The scull: principles of development and structure. The ...
The scull: principles of development and structure. The ...
The scull: principles of development and structure. The ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
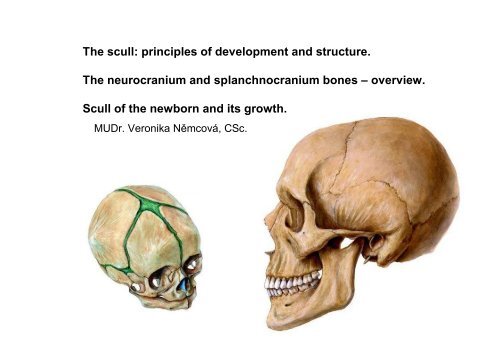
<strong>The</strong> <strong>scull</strong>: <strong>principles</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>development</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>structure</strong>.<br />
<strong>The</strong> neurocranium <strong>and</strong> splanchnocranium bones – overview.<br />
Scull <strong>of</strong> the newborn <strong>and</strong> its growth.<br />
MUDr. Veronika Němcová, CSc.
Neurocranium + splanchnocranium<br />
N<br />
L<br />
E<br />
Z<br />
Max<br />
F<br />
S<br />
M<br />
T<br />
P<br />
O
P<br />
O<br />
T (P)<br />
S<br />
Pal<br />
M<br />
Scull<br />
F<br />
N<br />
E<br />
V<br />
Max<br />
neurocranium<br />
capsula encephalica,<br />
capsula ethmoidalis,<br />
capsula optica,<br />
capsula otica<br />
splanchnocranium<br />
(viscerocranium)
Scull in the newborn, in 7 years <strong>and</strong> in adult<br />
proportions<br />
newborn<br />
7 years<br />
neurocranium<br />
splanchnocranium<br />
adult
Desmocranium <strong>and</strong> chondrocranium<br />
• intramenbranous ossification – directly<br />
from the mesenchymal connective tissue<br />
(most <strong>of</strong> the splanchnocranium <strong>and</strong><br />
calvaria)<br />
• enchondral ossification -ossification <strong>of</strong> the<br />
cartilaginous model (mainly bones <strong>of</strong> skull<br />
base)
PRIMITIVE CHONDROCRANIUM<br />
capsula<br />
ethmoidea<br />
branchial<br />
arches I<br />
capsula<br />
optica<br />
capsula<br />
otica<br />
occipital<br />
vertebrae<br />
CARTILAGINOUS CHONDROCRANIUM AND DESMOCRANIUM<br />
II<br />
VI<br />
desmocranium<br />
chondrocranium
Desmocranium <strong>and</strong> chondrocranium in the newborn<br />
os frontale<br />
os ethmoidale<br />
os nasale<br />
maxilla<br />
os lacrimale<br />
os zygomaticum<br />
desmocranium<br />
chondrocranium<br />
m<strong>and</strong>ibula Meckels<br />
cartilage<br />
os temporale -tympanic part<br />
os sphenoidale<br />
malleus<br />
os parietale<br />
squama ossis occipitalis<br />
os occipitale<br />
os temporale squama<br />
styloid process
Desmocranium <strong>and</strong> chondrocranium<br />
N<br />
L<br />
E<br />
Z<br />
Max<br />
F<br />
S<br />
M<br />
pyramis<br />
T<br />
P<br />
O<br />
mastoid process<br />
styloid process
prechordal cartilages<br />
ala orbitalis<br />
hypophysial cartilage<br />
ala temporalis<br />
parachordal<br />
cartilage<br />
periotic<br />
capsule<br />
occipital sclerotoms<br />
chorda dorsalis<br />
(notochord)<br />
Development <strong>of</strong> the <strong>scull</strong> base<br />
6 weeks<br />
Chondrocranium<br />
ethmoid bone<br />
lesser wing<br />
greater wing<br />
body sphenoid<br />
basilar part <strong>of</strong><br />
occipital bone<br />
occipital sclerotoms<br />
pyramis <strong>of</strong><br />
temporale bone
Development <strong>of</strong> the splanchnocranium – from branchial arches<br />
1. branchial arch<br />
incus<br />
stapes<br />
2. branchial arch<br />
styloid process<br />
stylohyoid ligament<br />
3. branchial arch<br />
