- Page 1 and 2:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 3 and 4:
Editors Prof. Wilfred Isioma Ukpere
- Page 5 and 6:
Electronic submission of manuscript
- Page 7 and 8:
Fees and Charges: Authors are requi
- Page 9 and 10:
Table of Contents: Volume 5 Number
- Page 11 and 12:
Table of Contents: Volume 5 Number
- Page 13 and 14: Table of Contents: Volume 5 Number
- Page 15 and 16: Table of Contents: Volume 5 Number
- Page 17 and 18: 7166 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. the high
- Page 19 and 20: 7168 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Cargo mov
- Page 21 and 22: 7170 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. has produ
- Page 23 and 24: 7172 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. resources
- Page 25 and 26: 7174 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. celebrate
- Page 27 and 28: 7176 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. effective
- Page 29 and 30: 7178 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. interacti
- Page 31 and 32: 7180 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. firstly,
- Page 33 and 34: 7182 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. TQM pract
- Page 35 and 36: 7184 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. with lowe
- Page 37 and 38: 7186 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. in a diff
- Page 39 and 40: African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 41 and 42: 7190 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Decision
- Page 43 and 44: 7192 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. restructu
- Page 45 and 46: 7194 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Performan
- Page 47 and 48: 7196 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. firm perf
- Page 49 and 50: African Journal Of Business Managem
- Page 51 and 52: 7200 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. to establ
- Page 53 and 54: 7202 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. marketing
- Page 55 and 56: 7204 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. initial a
- Page 57 and 58: 7206 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. from the
- Page 59 and 60: 7208 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Phillips
- Page 61 and 62: 7210 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. of the sa
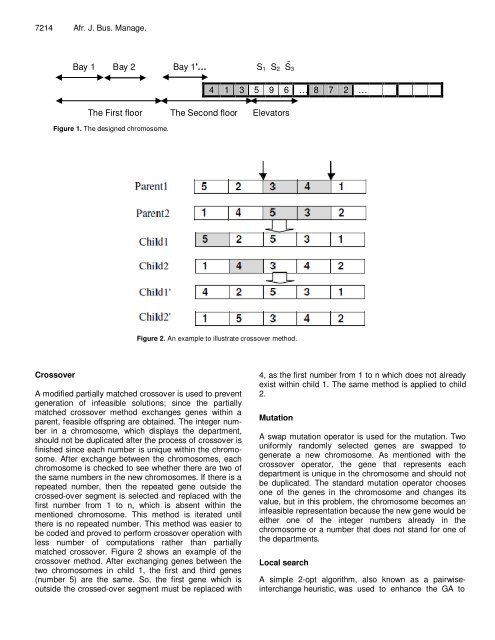
- Page 63: 7212 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. ′ w k m
- Page 67 and 68: African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 69 and 70: 7218 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Figure 2.
- Page 71 and 72: 7220 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. stimulate
- Page 73 and 74: 7222 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. these com
- Page 75 and 76: African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 77 and 78: 7226 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Figure 1.
- Page 79 and 80: 7228 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 2.
- Page 81 and 82: 7230 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Figure 4.
- Page 83 and 84: African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 85 and 86: 7234 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. CRM resea
- Page 87 and 88: 7236 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 2.
- Page 89 and 90: 7238 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. The one a
- Page 91 and 92: African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 93 and 94: 7242 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. and Norto
- Page 95 and 96: 7244 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 1.
- Page 97 and 98: 7246 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 5.
- Page 99 and 100: African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 101 and 102: 7250 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. DEFINING
- Page 103 and 104: 7252 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 1.
- Page 105 and 106: 7254 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 2.
- Page 107 and 108: 7256 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. critical
- Page 109 and 110: African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 111 and 112: 7260 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. external
- Page 113 and 114: 7262 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. represent
- Page 115 and 116:
7264 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 1.
- Page 117 and 118:
7266 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 3.
- Page 119 and 120:
7268 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 4.
