value of this voltage<br />
depends on the current transformation ratio and the power rating of<br />
the C.T. Open circuited C.T.'s can therefore produce high peak<br />
voltages which constitute a physical danger to the persons and can<br />
destroy the C.T. due to voltage breakthrough between windings.<br />
Driving the C.T. up into the saturation range will cause considerable<br />
reversal magnetization losses leading to a significant heating of<br />
the iron core and possibly destroying the C.T.<br />
So called open circuit safe C.T.'s are manufactured with winding<br />
insulation suficiently dimensioned to withstand open circuit output<br />
operation without suffering damage. The terminology "open circuit<br />
safe" does however not include that the open circuited output voltage<br />
will cause no harm to human beings.<br />
The C.T. destruction by internal breakthrough can be prevented by<br />
the application of suitable insulation techniques, not so however the<br />
C.T. destruction by threatening overheating.<br />
C.T.'s anyway have to withstand a winding test. It consists of applying<br />
to an open circuited C.T. an increasing primary current until either<br />
the nominal primary current value or the open circuited output<br />
voltage of 4.5kV is reached. This test must last one minute.<br />
It is therefore not necessary to separately point out the "open circuit<br />
output safety" of a C.T. as all of them have to withstand the 4.5kV<br />
anyway.<br />
Please not that even with sufficient C.T. insulation short time switching<br />
operations like a motor start-up will result in short duration primary<br />
currents many times the nominal value and hence in brief output<br />
voltages up to multiples of the 4.5kV tested.<br />
The term "open circuit safe" easily leads to the wrong conclusion<br />
that these C.T.'s can generally be operated with an open output circuit.<br />
This should under all circumstances be avoided, meaning that<br />
C.T.'s without load must always be operated with a short circuited output.