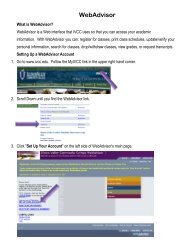
Sensation & Perception
Sensation & Perception
Sensation & Perception
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Visual System<br />
Normal vision is chromatic in the fovea and achromatic<br />
in the periphery.<br />
Photopigments in the cones allow for color vision. Three<br />
types of cones (red/green, blue/yellow, black/white) allow<br />
for trichromatic vision.<br />
When one type of cone is dysfunctional color blindness<br />
results, this is called dichromatic vision. If two types of<br />
cones are dysfunctional the result is monochromatic<br />
vision. If all three cones are dysfunctional the individual<br />
has achromatic vision.<br />
The trichromatic theory suggests that the relative<br />
activation of these three cone types accounts for the<br />
perception of colors that we see. It does not account for<br />
negative after-images. The Opponent-Process Theory<br />
does account for the negative after-image. Looking at a<br />
single color and then away from that color “turns on” the<br />
opponent color.