Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome Hypoglossal nerve injury ... - MDC
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome Hypoglossal nerve injury ... - MDC
Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome Hypoglossal nerve injury ... - MDC
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
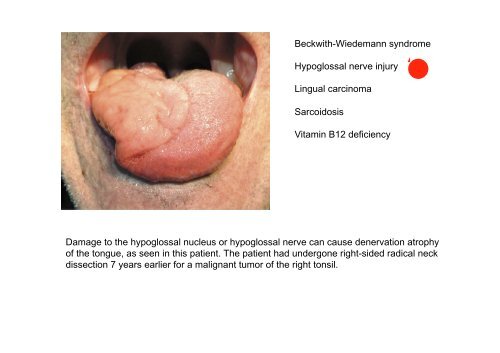
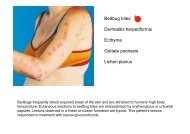
<strong>Beckwith</strong>-<strong>Wiedemann</strong> <strong>syndrome</strong><br />
<strong>Hypoglossal</strong> <strong>nerve</strong> <strong>injury</strong><br />
Lingual carcinoma<br />
Sarcoidosis<br />
Vitamin B12 deficiency<br />
Damage to the hypoglossal nucleus or hypoglossal <strong>nerve</strong> can cause denervation atrophy<br />
of the tongue, as seen in this patient. The patient had undergone right-sided radical neck<br />
dissection 7 years earlier for a malignant tumor of the right tonsil.
Young child with <strong>Beckwith</strong>-<br />
<strong>Wiedemann</strong> <strong>syndrome</strong>.<br />
Note the macroglossia,<br />
prominent eyes, eyelid<br />
nevus flammeus and<br />
barely visible linear ear<br />
creases.<br />
Note the wasted left side of the<br />
tongue and deviation to the left<br />
suggesting a left lower motor<br />
neurone lesion.
Thrombopoetin oder auch Thrombopoietin (Gen-Name: THPO) ist ein Hormon, das die Bildung und<br />
Differenzierung der Blutplättchen-bildenden Zellen, der Megakaryozyten, stimuliert. Es ist im<br />
Rahmen der Thrombopoese notwendig für die Produktion von Blutplättchen (Thrombozyten).<br />
Mutationen im THPO-Gen können zu (seltener) erblicher Thrombozythämie führen. Thrombopoetin<br />
wird in der Leber, der Niere, sowie in den Stromazellen des Knochenmarks gebildet. Es nimmt an<br />
verschiedenen Stellen Einfluss auf den Ablauf der Hämatopoese und wirkt dabei als Cytokin.<br />
Neben dem Einfluss auf Megakaryozyten und der einhergehenden Bildung der Thrombozyten wirkt<br />
Thrombopoetin auf hämatopoetische Stammzellen.<br />
Bei Eltrombopag handelt es sich um einen nicht-peptidischen, oral aktiven Thrombopoetin-<br />
Rezeptor-Agonisten. Dieser Wirkstoff stimuliert die Proliferation und Differenzierung von<br />
Megakaryozyten – den Vorläuferzellen der Thrombozyten (Blutplättchen) – was zu einer Erhöhung<br />
der Blutplättchenkonzentration führt.<br />
Die Resultate einer klinischen Phase-III-Studie zeigten, dass bei den 114 Probanden mit<br />
idiopathischer thrombozytopenischer Purpura die tägliche, orale Gabe von 50 mg Eltrombopag zu<br />
einem deutlichen Anstieg der Anzahl Blutplättchen führte. Bei 80 % der Patienten, die Eltrombopag<br />
erhalten, treten Nebenwirkungen auf.<br />
Dies sind hauptsächlich Kopfschmerzen,<br />
gastrointestinale Störungen (z.B. Übelkeit, Durchfall,<br />
Erbrechen), Schlaflosigkeit, Augentrockenheit und<br />
Hautausschlag. Schwerwiegende Nebenwirkungen<br />
wurden keine beobachtet. Die positiven Resultate<br />
der Phase-II-Studien wurden 2007 bereits publiziert.
Eltrombopag and Improved Hematopoiesis in Refractory Aplastic Anemia<br />
We conducted a phase 2 study involving patients with aplastic anemia that was refractory to<br />
immunosuppression to determine whether the oral thrombopoietin mimetic eltrombopag<br />
(Promacta) can improve blood counts. Twenty-five patients received eltrombopag at a dose of<br />
50 mg, which could be increased, as needed, to a maximum dose of 150 mg daily, for a total of<br />
12 weeks. Primary end points were clinically significant changes in blood counts or transfusion<br />
independence. Patients with a response continued to receive eltrombopag.<br />
The Venn diagrams show the numbers of patients with<br />
unilineage, bilineage, and trilineage hematologic responses.<br />
Patients with a response and their response pattern at 12<br />
weeks are shown on the left. Patients who met the response<br />
criteria at the most recent follow-up assessment are shown on<br />
the right.
