Acoustic Waveforms Acoustic Waveforms Simple Harmonic Motion ...
Acoustic Waveforms Acoustic Waveforms Simple Harmonic Motion ...
Acoustic Waveforms Acoustic Waveforms Simple Harmonic Motion ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
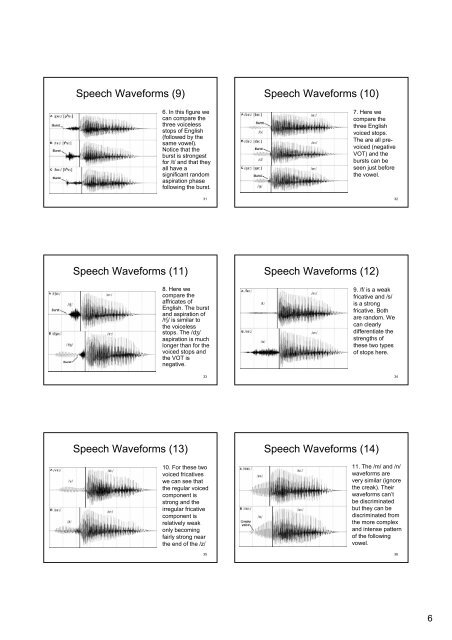
Speech <strong>Waveforms</strong> (9)<br />
6. In this figure we<br />
can compare the<br />
three voiceless<br />
stops of English<br />
(followed by the<br />
same vowel).<br />
Notice that the<br />
burst is strongest<br />
for /t/ and that they<br />
all have a<br />
significant random<br />
aspiration phase<br />
following the burst.<br />
Speech <strong>Waveforms</strong> (11)<br />
31<br />
8. Here we<br />
compare the<br />
affricates of<br />
English. The burst<br />
and aspiration of<br />
/tS/ is similar to<br />
the voiceless<br />
stops. The /dZ/<br />
aspiration is much<br />
longer than for the<br />
voiced stops and<br />
the VOT is<br />
negative.<br />
Speech <strong>Waveforms</strong> (13)<br />
33<br />
10. For these two<br />
voiced fricatives<br />
we can see that<br />
the regular voiced<br />
component is<br />
strong and the<br />
irregular fricative<br />
component is<br />
relatively weak<br />
only becoming<br />
fairly strong near<br />
the end of the /z/<br />
35<br />
Speech <strong>Waveforms</strong> (10)<br />
7. Here we<br />
compare the<br />
three English<br />
voiced stops.<br />
The are all prevoiced<br />
(negative<br />
VOT) and the<br />
bursts can be<br />
seen just before<br />
the vowel.<br />
Speech <strong>Waveforms</strong> (12)<br />
9. /f/ is a weak<br />
fricative and /s/<br />
is a strong<br />
fricative. Both<br />
are random. We<br />
can clearly<br />
differentiate the<br />
strengths of<br />
these two types<br />
of stops here.<br />
Speech <strong>Waveforms</strong> (14)<br />
32<br />
34<br />
11. The /m/ and /n/<br />
waveforms are<br />
very similar (ignore<br />
the creak). Their<br />
waveforms can’t<br />
be discriminated<br />
but they can be<br />
discriminated from<br />
the more complex<br />
and intense pattern<br />
of the following<br />
vowel.<br />
36<br />
6