Download PowerPoint-Präsentation - Institut für Radiologie ...
Download PowerPoint-Präsentation - Institut für Radiologie ...
Download PowerPoint-Präsentation - Institut für Radiologie ...
Erfolgreiche ePaper selbst erstellen
Machen Sie aus Ihren PDF Publikationen ein blätterbares Flipbook mit unserer einzigartigen Google optimierten e-Paper Software.
Großer Kurs Skelettdiagnostik<br />
Seronegative<br />
Spondyloarthritiden<br />
Matthias Bollow<br />
<strong>Institut</strong> <strong>für</strong> f r diagnostische und interventionelle<br />
<strong>Radiologie</strong> und Nuklearmedizin<br />
Augusta-Kranken<br />
Kranken-Anstalt Bochum<br />
www. radiologie-ruhrgebiet.de<br />
ruhrgebiet.de
Seronegative<br />
Spondyloarthritiden
Spondyloarthritiden<br />
Prävalenz:<br />
1,9 %<br />
Braun J, Bollow M, et al. Prevalence of SpA in HLA-B27<br />
B27-positive<br />
and -negativ blood donors. Arthritis Rheum 1998; 41: 58-67
Prototyp „ankylosierende Spondylitis“: : Invalidisierung nach Erkrankungsdauer von ca. 10 Jahren<br />
19
Die europäischen Väter V<br />
der<br />
ankylosierenden Spondylitis<br />
Deutschland<br />
Frankreich<br />
Russland
Spinale Manifestationen der Spondyloarthritiden<br />
• Bandscheiben und<br />
Wirbelkörperabschlussplatten<br />
• Wirbelkörperrandleisten<br />
• Facettengelenke<br />
• Rippen-Wirbel-Gelenke<br />
• Spinale Ligamente<br />
• Sakroiliakalgelenke
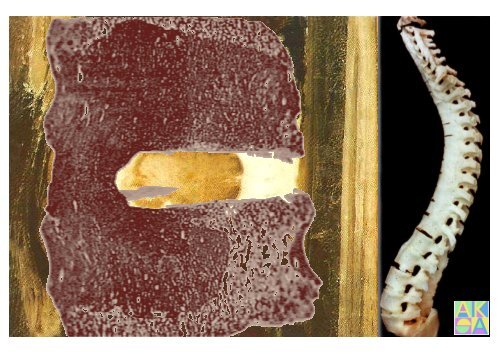
erosive aseptische Spondylodiszitis<br />
„entzündliche ndliche Andersson-Läsion<br />
sion“<br />
*Hermann KGA, Bollow M. Diagnostik der Spondyloarthritiden am Achsenskelett. <strong>Radiologie</strong> up2date 2009; 3: 205 - 228<br />
*Hermann KG, Bollow M. MRI of axial skeleton in rheumatic diseases. Bailliere´s Best Practice & Research Clinical Rheumatology 2004; 18: 881-907<br />
*Bollow M. Magnetresonanztomographie bei ankylosierender Spondylitis. Fortschr Röntgenstr 2002; 174: 1489-1499<br />
Andersson O. Röntgenbilden R<br />
vid spondylarthris ankylopoetica. Nord Med Tidskr 1937; 14: 2000-3<br />
*Bollow M, Enzweiler C, et al. Use of contrast enhanced MRI to detect spinal inflammation in patients with SpA. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2002; 20: 167-174
BWK 11<br />
Entzündliche<br />
ndliche Andersson-Läsion<br />
sion<br />
BWK 12
entzündliche<br />
ndliche Andersson-Läsion<br />
sion
Entzündungsmuster: ndungsmuster: entzündliche<br />
ndliche Andersson-Läsion<br />
sion<br />
floride Diszitis<br />
floride Spondylodiszitis<br />
ausgebrannte Spondylodiszitis<br />
transdiskale Ankylosierung<br />
Mohr W. Pathomorphologie der AS. Novartis Pharma Verl. 2001
ankylosierende Spondylitis „AS“ mit bambusstabartiger Wirbelsäulen<br />
ulen-Ankylose
Dihlmann W, Delling G. Disco-vertebral destructive lesions (so called Andersson lesions) associated with ankylosing spondylitis. Skeletal Radiol 1978; 3: 10-15<br />
transdiskale Ermüdungsbr<br />
dungsbrüche:<br />
„nicht entzündliche<br />
ndliche“ Andersson-Läsionen<br />
sionen
Dihlmann W, Delling G. Disco-vertebral destructive lesions (so called Andersson lesions) associated with ankylosing spondylitis. Skeletal Radiol 1978; 3: 10-15<br />
nicht entzündliche<br />
ndliche Andersson-Läsion<br />
sion
Spinale Manifestationen der Spondyloarthritiden<br />
• Bandscheiben und<br />
Wirbelkörperabschlussplatten<br />