Treatment with<br />
eltrombopag was<br />
associated with<br />
multilineage<br />
clinical responses<br />
in some patients<br />
with refractory<br />
severe aplastic<br />
anemia.
Renale Clearance bezeichnet die Clearance durch die Nieren, d. h. die Entfernung einer<br />
bestimmten exogenen oder endogenen Substanz aus dem Blut als spezifische Leistung der<br />
Nieren und gibt das Plasmavolumen an, welches pro Zeiteinheit von der entsprechenden<br />
Substanz befreit wird. So z. B. für die Kreatinin-Clearance:<br />
Die einfache Version der Cockcroft-Gault-Formel hilft, die Kreatinin-Clearance [ml/min] zu<br />
schätzen.<br />
The Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD)<br />
Study was the largest randomized clinical trial to<br />
test the hypothesis that protein restriction slows the<br />
progression of chronic renal disease. However, the<br />
primary results published in 1994 were not<br />
conclusive with regard to the efficacy of this<br />
intervention.
Cystatin C (auch: CysC) ist ein körpereigenes Protein, das in der Nierendiagnostik zur<br />
Bestimmung der glomerulären Filtrationsrate (GFR) verwendet wird.<br />
Die Serum-Normalwerte beim Menschen liegen für beide Geschlechter zwischen 0,53 und 0,95<br />
mg/l. Erhöhte Werte finden sich bei eingeschränkter glomerulärer Filtrationsrate (GFR).<br />
Cystatin C ist Mitglied der Cystatin-Familie der Cysteinproteasen-Inhibitoren. Cystatin C wird<br />
von den meisten kernhaltigen Zellen in relativ konstanter Rate produziert; die Produktion scheint<br />
auch bei entzündlichen Prozessen und anderen pathologischen Zuständen gleich zu bleiben.<br />
Seltene Mutationen im CST3-Gen können erbliche Amyloidose und Makuladegeneration<br />
verursachen.<br />
Bei nicht möglicher 24-stündiger Urinsammlung für eine renale Clearance-Bestimmung ist<br />
Cystatin C im Serum eine Alternative zur Diagnostik von Störungen der glomerulären Filtration.<br />
Durch die größere diagnostische Sensitivität als Kreatinin im Serum scheint es auch Aussagen<br />
im „Kreatinin-blinden Bereich“ zuzulassen.<br />
Kreatinin = 0,40 €<br />
Cystatin C = 4,0 €
Estimating Glomerular Filtration Rate from Serum Creatinine and Cystatin C<br />
Estimates of glomerular filtration rate (GFR) that are based on serum creatinine are routinely<br />
used; however, they are imprecise, potentially leading to the overdiagnosis of chronic kidney<br />
disease. Cystatin C is an alternative filtration marker for estimating GFR. Using cross-sectional<br />
analyses, we developed estimating equations based on cystatin C alone and in combination with<br />
creatinine in diverse populations totaling 5352 participants from 13 studies. These equations<br />
were then validated in 1119 participants from 5 different studies in which GFR had been<br />
measured. Cystatin and creatinine assays were traceable to primary reference materials. Bias<br />
was assessed as the median of the difference between measured GFR and estimated GFR, and<br />
precision was assessed as the interquartile range for the difference. Accuracy was assessed as<br />
the root-mean-square error and as the percentage of estimates that differed by more than 30%<br />
from the measured GFR (1–P30) or by more than 20% (1–P20). Confidence intervals were<br />
calculated by means of bootstrap methods (2000 bootstraps). The significance of the differences<br />
among equations was determined with the use of the signed-rank test for bias, the bootstrap<br />
method for the interquartile range and root-mean-square error from the 2000 bootstrap samples,<br />
and McNemar's test for 1–P30 and 1–P20.
A reduction in GFR to less than 60 ml per minute per 1.73 m2 for 3 months or longer is a diagnostic criterion<br />
for chronic kidney disease and is associated with an increased risk of adverse outcomes, including death.<br />
Bias with the new, combined creatinine–cystatin C equation and with the average of the new cystatin C<br />
equation and the creatinine equation was similar to that with the individual creatinine and cystatin C<br />
equations, but they had greater precision and accuracy and resulted in more accurate classification of<br />
measured GFR as less than 60 ml per minute per 1.73 m2 — the threshold for the diagnosis of chronic kidney<br />
disease. 3.6% of U.S. adults would be classified as having chronic kidney disease solely on the basis of a<br />
creatinine-based GFR estimate of 45 to 59 ml per minute per 1.73 m 2 . Our data suggest that a strategy of<br />
measuring cystatin C when the creatinine-based estimate is in this range and then reestimating GFR with the<br />
use of both these markers could correctly reclassify a substantial proportion of such patients as not having<br />
chronic kidney disease and not being at high risk. This more accurate classification would result in more<br />
selective use of resources, such as tests for complications of chronic kidney disease, adjustment of<br />
medication doses, and referrals to nephrologists.
