Chapter 10 Torsion Tests
Chapter 10 Torsion Tests
Chapter 10 Torsion Tests
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
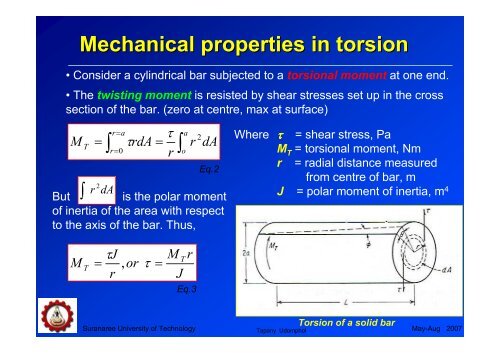
Mechanical properties in torsion<br />
• Consider a cylindrical bar subjected to a torsional moment at one end.<br />
• The twisting moment is resisted by shear stresses set up in the cross<br />
section of the bar. (zero at centre, max at surface)<br />
M<br />
T<br />
= = r a<br />
∫<br />
∫ dA<br />
r=<br />
0<br />
τ<br />
τrdA<br />
=<br />
r<br />
∫<br />
o<br />
a<br />
r<br />
2<br />
dA<br />
r<br />
But is the polar moment<br />
of inertia of the area with respect<br />
to the axis of the bar. Thus,<br />
2<br />
M<br />
T<br />
τ J<br />
= , or τ =<br />
r<br />
M<br />
J<br />
T<br />
r<br />
Eq.3<br />
Eq.2<br />
Where ττττ = shear stress, Pa<br />
M T = torsional moment, Nm<br />
r = radial distance measured<br />
from centre of bar, m<br />
J = polar moment of inertia, m 4<br />
<strong>Torsion</strong> of a solid bar<br />
Suranaree University of Technology May-Aug 2007<br />
Tapany Udomphol