Belize
Belize
Belize
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
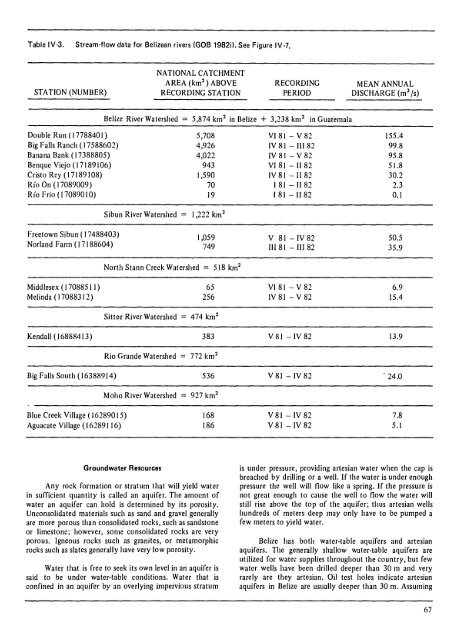
Table IV·3. Stream·flow data for <strong>Belize</strong>an rivers (GOB 1982il. See Figure IV·7.<br />
STATION (NUMBER)<br />
Double Run ( 1778840 I)<br />
Big Falls Ranch (17588602)<br />
Banana Bank (17388805)<br />
Benque Viejo (17189106)<br />
Cristo Rey (17189108)<br />
Rio On (17089009)<br />
Rio Frio (170890 10)<br />
Freetown Sibun ( 17488403)<br />
Norland Farm (17188604)<br />
Middlesex (17088511)<br />
Melinda ( 17088312)<br />
NATIONAL CA TCHM ENT<br />
AREA (km 2 ) ABOVE<br />
RECORDING STATION<br />
RECORDING<br />
PERIOD<br />
<strong>Belize</strong> River Watershed:::: 5,874 km 2 in <strong>Belize</strong> + 3,238 km 2 in Guatemala<br />
Sibun River Watershed<br />
5,708<br />
4,926<br />
4,022<br />
943<br />
1,590<br />
70<br />
19<br />
1,222 km 2<br />
1,059<br />
749<br />
North Stann Creek Watershed :::: 518 km 2<br />
65<br />
256<br />
Sittee River Watershed 474 km 2<br />
Kendall (16888413) 383<br />
Rio Grande Watershed :::: 772 km 2<br />
Big Falls South (16388914) 536<br />
Blue Creek Village (16289015)<br />
Aguacate VilIage (16289116)<br />
Moho River Watershed :::: 927 km 2<br />
Groundwater Resources<br />
168<br />
186<br />
Any rock formation or stratum that will yield water<br />
in sufficient quantity is called an aquifer. The amount of<br />
water an aquifer can hold is determined by its porosity.<br />
Unconsolidated materials such as sand and gravel generally<br />
are more porous than consolidated rocks, such as sandstone<br />
or limestone; however, some consolidated rocks are very<br />
porous. Igneous rocks such as granites, or metamorphic<br />
rocks such as slates generally have very low porosity.<br />
Water that is free to seek its own level in an aquifer is<br />
said to be under water-table conditions. Water that is<br />
confined in an aquifer by an overlying impervious stratum<br />
VI81 - V 82<br />
IV 81 - III 82<br />
IV 81 - V 82<br />
VI 81 - II 82<br />
IV81-1182<br />
I 81 - II 82<br />
181 - II 82<br />
V 81 -IV82<br />
III 81 - III 82<br />
VI 81 - V 82<br />
IV81-V82<br />
V 81 -IV 82<br />
V81-IV82<br />
V 81 -IV 82<br />
V 81 -IV 82<br />
MEAN ANNUAL<br />
DISCHARGE (m 3 Is)<br />
155.4<br />
99.8<br />
95.8<br />
51.8<br />
30.2<br />
2.3<br />
0.1<br />
50.5<br />
35.9<br />
6.9<br />
15.4<br />
13.9<br />
. 24.0<br />
7.8<br />
5.1<br />
is under pressure, providing artesian water when the cap is<br />
breached by driIling or a well. If the water is under enough<br />
pressure the well will flow like a spring. If the pressure is<br />
not great enough to cause the well to flow the water will<br />
still rise above the top of the aquifer; thus artesian wells<br />
hundreds of meters deep may only have to be pumped a<br />
few meters to yield water.<br />
<strong>Belize</strong> has both water-table aquifers and artesian<br />
aquifers. The generally shallow water-table aquifers are<br />
utilized for water supplies throughout the country, but few<br />
water wells have been drilled deeper than 30 m and very<br />
rarely are they artesian. Oil test holes indicate artesian<br />
aquifers in <strong>Belize</strong> are usually deeper than 30 m. Assuming<br />
67