Delirium ist ein akutes, schweres, prinzipiell reversibles, organisch bedingtes Psychosyndrom<br />
mit Bewusstseinsstörung. Kennzeichnend für das Delirium ist neben der Bewusstseinsstörung<br />
eine Störung der Aufmerksamkeit, der Wahrnehmung, des Denkens, der Kognition, des<br />
Gedächtnisses, der Psychomotorik und der Emotionalität. Pathognomonisch ist eine deutliche<br />
tageszeitliche Fluktuation der Symptome. Die akute psychische Störung hat entweder eine<br />
organische Ursache, oder entsteht aufgrund von Drogenwirkung oder Drogenentzug.<br />
Weitere Symptome sind Herabsetzung des abstrakten Denkvermögens, der Konzentration, ein<br />
eingeschränktes Kurzzeitgedächtnis und Desorientierung: Ein Betroffener ist nicht richtig<br />
orientiert, was Ort, Zeit, seine eigene Person oder Situation betreffen kann. Beim voll<br />
ausgeprägten Delirium kommt noch eine Störung des Schlaf-Wach-Rhythmus hinzu. Weitere<br />
Symptome, wie optische Halluzinationen, Wahnvorstellungen, motorische Unruhe und nestelnde<br />
Bewegungen sowie affektive Störungen wie Depression, Angst aber auch Euphorie oder<br />
Reizbarkeit und eine Agitation (krankhafte Unruhe) können auftreten. Der Beginn dieser akuten<br />
Störung ist plötzlich, die Symptomatik schwankt jedoch im Tagesverlauf. Die zwei Prägnanztypen<br />
sind hyperaktives und hypoaktives Delirium. Letzteres bietet mehr diagnostische Schwierigkeiten.<br />
Ebenso gibt es Mischformen mit Anteilen von beiden Typen.<br />
Unter Halluzination versteht man eine Wahrnehmung eines Sinnesgebietes, ohne dass eine<br />
nachweisbare Reizgrundlage vorliegt. Das bedeutet zum Beispiel, dass physikalisch nicht<br />
nachweisbare Objekte gesehen werden oder Stimmen gehört, ohne dass jemand spricht.<br />
Halluzinationen können alle Sinnesgebiete betreffen. Bei einer Illusion hingegen wird ein real<br />
vorhandener Sachverhalt verändert wahrgenommen: Ein tatsächlich vorhandener feststehender<br />
Gegenstand scheint sich zu bewegen oder in irregulären Mustern werden scheinbar Gesichter<br />
erkennbar. Bei optischen Halluzinationen kommt es zur Wahrnehmung nicht vorhandener<br />
Objekte. Am häufigsten sind kleine und bewegliche Objekte, deren Wahrnehmung dann meist<br />
sehr angstvoll erlebt wird. Dies kommt beispielsweise im Rahmen eines Deliriums vor. Bei<br />
akustischen Halluzinationen, die beispielsweise bei an Schizophrenie Erkrankten häufig sind,<br />
hören die Betroffenen oft imperative Stimmen.
Cognitive Trajectories after Postoperative Delirium<br />
Delirium is common after cardiac surgery and may be associated with long-term changes in<br />
cognitive function. We examined postoperative delirium and the cognitive trajectory during the first<br />
year after cardiac surgery. We enrolled 225 patients 60 years of age or older who were planning to<br />
undergo coronary-artery bypass grafting or valve replacement. Patients were assessed<br />
preoperatively, daily during hospitalization beginning on postoperative day 2, and at 1, 6, and 12<br />
months after surgery. Cognitive function was assessed with the use of the Mini–Mental State<br />
Examination (MMSE; score range, 0 to 30, with lower scores indicating poorer performance).<br />
Delirium was diagnosed with the use of the Confusion Assessment Method. We examined<br />
performance on the MMSE in the first year after surgery, controlling for demographic<br />
characteristics, coexisting conditions, hospital, and surgery type.
