Hand atlas of human anatomy - EducationNest
Hand atlas of human anatomy - EducationNest
Hand atlas of human anatomy - EducationNest
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Sulcus a. temporalis<br />
mediae<br />
Incisura parietalis<br />
Linea temporalis<br />
Fossa mastoidea<br />
Spina supra<br />
nieatum.<br />
Remains <strong>of</strong> the<br />
sutnra squamoso<br />
mastoidea<br />
Foramen mastoideum<br />
Pai-8 mastoidea<br />
Margo<br />
parietaliy<br />
Processus mastoideus<br />
rissura tympanomastoidea<br />
Bones <strong>of</strong> the Skull.<br />
Meatus acusticus externus<br />
Squama temitoraliis<br />
^ F.aciuH temporalis<br />
Margo<br />
sphenoidal is<br />
Processus<br />
zygomaticus<br />
Apex pyraraidis<br />
Tuberculum<br />
articulare<br />
Fossa mandibularis<br />
Fissura petrotympanic a [GlaseriJ<br />
Vagina processus styloidei<br />
Processus styloideus<br />
Pars tympanlca<br />
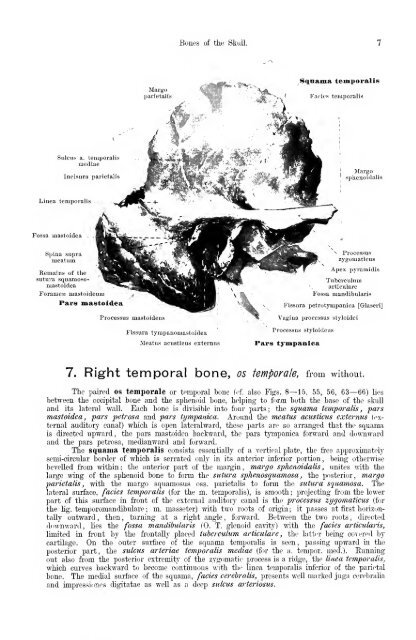
7. Right temporal bone, os temporale, from without.<br />
The paired os temporale or temporal bone (<strong>of</strong>. also Figs. 8—15, 55, 56, 63—66) lies<br />
between the occipital bone and the sphenoid bone, helping to foi'm both the base <strong>of</strong> the slnill<br />
and its lateral wall. Each bone is divisible into four parts; the squama temporalis, pars<br />
mastoidea, pars petrosa and pars tympanica. Around the meatus acusticus externus ((wternal<br />
auditory canal) which is open lateralward, these parts are so arranged that the squama<br />
is directed upward, the pars mastoidea baclvward, the pars tympanica forward and downward<br />
and the pars petrosa, medianward and forward.<br />
The squama temporalis consists essentially <strong>of</strong> a vertical plate, the fi'ee approximately<br />
semi-circular border <strong>of</strong> which is serrated only in its anterior inferior portion, being otherwise<br />
bevelled fi-om within; the anterior part <strong>of</strong> the margin, margo sphenoidalis , unites mth the<br />
large wing <strong>of</strong> the sphenoid bone to form the sutura sphenosquamosa , the posterior, margo<br />
parietalis, with the margo squamosus oss. parietalis to form the sutura squamosa. The<br />
lateral surface, fades temporalis (for the m. temporalis), is smooth : projecting fi-om the lower<br />
part <strong>of</strong> this surface in front <strong>of</strong> the external auditory canal is the processus zygomaticus (for<br />
the lig. temporomandibulare ; m. masseter) with two roots <strong>of</strong> origin; it passes at first horizon-<br />
tally outward , then , turning at a right angle , forward. Between the two roots , directed<br />
dim-nward, lies the fossa mandibularis (0. T. glenoid cavitjO with the fades articularis,<br />
limited in front by the fi'ontally placed tuberculum articulare , the lattrr being covered by<br />
cartilage. On the outer surface <strong>of</strong> the squama temporalis is seen, passing upward ia the<br />
posterior part, the sulcus arteriae temporalis mediae (for the a. temper, med.). Eunning<br />
out also from the posterior extremity <strong>of</strong> the zygomatic process is a ridge, the linea temporalis,<br />
which curves backward to become continuous with the linea temporalis inferior <strong>of</strong> the parietal<br />
bone. The medial surface <strong>of</strong> the squama, fades cerebralis, presents well marked juga cerebralia<br />
and impressiones digitatae as well as a deep sulcus arteriosus.