X2CrNiMo 17-12-2 - Schmolz + Bickenbach AG
X2CrNiMo 17-12-2 - Schmolz + Bickenbach AG
X2CrNiMo 17-12-2 - Schmolz + Bickenbach AG
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
C: max. 0,03<br />
Mn: 2,0<br />
Cr: 16,5 - 18,5<br />
Ni: 10,5 - <strong>12</strong>,0<br />
Mo: 2,0 - 2,5<br />
1.4404<br />
Stainless austenitic, chromium nickel molybdenum<br />
steel with low carbon content<br />
Relevant current and obsolete standards:<br />
EN 10088-3 : 1.4404 <strong>X2CrNiMo</strong> <strong>17</strong>-<strong>12</strong>-2<br />
AISI : 316 L<br />
UNS : S 31603<br />
BS : 316 S 11<br />
JIS : SUS 316 L<br />
AFNOR : Z3CND<strong>17</strong>-11-02/<br />
Z3CND <strong>17</strong>-<strong>12</strong>-02<br />
DIN <strong>17</strong>440 : 1.4404<br />
SIS : 2347 and 2348<br />
Special grades for particular applications<br />
fine wire grade<br />
extreme fine wire grade<br />
cold heading grade: DIN EN 10263-5<br />
improved machining grade: NIRO-CUT 4404<br />
drawing grade<br />
General properties<br />
corrosion resistance : very good<br />
mechanical properties : average<br />
forgeability : good<br />
weldability : excellent<br />
machinability : average<br />
Special properties<br />
non-magnetic grade (r 1,3)<br />
suited to cryogenic applications<br />
Suitable for use up to 700°C<br />
Physical Properties<br />
density (kg/dm 3 ) : 7,98<br />
electrical resistivity<br />
at 20°C ( mm 2 /m) : 0,75<br />
magnetisability : slight<br />
thermal conductivity<br />
at 20°C (W/m K) : 15<br />
specific heat capacity<br />
at 20°C (J/kg K) : 500<br />
thermal expansion<br />
(10 -6 K -1 ) between<br />
20 and 100°C : 16,0<br />
20 and 200°C : 16,5<br />
20 and 300°C : <strong>17</strong>,0<br />
20 and 400°C : <strong>17</strong>,5<br />
20 and 500°C : 18,0<br />
Typical applications<br />
1.4404<br />
<strong>X2CrNiMo</strong> <strong>17</strong>-<strong>12</strong>-2<br />
automotive industry<br />
construction industry<br />
chemical industry<br />
decorative applications and kitchen fittings<br />
food and beverage industries<br />
mechanical engineering<br />
aerospace applications<br />
medical and pharmaceutical applications<br />
Hint - additional information on the machi<br />
nability of this grade of stainless steel can<br />
be found in the brochure entitled NIRO-<br />
CUT .<br />
- available from stock<br />
- supplied in accordance with the Z-30.<br />
3-6 building regulation<br />
Processing properties<br />
automated machining : yes<br />
machinable : yes<br />
hammer and die forging : yes<br />
cold forming : yes<br />
cold heading : yes<br />
suited to polishing : yes<br />
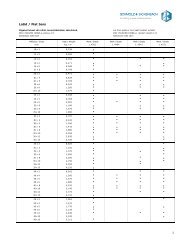
Finished product forms and conditions<br />
wire rod<br />
peeled bars 20 - 80<br />
bright bar h9, 2 – 80<br />
black bar 20 – 80<br />
bright coils h9, 0,8 - 20<br />
solution annealed and quenched<br />
direct quenched<br />
pickled<br />
drawn<br />
straightened<br />
peeled<br />
ground<br />
Demand tendency <br />
Revision No. 4404-0<br />
Created: 7.04.2000
Properties, applications and processing<br />
Corrosion resistance (PRE = 23.1 to 28.5)<br />
Due to the addition of between 2 and 3% molybdenum,<br />
the corrosion resistance of 1.4404 is<br />
significantly better than that of 1.4301 and<br />
1.4307, especially in chloride containing environments.<br />
1.4404 displays excellent resistance to corrosion<br />
in most natural waters and atmospheres (urban,<br />
rural and industrial), provided the chloride and<br />
salt concentrations are low to moderate. Resistance<br />
