Applications of AUSM+ Scheme on Subsonic, Supersonic and ...
Applications of AUSM+ Scheme on Subsonic, Supersonic and ...
Applications of AUSM+ Scheme on Subsonic, Supersonic and ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
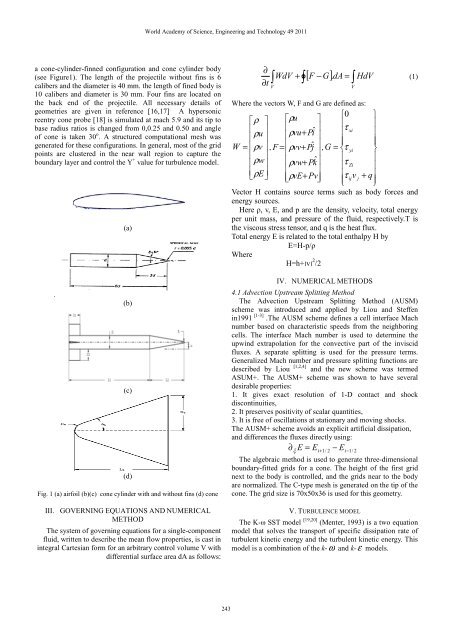
a c<strong>on</strong>e-cylinder-finned c<strong>on</strong>figurati<strong>on</strong> <strong>and</strong> c<strong>on</strong>e cylinder body<br />
(see Figure1). The length <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the projectile without fins is 6<br />
calibers <strong>and</strong> the diameter is 40 mm. the length <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> fined body is<br />
10 calibers <strong>and</strong> diameter is 30 mm. Four fins are located <strong>on</strong><br />
the back end <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the projectile. All necessary details <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
geometries are given in reference [16,17] . A hypers<strong>on</strong>ic<br />
reentry c<strong>on</strong>e probe [18] is simulated at mach 5.9 <strong>and</strong> its tip to<br />
base radius ratios is changed from 0,0.25 <strong>and</strong> 0.50 <strong>and</strong> angle<br />
<str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> c<strong>on</strong>e is taken 30 o . A structured computati<strong>on</strong>al mesh was<br />
generated for these c<strong>on</strong>figurati<strong>on</strong>s. In general, most <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the grid<br />
points are clustered in the near wall regi<strong>on</strong> to capture the<br />
boundary layer <strong>and</strong> c<strong>on</strong>trol the Y + value for turbulence model.<br />
.<br />
(a)<br />
(b)<br />
(c)<br />
(d)<br />
Fig. 1 (a) airfoil (b)(c) c<strong>on</strong>e cylinder with <strong>and</strong> without fins (d) c<strong>on</strong>e<br />
III. GOVERNING EQUATIONS AND NUMERICAL<br />
METHOD<br />
The system <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> governing equati<strong>on</strong>s for a single-comp<strong>on</strong>ent<br />
fluid, written to describe the mean flow properties, is cast in<br />
integral Cartesian form for an arbitrary c<strong>on</strong>trol volume V with<br />
differential surface area dA as follows:<br />
World Academy <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> Science, Engineering <strong>and</strong> Technology 49 2011<br />
243<br />
∂<br />
∂t<br />
∫<br />
V<br />
WdV +<br />
∫[<br />
F −G]<br />
dA = ∫<br />
. HdV (1)<br />
Where the vectors W, F <strong>and</strong> G are defined as:<br />
⎡ρ<br />
⎤ ⎡ρu<br />
⎤<br />
⎧0<br />
⎫<br />
⎢ ⎥ ⎢ ⎥<br />
⎪ ⎪<br />
⎢<br />
ρu<br />
⎥ ⎢ρvu+<br />
Piˆ<br />
⎥<br />
⎪<br />
τ xi ⎪<br />
W = ⎢ρv<br />
⎥ , ⎢ ⎥<br />
⎪ ⎪<br />
F = ρvv+<br />
Pˆj<br />
, G =<br />
⎢ ⎥ ⎢ ⎥<br />
⎨τ<br />
yi ⎬<br />
⎢ρw⎥<br />
⎢ρvw+<br />
Pkˆ<br />
⎥<br />
⎪ ⎪<br />
⎢<br />
⎣ρE⎥<br />
⎢ ⎥<br />
⎪<br />
τ Zi ⎪<br />
⎦ ⎢⎣<br />
ρvE+<br />
Pv⎥<br />
⎪ ⎪<br />
⎦ τ ijv<br />
j + q<br />
⎪⎩<br />
⎪⎭<br />
Vector H c<strong>on</strong>tains source terms such as body forces <strong>and</strong><br />
energy sources.<br />
Here ρ, v, E, <strong>and</strong> p are the density, velocity, total energy<br />
per unit mass, <strong>and</strong> pressure <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the fluid, respectively.Τ is<br />
the viscous stress tensor, <strong>and</strong> q is the heat flux.<br />
Total energy E is related to the total enthalpy H by<br />
E=H-p/ρ<br />
Where<br />
H=h+׀v׀ 2 /2<br />
IV. NUMERICAL METHODS<br />
4.1 Advecti<strong>on</strong> Upstream Splitting Method<br />
The Advecti<strong>on</strong> Upstream Splitting Method (AUSM)<br />
scheme was introduced <strong>and</strong> applied by Liou <strong>and</strong> Steffen<br />
in1991 [1-3] .The AUSM scheme defines a cell interface Mach<br />
number based <strong>on</strong> characteristic speeds from the neighboring<br />
cells. The interface Mach number is used to determine the<br />
upwind extrapolati<strong>on</strong> for the c<strong>on</strong>vective part <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the inviscid<br />
fluxes. A separate splitting is used for the pressure terms.<br />
Generalized Mach number <strong>and</strong> pressure splitting functi<strong>on</strong>s are<br />
described by Liou [1,2,4] <strong>and</strong> the new scheme was termed<br />
ASUM+. The <str<strong>on</strong>g>AUSM+</str<strong>on</strong>g> scheme was shown to have several<br />
desirable properties:<br />
1. It gives exact resoluti<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> 1-D c<strong>on</strong>tact <strong>and</strong> shock<br />
disc<strong>on</strong>tinuities,<br />
2. It preserves positivity <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> scalar quantities,<br />
3. It is free <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> oscillati<strong>on</strong>s at stati<strong>on</strong>ary <strong>and</strong> moving shocks.<br />
The <str<strong>on</strong>g>AUSM+</str<strong>on</strong>g> scheme avoids an explicit artificial dissipati<strong>on</strong>,<br />
<strong>and</strong> differences the fluxes directly using:<br />
∂ E = Ei<br />
− Ei<br />
ξ<br />
V<br />
+ 1/ 2 −1/<br />
2<br />
The algebraic method is used to generate three-dimensi<strong>on</strong>al<br />
boundary-fitted grids for a c<strong>on</strong>e. The height <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the first grid<br />
next to the body is c<strong>on</strong>trolled, <strong>and</strong> the grids near to the body<br />
are normalized. The C-type mesh is generated <strong>on</strong> the tip <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the<br />
c<strong>on</strong>e. The grid size is 70x50x36 is used for this geometry.<br />
V. TURBULENCE MODEL<br />
The K-ω SST model [19,20] (Menter, 1993) is a two equati<strong>on</strong><br />
model that solves the transport <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> specific dissipati<strong>on</strong> rate <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g><br />
turbulent kinetic energy <strong>and</strong> the turbulent kinetic energy. This<br />
model is a combinati<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>of</str<strong>on</strong>g> the k-ω <strong>and</strong> k-ε models.