2.3 Prozesse und Prozessmodelle 2.3.2 ARIS Modellierung
2.3 Prozesse und Prozessmodelle 2.3.2 ARIS Modellierung
2.3 Prozesse und Prozessmodelle 2.3.2 ARIS Modellierung
Sie wollen auch ein ePaper? Erhöhen Sie die Reichweite Ihrer Titel.
YUMPU macht aus Druck-PDFs automatisch weboptimierte ePaper, die Google liebt.
Angewandte Informatik (Wirtschaftsinformatik)<br />
Gr<strong>und</strong>lagen Wirtschaftsinformatik I<br />
<strong>2.3</strong> <strong>Prozesse</strong> <strong>und</strong> <strong>Prozessmodelle</strong><br />
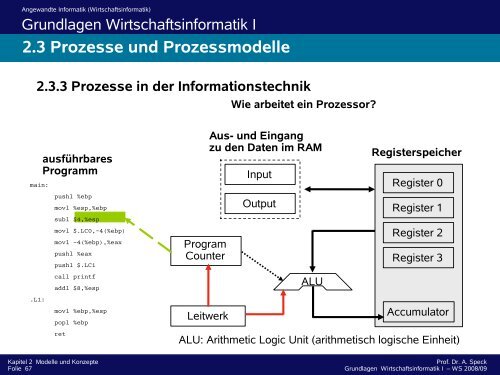
<strong>2.3</strong>.3 <strong>Prozesse</strong> in der Informationstechnik<br />
main:<br />
.L1:<br />
ausführbares<br />
Programm<br />
pushl %ebp<br />
movl %esp,%ebp<br />
subl $4,%esp<br />
movl $.LC0,-4(%ebp)<br />
movl -4(%ebp),%eax<br />
pushl %eax<br />
pushl $.LC1<br />
call printf<br />
addl $8,%esp<br />
movl %ebp,%esp<br />
popl %ebp<br />
ret<br />
Kapitel 2 Modelle <strong>und</strong> Konzepte<br />
Folie 67<br />
Program<br />
Counter<br />
Leitwerk<br />
Wie arbeitet ein Prozessor?<br />
Aus- <strong>und</strong> Eingang<br />
zu den Daten im RAM<br />
Input<br />
Output<br />
ALU<br />
Registerspeicher<br />
Register 0<br />
Register 1<br />
Register 2<br />
Register 3<br />
Accumulator<br />
ALU: Arithmetic Logic Unit (arithmetisch logische Einheit)<br />
Prof. Dr. A. Speck<br />
Gr<strong>und</strong>lagen Wirtschaftsinformatik I – WS 2008/09