Chapter 11 Slope Stabilization and Stability of Cuts
Chapter 11 Slope Stabilization and Stability of Cuts
Chapter 11 Slope Stabilization and Stability of Cuts
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
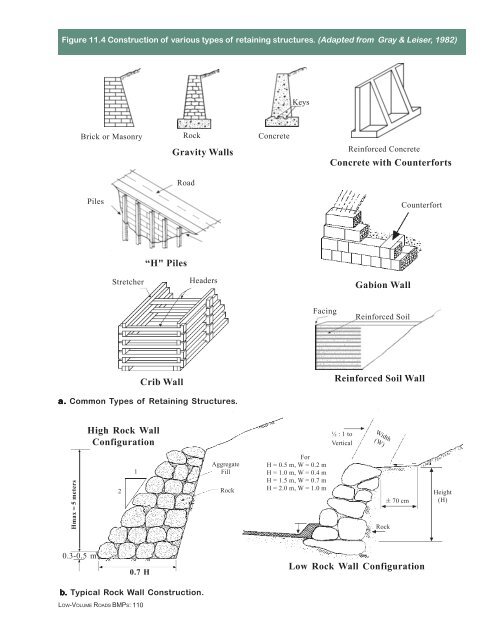
Figure <strong>11</strong>.4 Construction <strong>of</strong> various types <strong>of</strong> retaining structures. (Adapted from Gray & Leiser, 1982)<br />
a. a. Common Types <strong>of</strong> Retaining Structures.<br />
Hmax = 5 meters<br />
Brick or Masonry<br />
Piles<br />
0.3-0.5 m<br />
Stretcher<br />
High Rock Wall<br />
Configuration<br />
LOW-VOLUME ROADS BMPS: <strong>11</strong>0<br />
2<br />
“H" Piles<br />
Crib Wall<br />
Rock<br />
Road<br />
Headers<br />
b. Typical Rock Wall Construction.<br />
1<br />
0.7 H<br />
Gravity Walls<br />
Aggregate<br />
Fill<br />
Concrete<br />
Keys<br />
Facing<br />
For<br />
H = 0.5 m, W = 0.2 m<br />
H = 1.0 m, W = 0.4 m<br />
H = 1.5 m, W = 0.7 m<br />
H = 2.0 m, W = 1.0 m<br />
Reinforced Concrete<br />
Concrete with Counterforts<br />
Gabion Wall<br />
Reinforced Soil<br />
Counterfort<br />
Reinforced Soil Wall<br />
½ : 1 to<br />
Vertical<br />
Width<br />
(W)<br />
Rock Height<br />
(H)<br />
± 70 cm<br />
Rock<br />
Low Rock Wall Configuration