PHONETICS AND PHONOLOGY VOWEL SYSTEMS: SOLUTION ...
PHONETICS AND PHONOLOGY VOWEL SYSTEMS: SOLUTION ...
PHONETICS AND PHONOLOGY VOWEL SYSTEMS: SOLUTION ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>PHONETICS</strong> <strong>AND</strong> <strong>PHONOLOGY</strong><br />
<strong>VOWEL</strong> <strong>SYSTEMS</strong>: <strong>SOLUTION</strong><br />
Revise the lecture materials on the nature of vowel systems including the<br />
concept of symmetry and the dynamic processes of change.<br />
Vowel systems in language are usually symmetrical. Revise maximal<br />
contrast/dispersion as a perceptual requirement. Go over the idea of a single feature<br />
often used as contrast e.g. nasality, rounding, length.<br />
Activities<br />
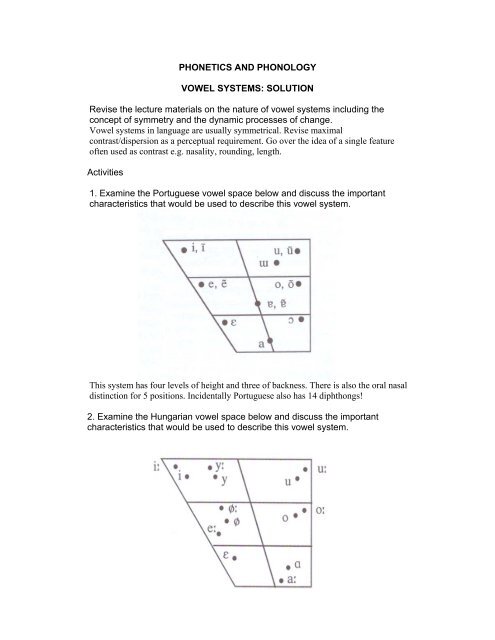
1. Examine the Portuguese vowel space below and discuss the important<br />
characteristics that would be used to describe this vowel system.<br />
This system has four levels of height and three of backness. There is also the oral nasal<br />
distinction for 5 positions. Incidentally Portuguese also has 14 diphthongs!<br />
2. Examine the Hungarian vowel space below and discuss the important<br />
characteristics that would be used to describe this vowel system.
Hungarian has seven basic vowel qualities occurring as long and short vowels at each<br />
place. The short vowels are generally lower and less peripheral<br />
3. A language with the vowel system illustrated below is in the process of<br />
undergoing a change such that the low central vowel is moving towards the<br />
back of the space. Discuss the potential implications of this shift. Assume that<br />
there are no length distinctions.<br />
If the low vowel moves back it will start to encroach upon the low back vowel which may<br />
have to change in some way to prevent a merger. Think of different ways the system could<br />
cope with this potential conflict. e.g. the back vowel could become rounded or more<br />
probably it would start to rise. This might set up a chain of events that could affect the<br />
entire back dimension with all vowels rising. But there would be a problem with /u/ unable<br />
to go any higher. What might be the possible effects on /u/ e.g. fronting or diphthongisation.<br />
4. A language has two diphthongs that rise from the low front and low back of the<br />
space. These diphthongs are closely associated with the two low monophthongs.<br />
Discuss the possible effect of monophthong raising on these two diphthongs. What<br />
impact might this have on the third diphthong in the language?<br />
Raising the two low monophthongs could cause a concomitant shift in the first target of the<br />
two associated diphthongs through the process of monophthong / diphthong<br />
interdependence. This would impact on the third diphthong because there would be two<br />
diphthongs in the system with the same trajectory pattern. This third diphthong would<br />
presumably also have to change to prevent merger.
5. The following is a corpus of words from French<br />
̃<br />
[si] “si” ‘if’ [se] “ses” ‘his,hers (p)’<br />
[s] “sait” ‘knows’ [sy] “su” ‘known’<br />
[sø] “ceux” ‘these’ [sœʁ] “soeur” ‘sister’<br />
[sə] “ce” ‘this’ [sa] “sa” ‘his, hers (f)’<br />
[su] “sous” ‘under’ [so] “sot” ‘silly’<br />
[sɔʁ] “sort” ‘fate’ [sɑ̃̃]<br />
“sans” ‘without’<br />
[sɔ̃] “son” ‘his,hers (m sg)’ [sɛ̃̃]<br />
“saint” ‘saint’<br />
Plot the approximate position of the vowels on the chart below and comment<br />
on the system of vowels used in this language. /a/ is low central
French vowel system has four degrees of height and three degrees of backness. All back<br />
vowels (except low) are rounded. The front vowel set has both unrounded and rounded<br />
elements at each place (except the low). There are no length contrasts for most speakers.<br />
French has four nasalised vowels but here we have only represented three because many<br />
speakers have merged the low and half low front nasalised vowels into the half low.<br />
6. Discuss potential difficulties that Japanese speakers might have with the<br />
differentiation and production of English vowels based on the following vowel space<br />
from Japanese. Japanese has a length contrast at each of these vowel places.<br />
There are potential problems with differentiating/producing the distinctions between the<br />
HAT vowel and the HUT vowel, also COT/CAUGHT. There is no central vowel so the<br />
HURT vowel could cause problems.