greater horn <strong>of</strong> the hyoid bone<br />
4. branchial arch<br />
6. branchial arch<br />
lesser horn <strong>of</strong> the hyoid bone<br />
epiglottis<br />
Meckels cartilage
Chondrocranium<br />
Ossification<br />
• os occipitale –basis <strong>and</strong> lateral<br />
parts<br />
• os temporale – pyramis <strong>and</strong><br />
mastoid process<br />
• os sphemnoidale (without<br />
medial lamina <strong>of</strong> pterygoid<br />
process)<br />
• os ethmoidale<br />
• inferior nasal concha<br />
• maleus, incus stapes<br />
• styloid process<br />
• hyoid bone<br />
• Desmocranium<br />
• os occipitale – squama<br />
• os parietale<br />
• os frontale<br />
• os temporale –squama<br />
• os tympanicum<br />
• os nasale<br />
• os lacrimale<br />
• vomer<br />
• medial lamina <strong>of</strong> pterygoid<br />
process<br />
• os palatinum<br />
• os zygomaticum<br />
• maxilla<br />
• m<strong>and</strong>ibula (Meckel cartilage)
Anterior aspect<br />
L<br />
Z<br />
S<br />
Max<br />
F<br />
M<br />
N<br />
E<br />
INC<br />
V
Openings for trigeminal nerve branches <strong>and</strong> spaces<br />
orbit<br />
pirifom aperture<br />
anterior nasal spine<br />
foramen<br />
supraorbitale<br />
foramen<br />
infraorbitale<br />
foramen<br />
mentale
Norma frontalis<br />
points for measurement<br />
zygion<br />
glabella<br />
nasion<br />
gnathion
Lateral aspect<br />
L<br />
N<br />
Frankfurt plane<br />
Max<br />
Z<br />
F<br />
S<br />
M<br />
T<br />
P<br />
O
opisthocranion<br />
bregma<br />
zygion<br />
gnathion<br />
Norma lateralis<br />
points for measurement<br />
glabella<br />
nasion
Inferior aspect<br />
palatine bone<br />
infreior nasal concha<br />
vomer<br />
styloid<br />
process<br />
mastoid<br />
process<br />
S<br />
O P<br />
Teeth<br />
T<br />
Z<br />
Maxilla<br />
tympanic<br />
bone
Inferior aspect<br />
choana<br />
foramen magnum<br />
Z<br />
M<br />
P<br />
V<br />
O<br />
S<br />
T
Norma basalis<br />
points for measurement<br />
opisthocranion<br />
basion
Calvaria from outside<br />
coronal suture<br />
bregma sagittal suture<br />
parietal foramen for emissary vein<br />
lambdoid suture<br />
lambda
Norma verticalis<br />
points for measurement<br />
euryon<br />
width<br />
glabella lenght<br />
opisthocranion<br />
euryon
Calvaria from inside<br />
sulci arteriae<br />
meningeae mediae<br />
granular foveolae<br />
diploe<br />
frontal sinus<br />
sulcus sinus<br />
sagittalis<br />
superioris<br />
sinus x sinus<br />
air filled cavity x vein between dura mater <strong>and</strong> periosteum or only between dura mater
grooves for<br />
middle<br />
meningeal<br />
artrery<br />
INC<br />
Skull – sagittal section - inner surface<br />
Max<br />
M<br />
F<br />
S<br />
groove - sulcus<br />
P<br />
O<br />
grooves for<br />
sinuses<br />
grooves for branches <strong>of</strong> cranial nerves
N<br />
Skull - midline section - inner surface<br />
E<br />
V<br />
P<br />
F<br />
S<br />
T<br />
P<br />
O
Os sphenoidale<br />
posterior aspect<br />
dorsum sellae<br />
body<br />
lesser wing<br />
pterygoid process<br />
greater wing<br />
(cerebral<br />
orbital<br />
temporal<br />
infratemporal<br />
+sphenomaxilar<br />
surfaces)
Sphenoid bone<br />
anterior aspect - schema<br />
greater wing<br />
lesser wing<br />
pterygoid process<br />
