248 Diffuse leprosy of Lucio and Latapi - LEPRA Health in Action
248 Diffuse leprosy of Lucio and Latapi - LEPRA Health in Action
248 Diffuse leprosy of Lucio and Latapi - LEPRA Health in Action
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
254<br />
F. Vargas-Ocampo<br />
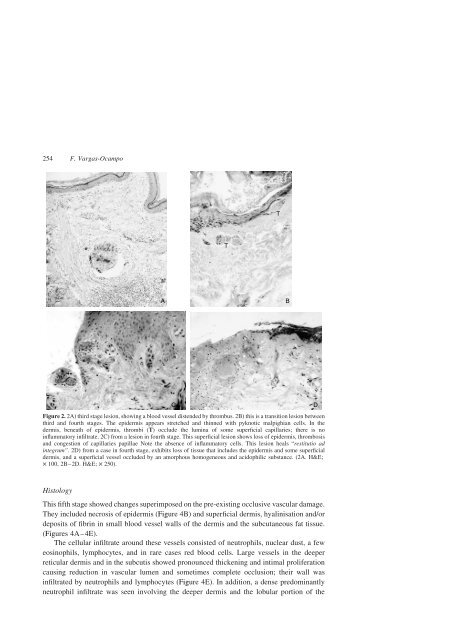
Figure 2. 2A) third stage lesion, show<strong>in</strong>g a blood vessel distended by thrombus. 2B) this is a transition lesion between<br />
third <strong>and</strong> fourth stages. The epidermis appears stretched <strong>and</strong> th<strong>in</strong>ned with pyknotic malpighian cells. In the<br />
dermis, beneath <strong>of</strong> epidermis, thrombi (T) occlude the lum<strong>in</strong>a <strong>of</strong> some superficial capillaries; there is no<br />
<strong>in</strong>flammatory <strong>in</strong>filtrate. 2C) from a lesion <strong>in</strong> fourth stage. This superficial lesion shows loss <strong>of</strong> epidermis, thrombosis<br />
<strong>and</strong> congestion <strong>of</strong> capillaries papillae Note the absence <strong>of</strong> <strong>in</strong>flammatory cells. This lesion heals “restitutio ad<br />
<strong>in</strong>tegrum”. 2D) from a case <strong>in</strong> fourth stage, exhibits loss <strong>of</strong> tissue that <strong>in</strong>cludes the epidermis <strong>and</strong> some superficial<br />
dermis, <strong>and</strong> a superficial vessel occluded by an amorphous homogeneous <strong>and</strong> acidophilic substance. (2A. H&E;<br />
£ 100, 2B–2D. H&E; £ 250).<br />
Histology<br />
This fifth stage showed changes superimposed on the pre-exist<strong>in</strong>g occlusive vascular damage.<br />
They <strong>in</strong>cluded necrosis <strong>of</strong> epidermis (Figure 4B) <strong>and</strong> superficial dermis, hyal<strong>in</strong>isation <strong>and</strong>/or<br />
deposits <strong>of</strong> fibr<strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong> small blood vessel walls <strong>of</strong> the dermis <strong>and</strong> the subcutaneous fat tissue.<br />
(Figures 4A–4E).<br />
The cellular <strong>in</strong>filtrate around these vessels consisted <strong>of</strong> neutrophils, nuclear dust, a few<br />
eos<strong>in</strong>ophils, lymphocytes, <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong> rare cases red blood cells. Large vessels <strong>in</strong> the deeper<br />
reticular dermis <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong> the subcutis showed pronounced thicken<strong>in</strong>g <strong>and</strong> <strong>in</strong>timal proliferation<br />
caus<strong>in</strong>g reduction <strong>in</strong> vascular lumen <strong>and</strong> sometimes complete occlusion; their wall was<br />
<strong>in</strong>filtrated by neutrophils <strong>and</strong> lymphocytes (Figure 4E). In addition, a dense predom<strong>in</strong>antly<br />
neutrophil <strong>in</strong>filtrate was seen <strong>in</strong>volv<strong>in</strong>g the deeper dermis <strong>and</strong> the lobular portion <strong>of</strong> the