Confusion Assessment Method (CAM; a<br />
diagnostic algorithm to determine the presence<br />
or absence of delirium on the basis of four<br />
features: acute change with a fluctuating course,<br />
inattention, disorganized thinking, and altered<br />
level of consciousness), and the Delirium<br />
Symptom Interview (an interview that assesses<br />
the presence or absence of eight features of<br />
delirium, including the four features of the CAM<br />
diagnostic algorithm).<br />
The 103 participants (46%) in whom delirium<br />
developed postoperatively had lower<br />
preoperative mean MMSE scores than those in<br />
whom delirium did not develop (25.8 vs. 26.9,<br />
P
A Pooled Analysis of Vitamin D Dose Requirements for Fracture Prevention<br />
The results of meta-analyses examining the relationship between vitamin D supplementation<br />
and fracture reduction have been inconsistent. We pooled participant-level data from 11<br />
double-blind, randomized, controlled trials of oral vitamin D supplementation (daily, weekly, or<br />
every 4 months), with or without calcium, as compared with placebo or calcium alone in<br />
persons 65 years of age or older. Primary end points were the incidence of hip and any<br />
nonvertebral fractures according to Cox regression analyses, with adjustment for age group,<br />
sex, type of dwelling, and study. Our primary aim was to compare data from quartiles of actual<br />
intake of vitamin D (including each individual participant's adherence to the treatment and<br />
supplement use outside the study protocol) in the treatment groups of all trials with data from<br />
the control groups.
In conclusion, our data suggest that high-dose vitamin D supplementation (≥800 IU per<br />
day) may reduce the risk of hip fracture in persons 65 years of age or older, independently<br />
of type of dwelling, age, and sex. Furthermore, our data support a 25-hydroxyvitamin D<br />
level above 60 nmol per liter for the prevention of fractures.
Shock-Wave Lithotripsy for Renal Calculi<br />
A 42-year-old man without a history of kidney stones had intermittent left flank pain for several<br />
weeks before being seen by his primary care doctor. Urinalysis revealed microhematuria.<br />
Computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis without contrast enhancement identified<br />
a calcification 12 mm in diameter in the left renal pelvis, associated with mild hydronephrosis and<br />
a normal-caliber ureter. The attenuation coefficient of the stone was 790 Hounsfield units, and the<br />
skin-to-stone distance was 8.5 cm. He was referred to a urologist, who reviewed the CT scan and<br />
recommended treatment with extracorporeal shock-wave lithotripsy.<br />
Nephrolithiasis is a common condition, with a lifetime prevalence of approximately 13% in men<br />
and 7% in women in the United States. Total health care expenditures reached nearly $4.5 billion<br />
annually, and this figure increased to $5.3 billion when the indirect costs of lost workdays were<br />
included.
European Association of Urology Urolithiasis Guideline Panel released comprehensive<br />
guidelines,45 recommending shock-wave lithotripsy as first-line therapy for non–lower-pole renal<br />
calculi less than 2 cm in diameter and for lower-pole renal calculi less than 1 cm in diameter. For<br />
larger stones in either location, percutaneous nephrolithotomy is the recommended primary<br />
treatment. For lower-pole stones between 1 and 2 cm in diameter without unfavorable<br />
anatomical factors or shock-wave–resistant stone composition, lithotripsy can be considered as<br />
an option for primary management.<br />
The patient described in the vignette has a stone with a size (less than 2 cm in diameter) and<br />
location (non–lower pole) that is considered to be favorable for treatment with shock-wave<br />
lithotripsy. Findings on CT imaging, including the attenuation coefficient (less than 1000<br />
Hounsfield units) and the skin-to-stone distance (less than 10 cm), also predict a favorable<br />
outcome. Although the stone composition cannot be reliably predicted by means of current CT<br />
findings, and the patient did not previously have a stone with a known composition, the favorable<br />
findings on CT suggest that the stone will probably fragment well and that the risk of obstructive<br />
complications will be low.<br />
Bei diesem Verfahren benötigt der Patient keine Vollnarkose, in<br />
der Regel wird nur ein leichtes Schmerzmittel intravenös<br />
verabreicht, der Patient bleibt ansprechbar. Gegen den bei der<br />
Behandlung entstehenden Lärm (rund 3000 niedrigfrequente<br />
Impulse in 30 Minuten) bekommt der Patient einen Gehörschutz.<br />
Sehr oft kann diese Behandlung auch ambulant durchgeführt<br />
werden. Die Belastung für den Patienten ist gering und durch die<br />
gezielte Bündelung der Stoßwellen weniger schmerzhaft als bei<br />
den Geräten erster Bauart mit Badewanne.