„the pilot sits“ in the<br />
hypophyseal fossa<br />
sphenoid<br />
rostrum<br />
sphenoid sinus<br />
superior<br />
orbital fissure<br />
foramen rotundum<br />
pterygoid canal
ethmoid, frontal,<br />
occipital; parietal,<br />
temporal<br />
Os sphenoidale - placement<br />
right orbit<br />
ethmoid, frontal, zygomatic
Os sphenoidale <strong>and</strong> maxilla, palatine bone <strong>and</strong> vomer<br />
pterygomaxillary fissure<br />
lateral aspect<br />
perpendicular plate<br />
<strong>of</strong> the palatine bone<br />
lateral wall <strong>of</strong> the nasal cavity<br />
vomer<br />
nasal septum
Os sphenoidale –<br />
inferior aspect<br />
Os palatinum<br />
Vomer
Os sphenoidale openings <strong>and</strong> grooves<br />
aspect from superoposterior left side<br />
sulcus prechiasmaticus<br />
superior orbital fissure<br />
turkish saddle<br />
optic canal<br />
canalis<br />
pterygoideus<br />
fossa hypophysialis<br />
sulcus caroticus<br />
foramen<br />
rotundum<br />
foramen<br />
spinosum<br />
foramen ovale
dorsum sellae<br />
Sella turcica<br />
(turkish saddle)<br />
hypohysial<br />
fossa<br />
anterior clinoid process<br />
sphenoid sinus
Os temporale- lateral aspect<br />
zygomatic bone<br />
graeter wing <strong>of</strong> sphenoid<br />
parietal bone<br />
temporale bone - squama<br />
occipital bone
Os temporale inferior aspect - parts<br />
zygomatic process<br />
tympanic part<br />
mastoid process<br />
squamous part<br />
petrosal part (pyramis)<br />
styloid process
Os temporale -superior aspect<br />
anterior <strong>and</strong> posterior wallgrooves<br />
<strong>of</strong> sinuses, nerves <strong>and</strong><br />
middle meningeal artery<br />
os petrosum – pyramis, inside are:<br />
1) bony labyrinth<br />
2) canalis caroticus<br />
3) canalis nervi facialis<br />
4) canalis musculotubarius<br />
5) canaliculus cochlea<br />
6) aquaeductus vestibuli<br />
7) canaliculus tympanicus (for branch <strong>of</strong> IX.n)<br />
8) canaliculus chordae tympani (from VII.n)<br />
9) canaliculus mastoideus (for external branch<br />
<strong>of</strong> X.n.)<br />
squama
Position <strong>of</strong> the inner ear in petrosal bone<br />
cochlea<br />
canales<br />
semicirculares<br />
(ant., post., lat.)<br />
n.vestibulocochlearis
Os temporale labyrinthus osseus<br />
1-squama<br />
2-porus acusticus int.<br />
n.VII +VIII)<br />
3-sulcus sinus sigmoidei<br />
4-apex pyramidis<br />
5-semicircular canals
Os temporale cochlea<br />
cochlea<br />
impressio n.trigemini<br />
squama ossis<br />
temporalis<br />
antrum<br />
mastoideum
Fossa cranii posterior<br />
meatus acusticus internus<br />
(n.VII. a n.VIII.)<br />
sulcus sinus petrosi<br />
inferioris<br />
foramen jugulare<br />
(n.IX., X., a XI.)<br />
canalis nervi hypoglossi<br />
Os petrosum (pyramis) - posterior wall<br />
fossa subarcuata<br />
apertura externa<br />
aquaeductus vestibuli<br />
sulcus sinus sigmoidei
Os petrosum (pyramis) - posterior wall<br />
sulcus<br />
meatus acusticus<br />
internus<br />
sinus<br />
petrosi apertura externa aquaeductus vestibuli<br />
nerves VII,VIII superioris<br />
semicircularendolymphatetic<br />
cochlea canals sac<br />
sulcus sinus<br />
petrosi inferioris<br />
incisura jugularis<br />
(jugular notch)<br />
sulcus sinus sigmoidei<br />
nerves IX,X,XI.
