Hand atlas of human anatomy - EducationNest
Hand atlas of human anatomy - EducationNest
Hand atlas of human anatomy - EducationNest
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
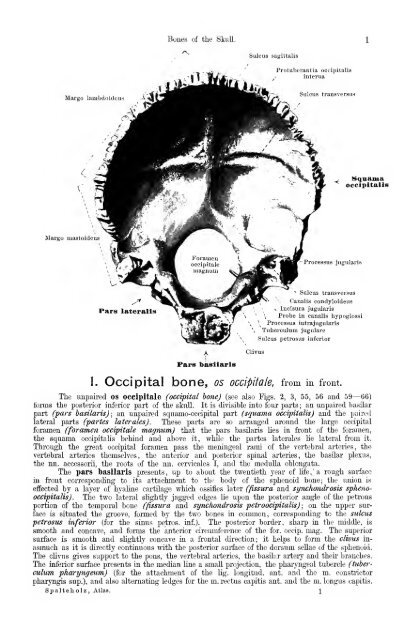
Margo lambcloideu.4<br />
Margo mastoideus<br />
Pars lateralis<br />
Bones <strong>of</strong> the Skull.<br />
Pars basllaris<br />
Sulcus sagittalis<br />
Protuberantia occipitalis<br />
interna<br />
Sulcus transversus<br />
Processus jugularis<br />
^ Sulcus transversus<br />
Canalis condyloideus<br />
s Incisura jugularis<br />
_, Manama<br />
occipitalis<br />
\ Probe in canalis hypoglossi<br />
\ Processus intrajugularis<br />
Tuberculura jugulare<br />
Sulcus petrosus inferior<br />
1. Occipital bone, os occipiiale, from in front.<br />
The impaired os occipitale (occipital hone) (see also Kgs. 2, 3, 55, 56 and 59— 66)<br />
forms the posterior inferior part <strong>of</strong> the sknll. It is divisible into four parts ; an unpaired basilar<br />
part (pars basilarisj; an unpaii-ed squamo-oocipital part (squama occipitalis) and the paired<br />
lateral parts (partes laterales). These parts are so arranged around the large occipital<br />
foramen (foramen occipitale magnum) that the pars basUaris lies in front <strong>of</strong> the foramen,<br />
the squama occipitalis behind and above it, while the partes laterales lie lateral fi'om it.<br />
Through the great occipital foramen pass the meningeal rami <strong>of</strong> the vertebral arteries, the<br />
vertebral arteries themselves, the anterior and posterior spinal arteries, the basilar plexus,<br />
the nn. accessorii, the roots <strong>of</strong> the nn. cervicales I, and the medulla oblongata.<br />
The pars basilaris presents, up to about the twentieth year <strong>of</strong> life,' a rough surface<br />
in front correspontling to its attachment to the body <strong>of</strong> the sphenoid bone; the union is<br />
effected by a layer <strong>of</strong> hyaline cartilage which ossifies later (fissura and synchondrosis sphenooccipitalis).<br />
The two lateral slightly jagged edges lie upon the posterior angle <strong>of</strong> the petrous<br />
portion <strong>of</strong> the temporal bone (fissura and synchondrosis petroocipitalis) ; on the upper siuface<br />
is situated the gi'oove, formed by the two bones in common, corresponding to the sulcus<br />
petrosus inferior (for the sinus petros. inf.). The posterior border, sharp in the middle, is<br />
smooth and concave, and forms the anterior cii-cimiferenoe <strong>of</strong> the for. occip. mag. The superior<br />
surface is smooth and slightly concave in a frontal direction; it helps to form the clivus inasmuch<br />
as it is directly continuous with the posterior surface <strong>of</strong> the dorsum seUae <strong>of</strong> the sphenoid.<br />
The clivus gives support to the pons, the vertebral arteries, the basilar artery and their branches.<br />
The inferior surface presents in the median line a small projection, the pharyngeal tubercle (tuberculum<br />
pharyngeum) (for the attachment <strong>of</strong> the lig. longitud. ant. and the m. constrictor<br />
pharyngis sup.), and also alternating ledges for the m. rectus capitis ant. and the m. longus capitis.<br />
Spalteholz, Atlas. \