Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
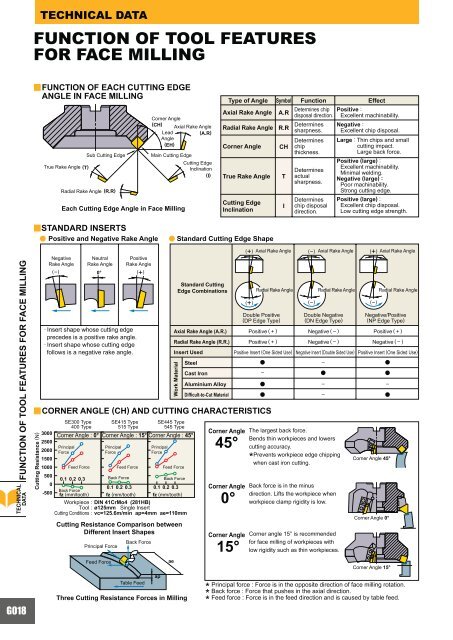
FUNCTION OF TOOL FEATURES FOR FACE MILLING<br />
<strong>TECHNICAL</strong><br />
<strong>DATA</strong><br />
G018<br />
<strong>TECHNICAL</strong> <strong>DATA</strong><br />
FUNCTION OF TOOL FEATURES<br />
FOR FACE MILLING<br />
yFUNCTION<br />
OF EACH CUTTING EDGE<br />
ANGLE IN FACE MILLING<br />
Radial Rake Angle (R.R)<br />
Corner Angle<br />
(CH)<br />
Axial Rake Angle<br />
Lead<br />
(A.R)<br />
Angle<br />
(EH)<br />
Sub Cutting Edge Main Cutting Edge<br />
True Rake Angle (T)<br />
Cutting Edge<br />
Inclination<br />
(I)<br />
Each Cutting Edge Angle in Face Milling<br />
ySTANDARD<br />
INSERTS<br />
a Positive and Negative Rake Angle a Standard Cutting Edge Shape<br />
Negative<br />
Rake Angle<br />
Neutral<br />
Rake Angle<br />
(-) 0°<br />
(+ )<br />
· Insert shape whose cutting edge<br />
precedes is a positive rake angle.<br />
· Insert shape whose cutting edge<br />
follows is a negative rake angle.<br />
Positive<br />
Rake Angle<br />
yCORNER<br />
ANGLE (CH) AND CUTTING CHARACTERISTICS<br />
Cutting Resistance (N)<br />
SE300 Type<br />
400 Type<br />
SE415 Type<br />
515 Type<br />
ap<br />
ae<br />
Work Material<br />
Cutting Resistance Comparison between<br />
Different Insert Shapes<br />
Standard Cutting<br />
Edge Combinations<br />
Axial Rake Angle<br />
Radial Rake Angle<br />
Corner Angle<br />
True Rake Angle<br />
Cutting Edge<br />
Inclination<br />
45°<br />
0°<br />
15°<br />
Type of Angle Symbol Function Effect<br />
A.R<br />
R.R<br />
CH<br />
T<br />
I<br />
(+) Axial Rake Angle (-) Axial Rake Angle (+) Axial Rake Angle<br />
(+)<br />
Double Positive<br />
(DP Edge Type)<br />
(-)<br />
Double Negative<br />
(DN Edge Type)<br />
Positive (large) :<br />
Excellent machinability.<br />
Minimal welding.<br />
Negative (large) :<br />
Poor machinability.<br />
Strong cutting edge.<br />
Positive (large) :<br />
Excellent chip disposal.<br />
Low cutting edge strength.<br />
Radial Rake Angle Radial Rake Angle<br />
Radial Rake Angle<br />
(-)<br />
Negative/Positive<br />
(NP Edge Type)<br />
Axial Rake Angle (A.R.) Positive ( + ) Negative (–) Positive ( + )<br />
Radial Rake Angle (R.R.) Positive ( + ) Negative (–) Negative (–)<br />
Insert Used<br />
Positive Insert (One Sided Use) Negative Insert (Double Sided Use) Positive Insert (One Sided Use)<br />
Steel<br />
a – a<br />
Cast Iron<br />
– a a<br />
Aluminium Alloy<br />
a – –<br />
Difficult-to-Cut Material<br />
a – a<br />
SE445 Type<br />
545 Type<br />
3000<br />
2500<br />
Corner Angle : 0° Corner Angle : 15° Corner Angle : 45°<br />
2000<br />
1500<br />
Principal<br />
Force<br />
Principal<br />
Force<br />
Principal<br />
Force<br />
1000 Feed Force<br />
Feed Force<br />
Feed Force<br />
500<br />
0.1 0.2 0.3<br />
Back Force<br />
Back Force<br />
0<br />
-500<br />
Back Force<br />
fz (mm/tooth)<br />
0.1 0.2 0.3<br />
fz (mm/tooth)<br />
0.1 0.2 0.3<br />
fz (mm/tooth)<br />
Workpiece : DIN 41CrMo4 (281HB)<br />
Tool : ø125mm Single Insert<br />
Cutting Conditions : vc=125.6m/min ap=4mm ae=110mm<br />
Principal Force<br />
Feed Force<br />
Back Force<br />
Table Feed<br />
Three Cutting Resistance Forces in Milling<br />
Corner Angle<br />
Corner Angle<br />
Corner Angle<br />
Determines chip<br />
disposal direction.<br />
Determines<br />
sharpness.<br />
Determines<br />
chip<br />
thickness.<br />
Determines<br />
actual<br />
sharpness.<br />
Determines<br />
chip disposal<br />
direction.<br />
The largest back force.<br />
Bends thin workpieces and lowers<br />
cutting accuracy.<br />
* Prevents workpiece edge chipping<br />
when cast iron cutting.<br />
Back force is in the minus<br />
direction. Lifts the workpiece when<br />
workpiece clamp rigidity is low.<br />
Corner angle 15° is recommended<br />
for face milling of workpieces with<br />
low rigidity such as thin workpieces.<br />
Positive :<br />
Excellent machinability.<br />
Negative :<br />
Excellent chip disposal.<br />
Large : Thin chips and small<br />
cutting impact.<br />
Large back force.<br />
Corner Angle 45°<br />
Corner Angle 0°<br />
Corner Angle 15°<br />
* Principal force : Force is in the opposite direction of face milling rotation.<br />
* Back force : Force that pushes in the axial direction.<br />
* Feed force : Force is in the feed direction and is caused by table feed.