Fundus meatus acustici interni – nerves VII. <strong>and</strong> VIII.<br />
right pyramis posterior aspect<br />
crista transversa<br />
A<br />
area n. facialis<br />
facial nerve –n.VII.<br />
cochlear nerve<br />
area<br />
vestibularis<br />
superior<br />
P<br />
area<br />
vestibularis<br />
inferior
Canalis nervi facialis<br />
1) anterolateraly<br />
2) posterolateraly<br />
3) caudaly<br />
internal acoustic<br />
meatus<br />
facial nerve (VII.n)<br />
cochlear nerve<br />
vestibular nerve<br />
greater<br />
petrosal nerve<br />
stylomastoid foramen
Important openings<br />
on the inferior wall<br />
<strong>of</strong> petrosal bone<br />
canaliculus mastoideus<br />
(ramus auricularis n.vagi)<br />
tympanomastoid fissure<br />
(ramus auricularis n.vagi)<br />
mastoid foramen<br />
(emissary vein)<br />
stylomastoid foramen<br />
(facial nerve – VII.n)<br />
petrotympanic fissure<br />
(chorda tympani)<br />
carotid canal<br />
internal carotid artery<br />
fossula petrosa<br />
(tympanic nerve)<br />
opening <strong>of</strong><br />
canaliculus cochleae<br />
jugular fossa<br />
(internal<br />
jugular vein)
Walls<br />
Middle ear cavity (cavum tympani)<br />
Lat.- membranous wall<br />
(drum)<br />
Sup.- tegmental wall – tegmen tympani<br />
post. mastoid wall<br />
ant. - carotic wall<br />
Inf.- jugular wall – jugular vein<br />
Med.- labyrinthic wall<br />
(inner ear)
Section -<br />
anterobasal wall<br />
<strong>of</strong> petrosal bone<br />
– medial wall <strong>of</strong><br />
the middle ear<br />
cavity<br />
Mastoid<br />
aer cells<br />
n. stapedius<br />
Mastoid<br />
antrum<br />
chorda<br />
tympani<br />
Epitympanic<br />
recess<br />
Facial canal<br />
Tympanic nerve<br />
(from IX.n)
Tympanic cavity – schematic frontal section<br />
Paries labyrinthicus – anterobasal wall <strong>of</strong> petrosal bone<br />
Recessus<br />
epitympanicus<br />
Membrana<br />
tympani<br />
chorda tympani<br />
Fossa cranii media<br />
M<br />
I<br />
S<br />
Bulbus v. jugularis int.<br />
Canalis semicircularis<br />
lateralis<br />
N. facialis<br />
Fenestra ovalis -<br />
vestbuli<br />
Promontorium – 1.<br />
convolution <strong>of</strong><br />
cochlea<br />
Fenestra rotunda -<br />
cochleae
Os ethmoidale<br />
posterior<br />
aspect<br />
bulla<br />
ethmoidale air cells ethmoidalis<br />
(cellulae ethmoidales)<br />
processus uncinatus<br />
concha nasalis media<br />
crista galli<br />
cribriform plate<br />
orbital plate<br />
perpendicular plate
frontal process<br />
zygomatic process<br />
corpus maxillae<br />
(body)<br />
Maxilla<br />
tuber maxillae<br />
alveolar process
praemaxilla<br />
(os incisivum)<br />
Maxilla<br />
palatine process
Maxilla<br />
maxillary sinus
M<strong>and</strong>ible lateral aspect<br />
alveolar<br />
process<br />
mental<br />
protuberance<br />
coronoid process<br />
m<strong>and</strong>ibular notch<br />
corpus m<strong>and</strong>ibulae<br />
condylar<br />
process<br />
ramus<br />
m<strong>and</strong>ibulae
M<strong>and</strong>ible<br />
anterolateral view<br />
pterygoid<br />
tuberosity<br />
m<strong>and</strong>ibular foramen<br />
masseteric<br />
tuberosity<br />
mental foramen<br />
pterygoid fossa
sublingual fossa<br />
mylohyoid line<br />
subm<strong>and</strong>ibular fossa<br />
m<strong>and</strong>ibular foramen<br />
mylohyoid groove
M<strong>and</strong>ible <strong>of</strong> Karel IV.<br />
Post traumatic changes A-C<br />
Correction <strong>of</strong> the occlusion
Skull <strong>of</strong> a newborn<br />
Lenght 11 cm<br />
Circumference 34 cm<br />
Fonticulus anterior<br />
it closes in 2-3 years
Lenght 11 cm<br />
Circumference 34 cm<br />
fontanellae = fonticuli cranii<br />
Fontanella major<br />
(it closes in 2. or 3.year)<br />
Fontanella minor<br />
