Demystifying Recurrent Oral Ulcerations - IneedCE.com
Demystifying Recurrent Oral Ulcerations - IneedCE.com
Demystifying Recurrent Oral Ulcerations - IneedCE.com
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
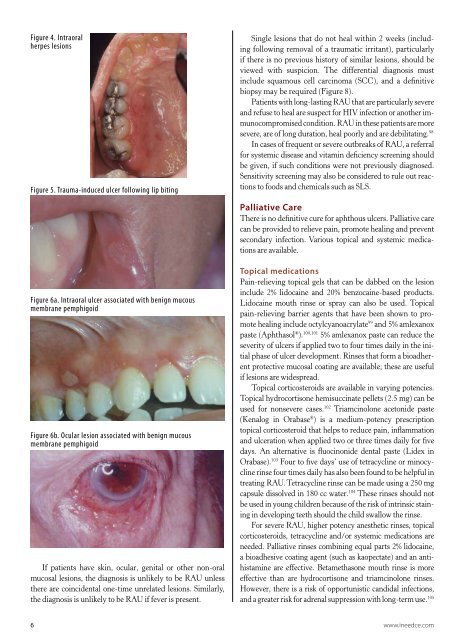
Figure 4. Intraoral<br />
herpes lesions<br />
Figure 5. Trauma-induced ulcer following lip biting<br />
Figure 6a. Intraoral ulcer associated with benign mucous<br />
membrane pemphigoid<br />
Figure 6b. Ocular lesion associated with benign mucous<br />
membrane pemphigoid<br />
If patients have skin, ocular, genital or other non-oral<br />
mucosal lesions, the diagnosis is unlikely to be RAU unless<br />
there are coincidental one-time unrelated lesions. Similarly,<br />
the diagnosis is unlikely to be RAU if fever is present.<br />
Single lesions that do not heal within 2 weeks (including<br />
following removal of a traumatic irritant), particularly<br />
if there is no previous history of similar lesions, should be<br />
viewed with suspicion. The differential diagnosis must<br />
include squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and a definitive<br />
biopsy may be required (Figure 8).<br />
Patients with long-lasting RAU that are particularly severe<br />
and refuse to heal are suspect for HIV infection or another immuno<strong>com</strong>promised<br />
condition. RAU in these patients are more<br />
severe, are of long duration, heal poorly and are debilitating. 98<br />
In cases of frequent or severe outbreaks of RAU, a referral<br />
for systemic disease and vitamin deficiency screening should<br />
be given, if such conditions were not previously diagnosed.<br />
Sensitivity screening may also be considered to rule out reactions<br />
to foods and chemicals such as SLS.<br />
Palliative Care<br />
There is no definitive cure for aphthous ulcers. Palliative care<br />
can be provided to relieve pain, promote healing and prevent<br />
secondary infection. Various topical and systemic medications<br />
are available.<br />
Topical medications<br />
Pain-relieving topical gels that can be dabbed on the lesion<br />
include 2% lidocaine and 20% benzocaine-based products.<br />
Lidocaine mouth rinse or spray can also be used. Topical<br />
pain-relieving barrier agents that have been shown to promote<br />
healing include octylcyanoacrylate 99 and 5% amlexanox<br />
paste (Aphthasol ® ). 100,101 5% amlexanox paste can reduce the<br />
severity of ulcers if applied two to four times daily in the initial<br />
phase of ulcer development. Rinses that form a bioadherent<br />
protective mucosal coating are available; these are useful<br />
if lesions are widespread.<br />
Topical corticosteroids are available in varying potencies.<br />
Topical hydrocortisone hemisuccinate pellets (2.5 mg) can be<br />
used for nonsevere cases. 102 Triamcinolone acetonide paste<br />
(Kena log in Orabase ® ) is a medium-potency prescription<br />
topical corticosteroid that helps to reduce pain, inflammation<br />
and ul cera tion when applied two or three times daily for five<br />
days. An alternative is fluocinonide dental paste (Lidex in<br />
Orabase). 103 Four to five days’ use of tetracycline or minocycline<br />
rinse four times daily has also been found to be helpful in<br />
treating RAU. Tetracycline rinse can be made using a 250 mg<br />
capsule dissolved in 180 cc water. 104 These rinses should not<br />
be used in young children because of the risk of intrinsic staining<br />
in developing teeth should the child swallow the rinse.<br />
For severe RAU, higher potency anesthetic rinses, topical<br />
corticosteroids, tetracycline and/or systemic medications are<br />
needed. Palliative rinses <strong>com</strong>bining equal parts 2% lidocaine,<br />
a bioadhesive coating agent (such as kaopectate) and an antihistamine<br />
are effective. Betamethasone mouth rinse is more<br />
effective than are hydrocortisone and triamcinolone rinses.<br />
However, there is a risk of opportunistic candidal infections,<br />
and a greater risk for adrenal suppression with long-term use. 105<br />
6 www.ineedce.<strong>com</strong>