• Wirbelkörperrandleisten<br />
• Facettengelenke<br />
• Rippen-Wirbel-Gelenke<br />
• Spinale Ligamente<br />
• Sakroiliakalgelenke
Veränderungen der Wirbelkörper<br />
rper-Randleisten<br />
1<br />
12<br />
2<br />
12<br />
12<br />
12<br />
12<br />
3<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
1<br />
4<br />
5<br />
T1wTSE<br />
T2wTSE<br />
STIR<br />
T1wGRE KM
T2wTSE<br />
T1wTSE<br />
T1wGRE KM<br />
STIR<br />
Spondylitis<br />
anterior<br />
„Romanus“<br />
Romanus R, Yden S. Destructive and ossifying spondylitic changes in rheumatoid ankylosing spondylitis. Acta Orthop Scand 1952; 22: 89-99<br />
99
Spondylitis marginalis<br />
Spondylitis posterior
„ausgebrannte und sklerosierte“ Spondylitis marginalis
Enthesitis<br />
Enthesiophyt<br />
Prädiskaler Syndesmophyt<br />
2004 2005 2008 2010<br />
normale<br />
Randleisten<br />
floride<br />
Spondylitis anterior<br />
ausgebrannte<br />
Spondylitis anterior<br />
modellierter<br />
Syndesmophyt
Anulus fibrosus-<br />
Syndesmophyt<br />
Spondylitis anterior mit „Shiny Corners“ zum Kastenwirbel
Periostale Appositionen und subperiostale Ossifikationen bei AS<br />
Normwirbel<br />
konkav<br />
Kastenwirbel<br />
gerade<br />
Tonnenwirbe<br />
konvex<br />
l
1. Stierhorntyp<br />
2<br />
1<br />
3<br />
2. Paradiskale Knochenspange<br />
1<br />
1<br />
3. Paradiskales Ossikel<br />
2<br />
1<br />
2<br />
Parasyndesmophyten
Paradiskale Knochenspangen<br />
Spondylitis psoriatica
Spinale Manifestationen der Spondyloarthritiden<br />
• Bandscheiben und<br />
Wirbelkörperabschlussplatten<br />
• Wirbelkörperrandleisten<br />
• Facettengelenke<br />
• Rippen-Wirbel-Gelenke<br />
• Spinale Ligamente<br />
• Sakroiliakalgelenke
Facettengelenke und ihre Enthesen an der HWS
Facettengelenke und ihre Enthesen an der LWS
MRT-Entz<br />
Entzündungsmuster ndungsmuster der Facettengelenk-Enthesen<br />
post-KM<br />
FS<br />
Norm<br />
physiologisches<br />
„Late<br />
Enhancement“<br />
floride Enthesitis<br />
ausgebrannte Enthesitis<br />
+ transartikuläre<br />
re Brücken<br />
komplette Ankylosierung
Spinale Manifestationen der Spondyloarthritiden<br />
• Bandscheiben und<br />
Wirbelkörperabschlussplatten<br />
• Wirbelkörperrandleisten<br />
• Facettengelenke<br />
• Rippen-Wirbel-Gelenke<br />
• Spinale Ligamente<br />
• Sakroiliakalgelenke<br />
Articulatio costotransversaria<br />
Articulatio<br />
capitis costae
Doughnut-Zeichen<br />
Enthesitis der Articulatio capitis costae /Articulatio<br />
costotransversaria
destruierende Enthesitiden: Articulatio capitis costae et costotransversaria
Transversale Entzündungsmuster ndungsmuster der Articulatio capitis costae und Articulatio o costotransversaria<br />
von der Norm<br />
zur Ankylose<br />
Enthesitis<br />
Enthesitis mit Osteitis<br />
Osteitis mit Fettakkumulationen<br />
transartikuläre<br />
re Knochenbrücken<br />
cken<br />
komplette Ankylose<br />
komplette Ankylose
Spinale Manifestationen der Spondyloarthritiden<br />
• Bandscheiben und<br />
Wirbelkörperabschlussplatten<br />
• Wirbelkörperrandleisten<br />
• Facettengelenke<br />
• Rippen-Wirbel-Gelenke<br />
• Spinale Ligamente<br />
• Sakroiliakalgelenke<br />
*Hermann<br />
*Hermann KG, Bollow M. Diagnostik der Spondyloarthritiden am Achsenskelett. <strong>Radiologie</strong> up2date 2009; 3: 205-28<br />
28<br />