- Page 121 and 122:
7270 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. business
- Page 123 and 124:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 125 and 126:
7274 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Satisfact
- Page 127 and 128:
7276 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Score of
- Page 129 and 130:
7278 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 2.
- Page 131 and 132:
7280 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 4.
- Page 133 and 134:
7282 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Satisfact
- Page 135 and 136:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 137 and 138:
7286 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 1.
- Page 139 and 140:
7288 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 3.
- Page 141 and 142:
7290 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 6.
- Page 143 and 144:
7292 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. determine
- Page 145 and 146:
7294 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 1.
- Page 147 and 148:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 149 and 150:
7298 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Procedure
- Page 151 and 152:
7300 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 2.
- Page 153 and 154:
7302 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Figure 1.
- Page 155 and 156:
7304 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 5.
- Page 157 and 158:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 159 and 160:
7308 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. required
- Page 161 and 162:
7310 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. This obse
- Page 163 and 164:
7312 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 3.
- Page 165 and 166:
7314 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 5.
- Page 167 and 168:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 169 and 170:
7318 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. expectati
- Page 171 and 172:
7320 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Compensat
- Page 173 and 174:
7322 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 1.
- Page 175 and 176:
7324 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Psychol.,
- Page 177 and 178:
7326 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. the resea
- Page 179 and 180:
7328 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Z( T, whe
- Page 181 and 182:
7330 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. (10) and
- Page 183 and 184:
7332 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. during wh
- Page 185 and 186:
7334 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. optimal v
- Page 187 and 188:
7336 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. satisfact
- Page 189 and 190:
7338 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 2.
- Page 191 and 192:
7340 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. female re
- Page 193 and 194:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 195 and 196:
7344 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Populatio
- Page 197 and 198:
7346 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 2.
- Page 199 and 200:
7348 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Figure 1.
- Page 201 and 202:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 203 and 204:
7352 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. ln S = ln
- Page 205 and 206:
7354 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Figure 1.
- Page 207 and 208:
7356 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. but some
- Page 209 and 210:
7358 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. investiga
- Page 211 and 212:
7360 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. when conf
- Page 213 and 214:
7362 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. PCs in a
- Page 215 and 216:
7364 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. supported
- Page 217 and 218:
7366 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Psychol.,
- Page 219 and 220:
7368 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. social pr
- Page 222 and 223:
Table 2. Companies and countries co
- Page 224 and 225:
to CSR clearly and reliably. The st
- Page 226 and 227:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 228 and 229:
consumers to participate with the t
- Page 230 and 231:
A Liao 7379 Figure 1. Example of ev
- Page 232 and 233:
Table 3. Summary statistics of the
- Page 234 and 235:
Table 5. Utilities for subject 1 Li
- Page 236 and 237:
REFERENCES Anderson JC, Narus JA (1
- Page 238 and 239:
7386 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. aggregate
- Page 240 and 241:
7388 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Analysis
- Page 242 and 243:
7390 Afr. J. Bus. Manage. Table 4.
- Page 244 and 245:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 246 and 247:
(Bass and Avolio, 1994). Leaders fo
- Page 248 and 249:
the employees. When employees are e
- Page 250 and 251:
Table 1. Means, standard deviation
- Page 252 and 253:
negativity in the organization. Tra
- Page 254 and 255:
of psychological ownership. Thus te
- Page 256 and 257:
Meyer JP, Becker TE, Vandenberghe C
- Page 258 and 259:
goods industry in the future. LITER
- Page 260 and 261:
F + 2 0. 110 * F + Table 3. Factor
- Page 262 and 263:
APPENDIX Data for evaluation on the
- Page 264 and 265:
anks. Camanho and Dyson (2005) enha
- Page 266 and 267:
Step A-4: Correlation analysis Star
- Page 268 and 269:
Table 1. Original raw data of input
- Page 270 and 271:
Table 5. Scenario table. Wang and W
- Page 272 and 273:
Delmas M, Toka Y (2005). Deregulati
- Page 274 and 275:
Technology managers need to attract
- Page 276 and 277:
λ is the parameter for risk aversi
- Page 278 and 279:
specified ranges of return, for eac
- Page 280 and 281:
Carlsson C, Fulle´r R, Majlender P
- Page 282 and 283:
Stock Exchange, (Rao, 2010) in Nati
- Page 284 and 285:
etween size and unsystematic risk i
- Page 286 and 287:
The research schema Figure 1 indica
- Page 288 and 289:
Table 3. Result of Freidman rank te
- Page 290 and 291:
Table 8. The result of Spearman cor
- Page 292 and 293:
significant differences between the
- Page 294 and 295:
leadership. The process of manageri
- Page 296 and 297:
indices of quality of life work. On
- Page 298 and 299:
Figure 2. The values of standardize
- Page 300 and 301:
Table 4. The values of coaching ind
- Page 302 and 303:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 304 and 305:
Table 1. Contrast between hedonic a
- Page 306 and 307:
in consumers’ shopping behavior.