A 31-year-old woman who had been unable to eat or drink for the preceding week was admitted<br />
to the hospital. For the preceding 8 months she had had nausea, vomiting, and abdominal<br />
discomfort and several episodes of crampy epigastric pain with vomiting and intermittent chills<br />
and sweats, but no documented fevers. She also had loose, pale stools occasionally, but these<br />
episodes did not represent a notable change from her baseline. Gradually increasing fatigue,<br />
loss of appetite, and a recent weight loss of several kilograms were also reported. The patient's<br />
medical history included hypertension, obesity, and migraine headaches. She had undergone<br />
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass 5 years before presentation and subsequently lost approximately 45<br />
kg (100 lb). Her weight had been stable for the past few years; her body-mass index (BMI, the<br />
weight in kilograms divided by the square of the height in meters) was 33. She had undergone<br />
laparoscopic cholecystectomy 10 years before presentation. Her only medication was nifedipine,<br />
and she took a multivitamin on occasion. Intravenous fluids were administered (1 liter of 0.90%<br />
sodium chloride followed by a continuous infusion of 5% dextrose in a solution of 0.45% sodium.<br />
chloride). The hematocrit was 29.4%, with a mean corpuscular volume<br />
of 109 fl. The white-cell count was 9350 per cubic millimeter<br />
and her platelet count 432,000 per cubic millimeter. The<br />
aspartate aminotransferase level was 210 U per liter, alanine<br />
aminotransferase 44 U per liter, alkaline phosphatase 191 U<br />
per liter, total bilirubin 0.6 mg per deciliter (10.3 µmol per<br />
liter), albumin 3.3 g per deciliter, prothrombin time 13.6<br />
seconds, and partial-thromboplastin time 33.8 seconds.<br />
Amylase and lipase levels were normal, and a serum test for<br />
beta human chorionic gonadotropin was negative. Abdominal<br />
computed tomography revealed a diffusely fatty liver, with<br />
focal sparing of the medial portion of the right lobe, and<br />
hepatomegaly, with a liver span of 26.5 cm; the spleen,<br />
measuring 14.2 cm, showed borderline enlargement.
On the second hospital day, confusion, blurry vision, and vertigo developed abruptly. A repeat<br />
examination revealed impaired lateral gaze in both eyes and nystagmus on both horizontal and<br />
upward gaze, with a positive Romberg test. The patient was noted to have a wide-based,<br />
unsteady gait and was able to take only a few steps, with assistance from two people.<br />
Enlargement of the mammillary bodies is shown in an image<br />
obtained with fluid-attenuated inversion recovery sequencing<br />
(Panel A, arrow), and enhancement is shown in a T1weighted<br />
magnetic resonance image obtained after the<br />
administration of contrast material (Panel B). The patient was<br />
given 500 mg of thiamine intravenously on an emergency<br />
basis. Subsequent testing revealed low levels of whole-blood<br />
thiamine (45 nmol per liter; normal range, 80 to 150) and of<br />
serum folate (4.6 ng per milliliter [10.4 nmol per liter]; normal<br />
range, 5.3 to 9.9 ng per milliliter [12.0 to 22.4 nmol per liter]),<br />
copper (46 µg per deciliter [7.2 µmol per liter]; normal range,<br />
80 to 155 µg per deciliter [12.6 to 24.4 µmol per liter]), zinc<br />
(57 µg per deciliter [8.7 µmol per liter]; normal range, 66 to<br />
120 µg per deciliter [10.0 to 18.4 µmol per liter]), and 25hydroxyvitamin<br />
D (6 ng per milliliter [15 nmol per liter];<br />
normal range, 25 to 80 ng per milliliter [62 to 200 nmol per<br />
liter]).
Die Hand-Fuß-Mund-Krankheit – Synonyme: Hand-Fuß-Mund-Exanthem, Falsche Maul- und<br />
Klauenseuche – ist eine viral bedingte, weltweit vorkommende, hoch ansteckende und deshalb<br />
epidemisch auftretende Infektionskrankheit. Nach einer durchschnittlichen Inkubationszeit von<br />
drei bis sechs Tagen kommt es in der Regel zu einer Erkrankung mit hohem Fieber,<br />
vorübergehenden Allgemeinsymptomen und einem symmetrischen Hautausschlag (Exanthem)<br />
mit Bläschenbildung an den Händen, Füßen und einem Enanthem der Mundschleimhaut, das<br />
sich mit kurzlebigen Bläschen von vier bis acht Millimeter Durchmesser in der Mundhöhle, vor<br />
allem im Bereich der Zunge, des Gaumens und der Wangenschleimhaut äußert. Lippen, weicher<br />
Gaumen, Tonsillen und Pharynx bleiben frei bzw. sind selten betroffen. Diese Bläschen wandeln<br />
sich in seichte, schmierig belegte, schmerzhafte Erosionen (Aphthen). Die Veränderungen an<br />
Händen und Füßen treten gleichzeitig oder nur kurze Zeit später auf und sind vermehrt an den<br />
Streckseiten der Finger und Zehen oder deren Seitenflächen, aber auch den Fußsohlen (Fersen)<br />
und Handflächen zu beobachten. Hände und Füße können dabei einen stechenden /<br />
spannenden Schmerz und starken Juckreiz aufweisen. Diese Erkrankung wird durch eine<br />
Infektion mit Coxsackie- (Typ A 5, 9, 10, 16, B2, 5), Echo- (Typ 6) oder Enteroviren (Humanes<br />
Enterovirus 71) verursacht. Möglicherweise verlaufen bis zu 70 % der Infektionen<br />
asymptomatisch (inapparente Infektion).