to reducing acids is restricted to low concentrations<br />
at low temperatures.<br />
Due to its low carbon content, 1.4404 is resistant<br />
to intergranular corrosion even after welding.<br />
Please note that 1.4404 is not resistant to sea<br />
water.<br />
Heat treatment / mechanical properties<br />
Optimal mechanical and fabrication properties<br />
are realised after solution annealing in the temperature<br />
range 1020 - 1<strong>12</strong>0°C followed by rapid<br />
cooling in air or water.<br />
In the solution annealed condition, the following<br />
mechanical properties may be attained when<br />
testing in the longitudinal direction:<br />
Property Specification Typical<br />
- yield strength (N/mm 2 ) Rp0,2 : 200 360<br />
- tensile strength (N/mm 2 ) Rm : 500 – 700 660<br />
- tensile elongation (%) A5 : 40 48<br />
- hardness HB : 215 200<br />
- impact energy (J) @ 25°C ISO-V : 100 220<br />
Elevated temperature properties<br />
The following minimum tensile properties at various<br />
temperatures are specified in the EN 10088-<br />
3 : 1995 standard.<br />
Minimum proof stress (N/mm 2 )<br />
250<br />
225<br />
200<br />
<strong>17</strong>5<br />
150<br />
<strong>12</strong>5<br />
100<br />
75<br />
0<br />
100<br />
0.2% proof stress<br />
200<br />
1% proof stress<br />
300<br />
Test temperature ( C)<br />
400<br />
500<br />
600<br />
Weldability<br />
1.4404 is readily weldable using all welding processes.<br />
Should a filler material be<br />
required, Novonit 4430, can be used. Maximum<br />
interpass temperature during welding is<br />
150°C.<br />
Heat treatment after welding is not necessary,<br />
and even large sections are resistant to intercrystalline<br />
corrosion after welding, due to the low<br />
carbon content.<br />
Forging<br />
Work pieces are usually pre-heated to between<br />
1150 - 1180°C with forging taking place between<br />
1180 und 950°C. After forging, the forged component<br />
must be rapidly cooled in either air or<br />
water to avoid the formation of any undesirable<br />
phases which might adversely affect the corrosion<br />
and/or mechanical properties.<br />
Machining<br />
The machinability of NIRO-CUT 4404 is better<br />
than that of NIRO-CUT 4401 as a result of its<br />
lower carbon content. The absence of titanium<br />
stabilisation also makes 1.4404 far more machinable<br />
than the titanium stabilised 1.4571 grade.<br />
The following machining parameters can be used<br />
as a guideline when machining NIRO-CUT 4404<br />
using a coated hard metal cutting tool.<br />
Depth of cut (mm)<br />
Tensile strengths<br />
Feed rate (mm/rev)<br />
Rm in N/mm 2 6 mm 3 mm 1 mm<br />
0,5 mm/r 0,4 mm/r 0,2 mm/r<br />
solution annealed<br />
(550 - 620) 135 m/min <strong>17</strong>0 m/min 215 m/min<br />
General comments<br />
Due to advances in the production of stainless<br />
steels, namely reduction of the carbon content to<br />
very low levels, 1.4404 has all but replaced the<br />
titanium stabilised 1.4571 grades. 1.4404 is just<br />
as resistant to intercrystalline corrosion as the<br />
titanium grades and does not suffer from knifeline<br />
corrosion. 1.4404 also has a much better<br />
surface finish that the titanium stabilised grade<br />
and can be readily mechanically and electropolished.<br />
Due to the absence of titanium additions<br />
and the resulting hard precipitates, 1.4307<br />
is much more machinable than 1.4541 which<br />
allows higher cutting speeds and results in longer<br />
tool life.<br />
Revision No. 4404-0<br />
Created: 7.04.2000