- Page 308 and 309:
et al., 2006; Carpenter, 2008). For
- Page 310 and 311:
Table 2. contd Shopping satisfactio
- Page 312 and 313:
value in the construct of clothing
- Page 314 and 315:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 316 and 317:
independence, assertiveness, innova
- Page 318 and 319:
over those of competitors in order
- Page 320 and 321:
Table 2. Demographic profile and ce
- Page 322 and 323:
Table 4. Service satisfaction level
- Page 324 and 325:
There is a strong significant corre
- Page 326 and 327:
Dean AM (2004). Rethinking customer
- Page 328 and 329:
as a margin rate of 10% and rest to
- Page 330 and 331:
(7) Table 1. Descriptive statistics
- Page 332 and 333:
APPENDIX A Table 1. Failure rate te
- Page 334 and 335:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 336 and 337:
Table 1. Results of the multivarian
- Page 338 and 339:
Figure 3. Entrepreneurship as a fun
- Page 340 and 341:
Furkukawa K, Shafer WE, Lee GM (200
- Page 342 and 343:
happen to firms of any and all size
- Page 344 and 345:
participants attributed their failu
- Page 346 and 347:
Table 1. Descriptive statistics of
- Page 348 and 349:
Table 4 Contd. Inconsideration of l
- Page 350 and 351:
Table 5 Contd. Manufacturing 2.17 1
- Page 352 and 353:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 354 and 355:
The CLRP is an NP-hard problem, so
- Page 356 and 357:
No START Form a new cluster. Select
- Page 358 and 359:
Table 1. Computational results of G
- Page 360 and 361:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 362 and 363:
Table 1. Correlation of facets of C
- Page 364 and 365:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 366 and 367:
Figure 1. Theoretical approach adop
- Page 368 and 369:
quadrant (III), including product v
- Page 370 and 371:
consistently showed negative (posit
- Page 372 and 373:
signal. This hypothesis predicts a
- Page 374 and 375:
Variables are defined as in the ful
- Page 376 and 377:
Table 3. The results of model (2).