Autopsy Findings in Children with Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease<br />
(etwa wie Maul und Klauenseuche)<br />
From May 2008 through July 2010, an epidemic of hand, foot, and mouth disease occurred in<br />
Guangxi, China. During the epidemic, some children died of progressive cardiorespiratory<br />
failure. Postmortem pathological examinations were performed for 14 patients. Reversetranscriptase–polymerase-chain-reaction<br />
assays of various specimens (throat swabs or stool<br />
samples) were performed to detect enterovirus 71, coxsackievirus A17, and pan-enterovirus<br />
messenger RNA. Assays for enterovirus 71 were positive in 12 patients. Assays to detect<br />
coxsackievirus A17 were positive in 1 patient, and assays to detect other enteroviruses were<br />
positive in 1 patient.<br />
Sections of brain-biopsy specimens were<br />
stained with hematoxylin and eosin. A<br />
photomicrograph at low magnification<br />
(Panel A) shows neuronal necrosis and<br />
softening in the brain stem (arrow), and<br />
higher magnification (Panel B) reveals the<br />
neuronophagia phenomenon (blue arrow)<br />
and colloid (black arrow) in the brain stem.<br />
A photomicrograph at low magnification<br />
(Panel C) shows perivascular cuffing in the<br />
brain stem (arrow). A view of the medulla<br />
oblongata at low magnification (Panel D)<br />
shows hemorrhage (arrow).
A 68-year-old man complained of urinary frequency and hypogastric discomfort. He was a<br />
smoker and had hypertension. Digital rectal examination showed a painful prostate but he had no<br />
fever. Urine analysis showed a pyuria and a bacteriuria of enterococcus species. The patient was<br />
treated with amoxicillin. 2 days after his admission, he suddenly developed acute right flank pain<br />
with hypotension.<br />
(A) Axial non-contrast-enhanced <strong>MDC</strong>T of the abdomen showing retroperitoneal haematoma (asterisk)<br />
surrounding a fissured infrarenal abdominal aneurysm (arrowheads). Contrast-enhanced <strong>MDC</strong>T angiography in<br />
axial (B) and sagittal (C) reformation with maximum intensity projection algorithm; CT angiogram shows<br />
anterior rupture from the wall of the abdominal aortic aneurysm (arrow), with massive intraperitoneal bleeding<br />
(contrast extravasation).
Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9, also known as PCSK9, is an enzyme which in<br />
humans is encoded by the PCSK9 gene. The encoded protein is synthesized as a soluble<br />
zymogen that undergoes autocatalytic intramolecular processing in the endoplasmic reticulum.<br />
The protein may function as a proprotein convertase. This protein plays a major regulatory role in<br />
cholesterol homeostasis. PCSK9 binds to the epidermal growth factor-like repeat A (EGF-A)<br />
domain of the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR), inducing LDLR degradation. Reduced<br />
LDLR levels result in decreased metabolism of low-density lipoproteins, which could lead to<br />
hypercholesterolemia. Alnylam Pharmaceuticals has recently shown, in initial clinical trials,<br />
positive results of ALN-PCS, which acts by means of RNA interference, as an effective means of<br />
PCSK9 inhibition. Mutations in this gene have been associated with a rare form of autosomal<br />
dominant familial hypercholesterolemia (HCHOLA3). The mutations appear to cause the disease<br />
by increasing its protease activity, reducing LDL receptor levels and thereby preventing the<br />
uptake of cholesterol into the cells.
Effect of a monoclonal antibody to PCSK9, to reduce low-density lipoprotein<br />
cholesterol in patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia on<br />
stable statin dose with or without ezetimibe therapy: a phase 2 trial<br />
Inhibition of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 serine protease (PCSK9) resulted in<br />
large reductions of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in phase 1 trials. We assessed<br />
the efficacy and safety of various doses and dosing intervals of REGN727, a monoclonal<br />
antibody to PCSK9, added to statins, to further lower LDL-C in patients with heterozygous<br />
familial hypercholesterolaemia. This multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 2 trial<br />
was done at 16 lipid clinics, we enrolled adults with heterozygous familial<br />
hypercholesterolaemia and LDL-C concentrations of 2·6 mmol/L or higher on stable diet and<br />
statin dose, with or without ezetimibe. Patients were randomly assigned to receive REGN727<br />
150 mg, 200 mg, or 300 mg every 4 weeks, or 150 mg every 2 weeks, or placebo every 2<br />
weeks (ratio 1:1:1:1:1). Randomisation was stratified by concomitant use of ezetimibe at<br />
baseline. Investigators, study staff, and patients were masked to treatment group. Blinding was<br />
maintained by administration of placebo alternating with REGN727 for the groups of 4 week<br />
dosing. The primary endpoint was mean percent reduction in LDL-C from baseline at week 12<br />
and was analysed in the modified intention-to-treat population with an analysis of covariance<br />
(ANCOVA) model with treatment group.
