PDF version of Lecture Slides - Speech Resource Pages ...
PDF version of Lecture Slides - Speech Resource Pages ...
PDF version of Lecture Slides - Speech Resource Pages ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
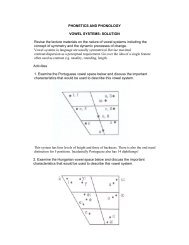
Phoneme Inventory Effects (3)<br />
• In Arabic there are three long vowels and<br />
three short vowels (plus some diphthongs).<br />
• There are two high vowel positions (front<br />
and back) and no mid vowels. Arabic high<br />
vowels can move down to mid-high<br />
positions without confusion and can also<br />
move a small distance towards the high<br />
central position without being confused.<br />
Phoneme Inventory Effects (5)<br />
• In English there are only three stop places<br />
<strong>of</strong> articulation (or four if the post-alveolar<br />
affricate is treated as a stop).<br />
• English alveolars can move to dental<br />
without confusion.<br />
• English velars can, and do, move between<br />
palatal and uvular as a consequence <strong>of</strong><br />
coarticulation with adjacent sounds<br />
(particularly vowels).<br />
Prosody, Stress & Coarticulation<br />
• One <strong>of</strong> the reasons why we stress a<br />
syllable or accent a word is to slow it<br />
down so that its articulatory patterns are<br />
more readily perceived.<br />
• Even in Australian Aboriginal languages<br />
the distinction between stop places <strong>of</strong><br />
articulation is relaxed in weaker syllables<br />
and is only completely clear in strong<br />
syllables.<br />
Phoneme Inventory Effects (4)<br />
• The Arabic low vowels can move around<br />
quite freely in the mid-low to low part <strong>of</strong><br />
the vowel space and from front to back in<br />
this part <strong>of</strong> the vowel space.<br />
• There are significant differences in vowel<br />
production (and therefore formant values)<br />
in the context <strong>of</strong> different consonants and<br />
the pattern varies between dialects.<br />
Phoneme Inventory Effects (6)<br />
• Most Australian Aboriginal languages have<br />
a much larger number <strong>of</strong> places <strong>of</strong><br />
articulation for oral stops.<br />
• Compared to English there is much less<br />
freedom to move stop place <strong>of</strong> articulation<br />
around without the possibility <strong>of</strong> perceptual<br />
confusion.<br />
Locus Theory (1)<br />
• In its original form, locus theory assumed a<br />
fixed ideal target for each phoneme. This<br />
target would be achieved by the articulators<br />
if there was enough time to do so.<br />
• Undershoot is said to occur if the ideal target<br />
is not reached in time. The idea <strong>of</strong><br />
“undershoot” implies a fixed ideal target.<br />
3