RelyX™ Luting and RelyX™ Luting Plus Cement - 3M
RelyX™ Luting and RelyX™ Luting Plus Cement - 3M
RelyX™ Luting and RelyX™ Luting Plus Cement - 3M
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
14<br />
Source: <strong>3M</strong> ESPE Laboratory<br />
test data<br />
Source: <strong>3M</strong> ESPE Laboratory<br />
test data<br />
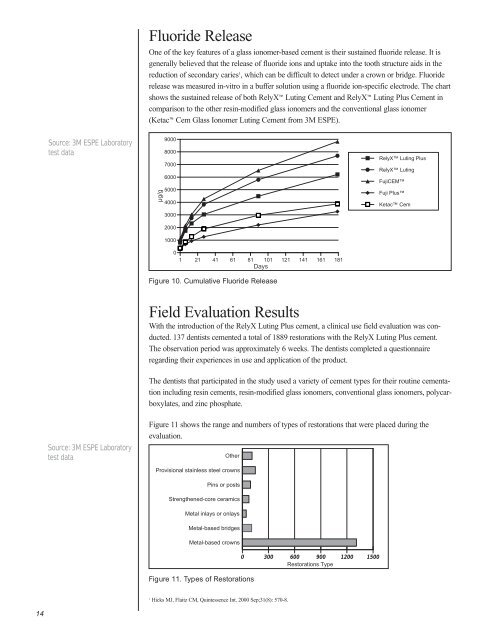
Fluoride Release<br />
One of the key features of a glass ionomer-based cement is their sustained fluoride release. It is<br />
generally believed that the release of fluoride ions <strong>and</strong> uptake into the tooth structure aids in the<br />
reduction of secondary caries 1 , which can be difficult to detect under a crown or bridge. Fluoride<br />
release was measured in-vitro in a buffer solution using a fluoride ion-specific electrode. The chart<br />
shows the sustained release of both RelyX <strong>Luting</strong> <strong>Cement</strong> <strong>and</strong> RelyX <strong>Luting</strong> <strong>Plus</strong> <strong>Cement</strong> in<br />
comparison to the other resin-modified glass ionomers <strong>and</strong> the conventional glass ionomer<br />
(Ketac Cem Glass Ionomer <strong>Luting</strong> <strong>Cement</strong> from <strong>3M</strong> ESPE).<br />
µg/g<br />
9000<br />
8000<br />
7000<br />
6000<br />
H<br />
J<br />
B<br />
H<br />
J<br />
B<br />
H<br />
B<br />
J<br />
B<br />
H<br />
BJ<br />
F<br />
F<br />
F F<br />
5000<br />
4000<br />
3000<br />
F<br />
2000<br />
F<br />
1000<br />
0<br />
1 21 41 61 81 101<br />
Days<br />
121 141 161 181<br />
Figure 10. Cumulative Fluoride Release<br />
Field Evaluation Results<br />
With the introduction of the RelyX <strong>Luting</strong> <strong>Plus</strong> cement, a clinical use field evaluation was conducted.<br />
137 dentists cemented a total of 1889 restorations with the RelyX <strong>Luting</strong> <strong>Plus</strong> cement.<br />
The observation period was approximately 6 weeks. The dentists completed a questionnaire<br />
regarding their experiences in use <strong>and</strong> application of the product.<br />
The dentists that participated in the study used a variety of cement types for their routine cementation<br />
including resin cements, resin-modified glass ionomers, conventional glass ionomers, polycarboxylates,<br />
<strong>and</strong> zinc phosphate.<br />
Figure 11 shows the range <strong>and</strong> numbers of types of restorations that were placed during the<br />
evaluation.<br />
Other<br />
Provisional stainless steel crowns<br />
Pins or posts<br />
Strengthened-core ceramics<br />
Metal inlays or onlays<br />
Metal-based bridges<br />
Metal-based crowns<br />
Figure 11. Types of Restorations<br />
1 Hicks MJ, Flaitz CM, Quintessence Int. 2000 Sep;31(8): 570-8.<br />
H<br />
J<br />
0 300 600 900 1200 1500<br />
Restorations Type<br />
H<br />
J<br />
B<br />
B RelyX <strong>Luting</strong> <strong>Plus</strong><br />
J RelyX <strong>Luting</strong><br />
H FujiCEM<br />
F Fuji <strong>Plus</strong><br />
Ketac Cem