REGN727 was well tolerated and achieved substantial further LDL-C reduction in patients with<br />
heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia and elevated LDL-C treated with high-dose<br />
statins, with or without ezetimibe. REGN727 has the potential to provide optimum control of<br />
LDL-C in patients with this disorder.
Epidemiology of multimorbidity and implications for health care, research, and<br />
medical education: a cross-sectional study<br />
Long-term disorders are the main challenge facing health-care systems worldwide, but health<br />
systems are largely configured for individual diseases rather than multimorbidity. We examined<br />
the distribution of multimorbidity, and of comorbidity of physical and mental health disorders, in<br />
relation to age and socioeconomic deprivation. In a cross-sectional study we extracted data on<br />
40 morbidities from a database of 1 751 841 people registered with 314 medical practices in<br />
Scotland as of March, 2007. We analysed the data according to the number of morbidities,<br />
disorder type (physical or mental), sex, age, and socioeconomic status. We defined<br />
multimorbidity as the presence of two or more disorders.
Our findings challenge the single-disease<br />
framework by which most health care, medical<br />
research, and medical education is configured.<br />
A complementary strategy is needed, supporting<br />
generalist clinicians to provide personalised,<br />
comprehensive continuity of care, especially in<br />
socioeconomically deprived areas.
Magnesium for aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage (MASH-2): a<br />
randomised placebo-controlled trial<br />
Magnesium sulphate is a neuroprotective agent that might improve outcome after aneurysmal<br />
subarachnoid haemorrhage by reducing the occurrence or improving the outcome of delayed<br />
cerebral ischaemia. We did a trial to test whether magnesium therapy improves outcome after<br />
aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage. We did this phase 3 randomised, placebo-controlled<br />
trial in eight centres in Europe and South America. We randomly assigned (with computergenerated<br />
random numbers, with permuted blocks of four, stratified by centre) patients aged<br />
18 years or older with an aneurysmal pattern of subarachnoid haemorrhage on brain imaging<br />
who were admitted to hospital within 4 days of haemorrhage, to receive intravenous<br />
magnesium sulphate, 64 mmol/day, or placebo. We excluded patients with renal failure or<br />
bodyweight lower than 50 kg. Patients, treating physicians, and investigators assessing<br />
outcomes and analysing data were masked to the allocation. The primary outcome was poor<br />
outcome—defined as a score of 4—5 on the modified Rankin Scale—3 months after<br />
subarachnoid haemorrhage, or death. We analysed results by intention to treat. We also<br />
updated a previous meta-analysis of trials of magnesium treatment for aneurysmal<br />
subarachnoid haemorrhage.
The MASH 2 trial has implications for clinical<br />
practice. Administration of magnesium after<br />
aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage is<br />
standard practice in many centres. On the basis<br />
of the results of MASH 2—a trial of treatment of<br />
aneurysmal subarachnoid haemorrhage with<br />
sufficient power to detect a clinically significant<br />
improvement in outcome—and in combination<br />
with data from other trials, we do not<br />
recommend routine use of intravenous<br />
magnesium 64 mmol/day for the improvement of<br />
outcome after aneurysmal subarachnoid<br />
haemorrhage.
The 10/66 Dementia Research Group is a collective of researchers carrying out populationbased<br />
research into dementia, non-communicable diseases and ageing in low and middle<br />
income countries.10/66 refers to the two-thirds (66%) of people with dementia living in low and<br />
middle income countries, and the 10% or less of population-based research that has been<br />
carried out in those regions.10/66 is a part of Alzheimer's Disease International, and is coordinated<br />
from the Institute of Psychiatry, King's College London.<br />
Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fourth Edition (DSM-IV). DSM-IV<br />
manual is published by the American Psychiatric Association and covers all mental health<br />
disorders for both children and adults. It also lists known causes of these disorders, statistics in<br />
terms of gender, age at onset, and prognosis as well as some research concerning the optimal<br />
treatment approaches. Mental Health Professionals use this manual when working with patients<br />
in order to better understand their illness and potential treatment and to help 3rd party payers<br />
(e.g., insurance) understand the needs of the patient. The book is typically considered the<br />
‘bible’ for any professional who makes psychiatric diagnoses in the United States and many<br />
other countries. Much of the diagnostic information on these pages is gathered from the DSM<br />
IV.