(it closes in 3.month)
Fonticulus minor<br />
Tuber<br />
parietale<br />
Fonticulus major<br />
Tuber<br />
frontale<br />
Tuber
Sutura metopica<br />
Fonticulus major<br />
Symphysis menti Angulus m<strong>and</strong>ibulae
Fonticulus<br />
sphenoidalis<br />
Sutura<br />
mendosa<br />
Fonticulus<br />
angulus m<strong>and</strong>ibulae<br />
Anulus tympanicus mastoideus
Synchondrosis sphenooccipitalis<br />
Symphysis menti<br />
Synchondrosis<br />
intraoccipitalis<br />
anterior<br />
Fonticulus<br />
mastoideus<br />
Synchondrosis<br />
intraoccipitalis<br />
posterior
Craniosynostoses<br />
premature<br />
closure <strong>of</strong> cranial<br />
sutures<br />
trigonocephaly<br />
tuber frontale<br />
sutura coronalis<br />
tuber parietale<br />
brachycephaly<br />
sutura lambdoidea<br />
anterior<br />
plagiocephaly<br />
sutura metopica<br />
fonticulus anterior<br />
sutura sagittalis<br />
fonticulus posterior<br />
posterior plagiocephaly<br />
dolichocephaly<br />
(scaphocephaly)
Skull <strong>of</strong> a newborn<br />
Big neurocranium<br />
Small splanchnocranium<br />
Prominent tubera frontalia et parietalia (centers <strong>of</strong> ossification)<br />
Fonticuli cranii<br />
Possible movement among bones <strong>of</strong> the calvaria<br />
Paranasal sinuses are not fully developed<br />
Os frontale divided by a suture<br />
Suture between maxilla <strong>and</strong> premaxilla<br />
Symphysis menti<br />
Angle <strong>of</strong> m<strong>and</strong>ible -150-160 degree<br />
Os tympanicum – anulus tympanicus
X-ray skull <strong>of</strong> a newborn
Lenticular left parietal calvarial mass-like lesion with<br />
peripheral sclerosis/calcification <strong>and</strong> central lucency.<br />
<strong>The</strong> lesion does not cross suture lines<br />
Subperiosteal cephalohematoma.
Cranial nerves !!!<br />
• I. nn. olfactorii<br />
• II. n. opticus<br />
• III. n. oculomotorius<br />
• IV. n. trochlearis<br />
• V. n. trigeminus 1.ophthalmicus<br />
• 2.maxillaris<br />
• 3.m<strong>and</strong>ibularis<br />
• VI. n. abducens<br />
• VII. n. facialis<br />
• VIII. n. vestibulocochlearis<br />
• IX. n. glossopharyngeus<br />
• X. n. vagus<br />
• XI. n. accessorius<br />
• XII. n. hypoglossus
Development<br />
<strong>of</strong> the face<br />
1- maxillary process<br />
2-m<strong>and</strong>ibular process<br />
3-second branchial arch<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1
Development<br />
<strong>of</strong> the face<br />
1-maxillary process<br />
2- m<strong>and</strong>ibular process<br />
3-medial nasal process<br />
4-lateral nasal process<br />
stadium 12<br />
I<br />
II<br />
stadium 13<br />
1<br />
1<br />
2<br />
3<br />
stadium 15<br />
2<br />
4<br />
3
prominentia<br />
nas<strong>of</strong>rontalis<br />
oropharyngeal<br />
membrane<br />
Development <strong>of</strong> the face<br />
4 weeks<br />
6 weeks<br />
maxillar<br />
process<br />
5 weeks<br />
7 weeks<br />
internasal<br />
groove<br />
5,5 weeks<br />
9 weeks
Development <strong>of</strong> palate <strong>and</strong> nasal septum <strong>and</strong> nose<br />
medial nasal process<br />
lateral nasal<br />
process<br />
maxillar<br />
process<br />
primary palate<br />
nasal septum<br />
palatine process<br />
internasal groove
Meckel<br />
cartilage<br />
Development <strong>of</strong> the palatine processes<br />
palatine<br />
process<br />
nasal septum<br />
tongue<br />
palatine process
Sources<br />
• Čihák, Anatomie 1<br />
• Gray, Anatomy<br />
• Petrovický a spol., Anatomie 1<br />
• Sobotta , Atlas anatomie člověka<br />
• Ten Donkelaar, Lohmann en Moorman, Klinische<br />
Anatomie en Embryologie<br />
• Thieme, Atlas <strong>of</strong> Anatomy<br />
• http://anat.lf1.cuni.cz/muzeum/kranio.html<br />
• Personal archiv