- Page 378 and 379:
around the world. Q. Rev. Econ. Fin
- Page 380 and 381:
tourism industry development. In th
- Page 382 and 383:
Table 2. Canonical correlation. 2 C
- Page 384 and 385:
Table 5. Bilateral analysis and ran
- Page 386 and 387:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 388 and 389:
strategies (Hart, 1995; Tello and Y
- Page 390 and 391:
Table 1. Reliability and construct
- Page 392 and 393:
Table 3. Latent variables test. She
- Page 394 and 395:
Haines R, Street M, Haines D (2008)
- Page 396 and 397:
owned insurance firm to enter the m
- Page 398 and 399:
affective commitment; organizationa
- Page 400 and 401:
Figure 1. Structural relationships
- Page 402 and 403:
Prior to analysis, variables were e
- Page 404 and 405:
Table 1. Effect decomposition for M
- Page 406 and 407:
Figure 5. Unstandardized estimates
- Page 408 and 409:
prospects. In other words, less wor
- Page 410 and 411:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 412 and 413:
goal of a SCM process is to create
- Page 414 and 415:
Sale Lean Supply Chain (LSC) Growth
- Page 416 and 417:
Upper Saddle River: Pearson Prentic
- Page 418 and 419:
the green awareness movement by ado
- Page 420 and 421:
usiness practices than smaller firm
- Page 422 and 423:
Table 3. Descriptive statistics and
- Page 424 and 425:
China. Green leadership could be em
- Page 426 and 427:
APPENDIX Appendix 1: Measures of ob
- Page 428 and 429:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 430 and 431:
Emotional intelligence Self monitor
- Page 432 and 433:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 434 and 435:
ship between a people’s perceived
- Page 436 and 437:
Table 1. Analysis of the reliabilit
- Page 438 and 439:
Table 4. Results from hypothesis te
- Page 440 and 441:
Ajzen I, Driver BL (1992). Applicat
- Page 442 and 443:
mono production economy, and rural
- Page 444 and 445:
Table 2. Pearson correlation betwee
- Page 446 and 447:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 448 and 449:
Table 1. Behavioral Phenomenon that
- Page 450 and 451:
Table 3. Test period data. Table 4.
- Page 452 and 453:
Prospect value Figure 3. Expected v
- Page 454 and 455:
Tversky A, Gilovich T (1989). The H
- Page 456 and 457:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 458 and 459:
Table 1. Components of a mentoring
- Page 460 and 461:
Table 3. Perceptions on the success
- Page 462 and 463:
Table 5. Characteristics of a mento
- Page 464 and 465:
terms of sustained development, are
- Page 466 and 467:
Table 7. Ideal characteristics of m
- Page 468 and 469:
qualitative analysis of fifteen hou
- Page 470 and 471:
section. In Section 3, we will disc
- Page 472 and 473:
Table 1. Participants’ demographi
- Page 474 and 475:
of Am. Acad. of Bus., Cambridge. 4(
- Page 476 and 477:
directors and propose the board ind
- Page 478 and 479:
composition is the outcome of a neg
- Page 480 and 481:
Table 1. Descriptive statistics. Ti
- Page 482 and 483:
Table 3. The determinants of board
- Page 484 and 485:
Booth JR, Cornett M, Tehranian H (2
- Page 486 and 487:
provides a wider response and swift
- Page 488 and 489:
Correlation “Customary Approach
- Page 490 and 491:
Table 2. Correlation matrix of EAC
- Page 492 and 493:
Table 9. Intra-EAC imports as share
- Page 494 and 495:
Martin JC (1999). The European Mone
- Page 496 and 497:
participate in the highest degree o
- Page 498 and 499:
innovation. A secondary innovation
- Page 500 and 501:
Figure 2. The switching ecology of
- Page 502 and 503:
Table 1. Revenue growth rate and CA
- Page 504 and 505:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 506 and 507:
variables (Beattie and Jones, 1999a
- Page 508 and 509:
Table 3. Explanations of dependent
- Page 510 and 511:
Courtis JK (1997). Corporate annual
- Page 512 and 513:
treated in the literature, its rela
- Page 514 and 515:
company. METHODOLOGY Table 1. Quest
- Page 516 and 517:
as an important factor in the manag
- Page 518 and 519:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 520 and 521:
satisfaction may also reduce the ov
- Page 522 and 523:
Table 1. Customer expectations on s
- Page 524 and 525:
Table 2. Contd. Machirori and Fatok
- Page 526 and 527:
and travelling may lead to satisfac
- Page 528 and 529:
and professionally developmental pr
- Page 530 and 531:
Table 1. Organizational elements mo
- Page 532 and 533:
Table 2. Studying the demographical
- Page 534 and 535:
education might involve plenty of c
- Page 536 and 537:
African Journal of Business Managem
- Page 538 and 539:
(Deng et al., 2010). To date, there
- Page 540 and 541:
Table 2. Results of hierarchical re
- Page 542 and 543:
WOM. The comparison can be seen in
- Page 544 and 545:
UPCOMING CONFERENCES International
- Page 546:
African Journal of Business Managem