Sanitary Landfills: Toward Sustainable Development - lumes
Sanitary Landfills: Toward Sustainable Development - lumes
Sanitary Landfills: Toward Sustainable Development - lumes
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
5 Case Study of Malaysia<br />
LUMES 2000-2001<br />
<strong>Sanitary</strong> <strong>Landfills</strong>: <strong>Toward</strong> <strong>Sustainable</strong> <strong>Development</strong><br />
5.1 Background<br />
One of the major consequences of rapid economic growth, urbanisation, industrialisation and<br />
population growth is the massive generation of solid wastes. As a country that moving forward to<br />
achieve the industrialised country status by the year 2020, Malaysia cannot escape from facing<br />
the solid waste management problems. As indicated in World Bank report (1993), solid waste is<br />
one of the major environmental problems faced by most municipalities in Malaysia. The<br />
municipalities are not only facing the increasing municipal solid waste and its rising complexity,<br />
they are also lacking of funding to carry out the sound solid waste management. The lack of a<br />
uniform national solid waste policy coupled with insufficient legislation has further complicated<br />
the solid waste problems in Malaysia.<br />
5.1.1 Waste Generation and Composition<br />
The amount of solid waste has been increasing continuously since the 1980’s. The per capital<br />
waste generation has increased 2 folds from 0.5kg/capital/day in the early 1980’s to current<br />
volume of 1kg/capital/day (Agamuthu, 2001) The huge increased in solid waste generation<br />
attributes to the rapid economic growth, increasing urbanisation, rising living standard, changes<br />
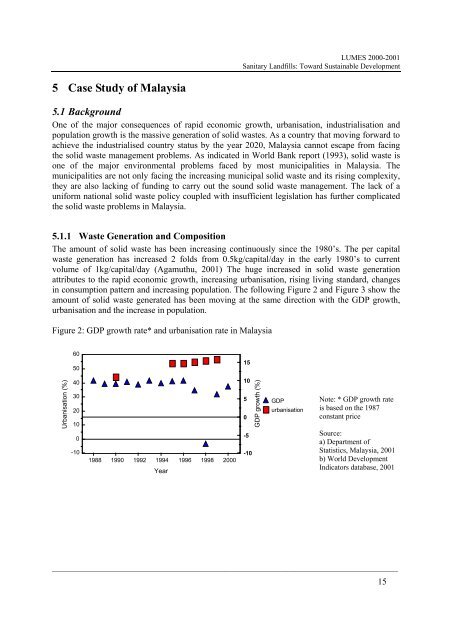
in consumption pattern and increasing population. The following Figure 2 and Figure 3 show the<br />
amount of solid waste generated has been moving at the same direction with the GDP growth,<br />
urbanisation and the increase in population.<br />
Figure 2: GDP growth rate* and urbanisation rate in Malaysia<br />
Urbanisation (%)<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
0<br />
-10<br />
1988 1990 1992 1994<br />
Year<br />
1996 1998 2000<br />
Note: * GDP growth rate<br />
is based on the 1987<br />
constant price<br />
Source:<br />
a) Department of<br />
Statistics, Malaysia, 2001<br />
b) World <strong>Development</strong><br />
Indicators database, 2001<br />
______________________________________________________________________________<br />
15<br />
10<br />
5<br />
0<br />
-5<br />
-10<br />
GDP growth (%)<br />
GDP<br />
urbanisation<br />
15