Dementia incidence and mortality in middle-income countries, and<br />
associations with indicators of cognitive reserve<br />
Results of the few cohort studies from countries with low incomes or middle incomes suggest a<br />
lower incidence of dementia than in high-income countries. We assessed incidence of dementia<br />
according to criteria from the 10/66 Dementia Research Group and Diagnostic and Statistical<br />
Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) IV, the effect of dementia at baseline on mortality, and the<br />
independent effects of age, sex, socioeconomic position, and indicators of cognitive reserve. We<br />
did a population-based cohort study of all people aged 65 years and older living in urban sites in<br />
Cuba, the Dominican Republic, and Venezuela, and rural and urban sites in Peru, Mexico, and<br />
China, with ascertainment of incident 10/66 and DSM-IV dementia 3—5 years after cohort<br />
inception. We used questionnaires to obtain information about age in years, sex, educational<br />
level, literacy, occupational attainment, and number of household assets. We obtained<br />
information about mortality from all sites. For participants who had died, we interviewed a friend<br />
or relative to ascertain the likelihood that they had dementia before death.
In this study of more than 12 800 individuals, incidence rates for 10/66 dementia were roughly 1·5<br />
—2·5 times higher than those for DSM-IV dementia. Mortality hazards were higher in individuals<br />
with dementia at baseline than in dementia-free individuals. Informant reports suggested a high<br />
incidence of dementia before death; overall incidence could be between 4% and 19% higher if<br />
these data were included. 10/66 dementia incidence was independently associated with increased<br />
age, female gender, and low education, but not with occupational attainment. Our results provide<br />
supportive evidence for the cognitive reserve hypothesis, showing that in middle-income countries<br />
as in high-income countries, education, literacy, verbal fluency, and motor sequencing confer<br />
substantial protection against the onset of dementia.
Sport and exercise as contributors to the health of nations<br />
Self-reported rates of participation in sport vary by country. In the UK, about 40% of men and<br />
women aged 16 years or older participate in at least one sport every week. Although few data exist<br />
to assess trends for participation in sport, there is little evidence of change in the past decade<br />
among adults. Large cohort studies suggest that such participation in sport is associated with a 20<br />
—40% reduction in all-cause mortality compared with non-participation. Randomised trials and<br />
crossover clinical studies suggest that playing sport is associated with specific health benefits.<br />
Some sports have relatively high <strong>injury</strong> risk although neuromuscular training programmes can<br />
prevent various lower extremity injuries. Clinicians can influence a large number of patients through<br />
brief interventions that promote physical activity, and encouragement toward participation in sport<br />
for some physically inactive patients qualifies as evidence-based therapy. Exercise might also be<br />
considered as a fifth vital sign and should be recorded in patients' electronic medical records and<br />
routine histories.<br />
Sport, exercise, and physical activity<br />
(A) Domains of sport, exercise, and physical activity. (B)<br />
Individual who exercises and plays sport but is otherwise<br />
sedentary. (C) Physically active individual who does no explicit<br />
sport or exercise.
39-year-old woman presented complaining of a 1-day history of vomiting and abdominal pain.<br />
She had had three or four episodes, with no infective prodrome. She was a physiotherapist and<br />
a competent long-distance runner; 2 days earlier she had run a 5 km race, and that morning<br />
had done her daily exercise workout. On examination there were no physical signs other than<br />
sinus tachycardia. Within 2 h, she collapsed and was moribund in acute cardiogenic shock.<br />
Chest radiography showed pulmonary congestion. Transthoracic echocardiography showed a<br />
slightly dilated, poorly functioning heart with no pericardial effusion. Cardiac catheterisation was<br />
done to exclude coronary artery disease, and an intra-aortic balloon pump was placed for<br />
circulatory support. She had no arrhythmias. Acute myocarditis was suspected and she was<br />
transferred to our cardiothoracic centre. She arrived 8 h after first presentation, was found to be<br />
in extremis, with fixed mottling of her trunk and limbs and hypotension despite epinephrine<br />
infusing at >1 µg/kg per min. She was anuric, profoundly acidaemic, and hypoxic on 100%<br />
oxygen (PaO2 6·1 kPa, pH 6·9, lactate 16 mmol/L, base excess −13). The heart was tense and<br />
dilated and a myocardial biopsy sample was taken from the left ventricle. Central veno-arterial<br />
extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) was established; a cannula was inserted via<br />
the abdominal wall into the right atrium to drain systemic venous blood into the ECMO pump,<br />
which returned oxygenated blood via a separate cannula into the ascending aorta<br />
CT of the abdomen showed a large left adrenal mass (5×6 cm).<br />
Left adrenalectomy was done (day 3) with concurrent ECMO<br />
support. Subsequent echocardiography showed recovering<br />
biventricular function (day 5) and ECMO was discontinued.
Myocyte necrosis with contraction bands,<br />
perivascular edema, and microvascular<br />
endothelial swelling with no evidence of<br />
myocarditis. Immunohistochemical staining for<br />
C4d was strongly positive along the<br />
microvasculature and in rare individual myocytes<br />
with contraction band <strong>injury</strong><br />
Hematoxylin & eosin, 10X. Myocardium with<br />
coagulative myocyte necrosis in center and lower right<br />
corner.