Physical Chemistry 2.pdf - OER@AVU - African Virtual University
Physical Chemistry 2.pdf - OER@AVU - African Virtual University
Physical Chemistry 2.pdf - OER@AVU - African Virtual University
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
1.9.2 Osmosis<br />
<strong>African</strong> <strong>Virtual</strong> <strong>University</strong><br />
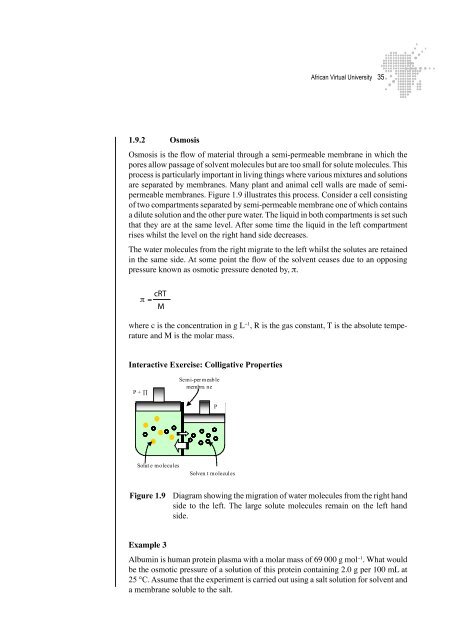
Osmosis is the flow of material through a semi-permeable membrane in which the<br />
pores allow passage of solvent molecules but are too small for solute molecules. This<br />
process is particularly important in living things where various mixtures and solutions<br />
are separated by membranes. Many plant and animal cell walls are made of semipermeable<br />
membranes. Figure 1.9 illustrates this process. Consider a cell consisting<br />
of two compartments separated by semi-permeable membrane one of which contains<br />
a dilute solution and the other pure water. The liquid in both compartments is set such<br />
that they are at the same level. After some time the liquid in the left compartment<br />
rises whilst the level on the right hand side decreases.<br />
The water molecules from the right migrate to the left whilst the solutes are retained<br />
in the same side. At some point the flow of the solvent ceases due to an opposing<br />
pressure known as osmotic pressure denoted by, π.<br />
cRT<br />
π =<br />
M<br />
where c is the concentration in g L −1 , R is the gas constant, T is the absolute temperature<br />
and M is the molar mass.<br />
Interactive Exercise: Colligative Properties<br />
P + ∏<br />
Solut e molecules<br />
Semi-per meab le<br />
membra ne<br />
P<br />
Solven t molecules<br />
F ig ure 1.9 Diagram<br />
showing the migration of<br />
water m olecules from the<br />
right hand side side. to the left.<br />
The large solu te molecu les<br />
remain on the left hand<br />
side.<br />
Figure 1.9 Diagram showing the migration of water molecules from the right hand<br />
side to the left. The large solute molecules remain on the left hand<br />
Example 3<br />
Albumin is human protein plasma with a molar mass of 69 000 g mol−1 . What would<br />
be the osmotic pressure of a solution of this protein containing 2.0 g per 100 mL at<br />
25 °C. Assume that the experiment is carried out using a salt solution for solvent and<br />
a membrane soluble to the salt.