*Hermann KG, Eshed I, Bollow M. Bildgebung der Enthesitis. Fortschr Röntgenstr R<br />
2006; 178: 578-589<br />
589<br />
*Eshed I, *Bollow M, et al. MRI of enthesitis of appendicular skeleton in SpA. Ann Rheum Dis 2007; 66: 1553-9
Enthese<br />
Enthesitis<br />
Enthesiophyt<br />
Enthesitis der Ligamenta interspinalia
Enthesitis der Ligamenta supraspinalia
Enthesitiden der Ligamenta flava und der Facettengelenkkapseln
Enthesitiden und Enthesiophyten der Ligamenta flava<br />
Mohr W. Pathomorphologie der AS. Novartis Pharma Verl. 2001
Enthesiophyten: Ligamenta supra- / interspinalia / flava
R<br />
L<br />
ankylosiernde Spondylitis an der HWS
Spinale Manifestationen der Spondyloarthritiden<br />
• Bandscheiben und<br />
Wirbelkörperabschlussplatten<br />
• Wirbelkörperrandleisten<br />
• Facettengelenke<br />
• Rippen-Wirbel-Gelenke<br />
• Spinale Ligamente<br />
• Sakroiliakalgelenke
Radiographisches Scoring der Sakroiliitis<br />
IV<br />
III<br />
II<br />
I<br />
*Dale K. Radiograph grading of sacroiliitis in Bechterew´s s syndrome a. allied disorders. Scan J Rheumatol 1980; 100: 92-97<br />
97
Nachteile der CT<br />
CT-<br />
Scoring<br />
I<br />
II<br />
Strahlenexposition<br />
der<br />
fehlende Kriterien<br />
Sakroiliitis<br />
<strong>für</strong> r akute Stadien<br />
Fam AB, et al. CT in the<br />
diagnosis of early ankylosing<br />
spondylitis.<br />
Arthritis Rheum 1983; 26:<br />
930-937<br />
937<br />
III<br />
IV<br />
Hermann KGA, Bollow M.<br />
Diagnostik der<br />
Spondyloarthritiden<br />
am Achsenskelett.<br />
<strong>Radiologie</strong> up2date 2009; 3:<br />
205-228<br />
228
MR-Anatomie<br />
der Sakroiliakalgelenke<br />
*Bollow M, Braun J, Hermann KG. Sakroiliakalgelenk. In: MRT des Bewegungsapparates. Vahlensieck M, Reiser M (Hrsg.) 3. Auflage. Thieme Verlag 2006<br />
*Hermann KG, Braun J, Fischer T, Reißhauer H, Bollow M. MRT der Sakroiliitis: Anatomie, Pathohistologie, ie, MR-Morphologie Morphologie und Graduierung. Radiologe 2004; 44; 217-228<br />
228<br />
*Bollow M, Braun J, et al. Normal morphology of sacroiliac joints s in children: magnetic resonance studies related to age and sex. . Skeletal Radiol 1997; 26: 697-704<br />
704
MR-Anatomie der Sakroiliakalgelenke:<br />
` articular ' fibrocartilaginous entheses<br />
*Bollow M, Braun J, Hermann KG. Sakroiliakalgelenk. . In: MRT des Bewegungsapparates. Vahlensieck M, Reiser M (Hrsg.) 3. Auflage. Thieme Verlag 2006<br />
*Hermann KG, Braun J, Fischer T, Reißhauer H, Bollow M. MRT der Sakroiliitis: : Anatomie, Pathohistologie, MR-Morphologie<br />
Morphologie und Graduierung. Radiologe 2004; 44; 217-228<br />
228<br />
*Bollow M, Braun J, et al. Normal morphology of sacroiliac joints in children: magnetic resonance studies related to age and sex. Skeletal Radiol 1997; 26: 697-704<br />
704
Normale Sakroiliakalgelenke
Sakroiliitis: chronische Stadien<br />
metaplastisches Knorpelgewebe<br />
Knorpelinseln<br />
zelluläre Infiltrationen<br />
Knochenneubildungen<br />
Angioneogenese<br />
Asbestfaserung<br />
Blasen- / SäulenknorpelS<br />
*Bollow M, Braun J, Hamm B, et al. Early sacroiliitis in patients s with spondylarthropathy: evaluation with dynamic Gd-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 1995; 194: 529-536<br />
536<br />
*Bollow M, Fischer T, et al. Quantitative analysis of sacroiliac biopsies in spondyloarthropathies. Ann Rheum Dis 2000; 59: 135-140<br />
140<br />
*Muche B, Bollow M, et al. Anatomical structures involved in early<br />
ly- and late-stage sacroiliitis in SpA. Arthritis Rheum 2003; 48: 1374-1384<br />
1384
Bollow M, et al. Intraarticular corticosteroid injection into the e SIJ using CT guidance in patients<br />
with SpA: indication and follow-up with contrast-enhanced MRI. J CAT 1996; 20: 512-521<br />
Chronizitäts<br />
ts-Score<br />
IV<br />
521
Chronizitäts<br />
ts-Score III
Chronizitäts<br />
ts-Score II
Chronizitäts<br />
ts-Score I
*Bollow M, Braun J, Hamm B, et al. Early sacroiliitis in patients with SpA: evaluation with dynamic Gd-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 1995; 194: 529-536<br />
*Muche B, Bollow M, et al. Anatomical structures involved in early- and late-stage sacroiliitis in SpA. Arthritis Rheum 2003; 48: 1374-1384<br />
*Bollow M, Hermann KGA, et al. Very early spondyloarthritis: where the inflammation in the sacroiliac joints starts. Ann Rheum Dis 2005; 64: 1644-1646<br />
Sakroiliitis: : akute Stadien
Sakroiliitis: : akute Stadien
Angioneogenese<br />
Goldner<br />
Fibroblasten-Proliferate mit Knorpelinfiltration<br />
Lakunen<br />
*Bollow M, Braun J, Hamm B, et al. Early sacroiliitis in patients with spondylarthropathy: evaluation with dynamic Gd-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology 1995; 194: 529-536<br />
*Bollow M, Braun J, Biedermann T, et al. Use of contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging to detect sacroiliitis in children. Skeletal Radiol 1998; 27: 606-616<br />
*Bollow M, Fischer T, et al. Quantitative analysis of sacroiliac biopsies in spondyloarthropathies. Ann Rheum Dis 2000; 59: 135-140<br />
*Muche B, Bollow M, et al. Anatomical structures involved in early- and late-stage sacroiliitis in SpA. Arthritis Rheum 2003; 48: 1374-1384<br />
*Bollow M, Hermann KGA, et al. Very early spondyloarthritis: where the inflammation in the sacroiliac joints starts. Ann Rheum Dis 2005; 64: 1644-1646
CD68+-Makrophagen<br />
Immunohistologie<br />
CD3+-T-Lymphozyten<br />
TNFα mRNA<br />
*Braun J, Bollow M, et al. Use of immunohistologic and in situ hybridization techniques in the examination of sacroiliac joint biopsy<br />
specimens from patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum 1995; 38: 499-505<br />
*Braun J, Sieper J. Anti-TNFalpha: a new dimension in the pharmacotherapy of the spondyloarthropathies.Ann Rheum Dis 2000; 59: 404-7
vor Anti-TNF-♋<br />
nach Anti-TNF-<br />
♋
Aktivitäts<br />
ts-Score:<br />
Semiquantitative Vierquadranten-Methode<br />
*Bollow M , Braun J , Hermann KG . Sakroiliakalgelenk. In: MRT des Bewegungsapparates. Vahlensieck M, Reiser M (Hrsg.) 3. Auflage. Thieme Verlag 2006<br />
*Hermann KG, Braun J, Fischer T, Reißhauer H, Bollow M. MRT der Sakroiliitis: Anatomie, Pathohistologie, MR-Morphologie u. Graduierung. Radiologe 2004; 44; 217-28
Aktivitäts<br />
ts-Score<br />
pro Quadrant<br />
0 keine Veränderungen<br />
1 1<br />
1 1 4<br />
4 4<br />
4<br />
1 ≤ 10% des Quadranten<br />
(Gelenkraum, Erosionen, Kapsel;<br />
kein Knochenmark !)<br />
2 11-33% des Quadranten<br />
3 34-66% des Quadranten<br />
4 > 66% des Quadranten<br />
rechts: 4 links: 16
Sakroiliitis: Scoring<br />
7/08: 0/0 II/16<br />
5/10: II/4 III/6
Seronegative<br />
Spondyloarthritiden<br />
..