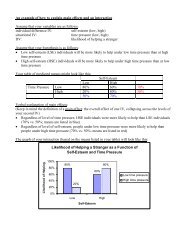
Mapping sentence form onto meaning: The syntax–semantic interface
Mapping sentence form onto meaning: The syntax–semantic interface
Mapping sentence form onto meaning: The syntax–semantic interface
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Gorrell, P., 1995. Syntax and Parsing. Cambridge Univ. Press,<br />
Cambridge, England.<br />
Gorrell, P, 1998. Syntactic analysis and reanalysis in <strong>sentence</strong><br />
processing. In: Fodor, J.D., Ferreira, F. (Eds.), Reanalysis in<br />
Sentence Processing. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht,<br />
NL.<br />
Grodzinsky, Y., Friederici, A.D., 2006. NeuroImaging of syntax and<br />
syntactic processing. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 16, 240–246.<br />
Gunter, T.C., Stowe, L.A., Mulder, G., 1997. When syntax meets<br />
semantics. Psychophysiology 34, 660–676.<br />
Gunter, T.C., Friederici, A.D., Hahne, A., 1999. Brain responses<br />
during <strong>sentence</strong> reading: visual input affects central processes.<br />
NeuroReport 10, 3175–3178.<br />
Gunter, T.C., Friederici, A.D., Schriefers, H., 2000. Syntactic gender<br />
and semantic expectancy: ERPs reveal early autonomy and late<br />
interaction. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 12, 556–568.<br />
Hagoort, P., 2003. Interplay between syntax and semantics during<br />
<strong>sentence</strong> comprehension: ERP effects of combining syntactic<br />
and semantic violations. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 15, 883–899.<br />
Hagoort, P., Brown, C., 1999. Gender electrified: ERP evidence oil<br />
the syntactic nature of gender processing. J. Psycholinguist.<br />
Res. 28, 715–728.<br />
Hagoort, P., Brown, C., Groothusen, J., 1993. <strong>The</strong> syntactic positive<br />
shift (SPS) as an ERP measure of syntactic processing. Lang.<br />
Cogn. Processess 8, 439–483.<br />
Hagoort, P., Brown, C.M., Osterhout, L., 1999. <strong>The</strong> neurocognition of<br />
syntactic processing. In: Brown, C.M., Hagoort, P. (Eds.), <strong>The</strong><br />
Neurocognition of Language. Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford,<br />
pp. 273–316.<br />
Hagoort, P., Wassenaar, M., Brown, C.A., 2003. Syntax-related<br />
ERP-effects in Dutch. Brain Res. 16, 38–50.<br />
Hahne, A., Friederici, A.D., 1999. Electrophysiological evidence for<br />
two steps in syntactic analysis: early automatic and late<br />
controlled processes. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 11, 194–205.<br />
Hahne, A., Friederici, A.D., 2002. Differential task effects on<br />
semantic and syntactic processes as revealed by ERPs. Brain<br />
Res. 13, 339–356.<br />
Hemforth, B., Konjeczny, L. (Eds.), 2000. German Sentence<br />
Processing. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht.<br />
Jackendoff, R., 2002. <strong>The</strong> mind doesn’t work that way: the scope<br />
and limits of computational psychology. Language 78, 164–170.<br />
Kaan, E., Harris, A., Gibson, E., Holcomb, P., 2000. <strong>The</strong> P600 as an<br />
index of syntactic integration difficulty. Lang. Cogn. Proc. 15,<br />
159–201.<br />
Kemmer, L., Kutas, M., 2006. Salience of grammatical violations,<br />
but not verb (ir)regularity, affects the P600: an event-related<br />
brain potential study. J. Cong. Neurosci. 125.<br />
Knösche, T., Maess, B., Friederici, A.D., 1999. Processing of<br />
syntactic in<strong>form</strong>ation monitored by brain surface current<br />
density mapping based on MEG. Brain Topogr. 12, 75–87.<br />
Kubota, M., Ferrari, P., Robert, T.P.L., 2004. Human neuronal<br />
encoding of English syntactic violations as revealed by both L1<br />
and L2 speakers. Neurosci. Lett. 368, 235–240.<br />
Kuperberg, G.R., 2007. Neural mechanisms of language<br />
comprehension: Challenges to syntax. Brain Res. 1146, 23–49.<br />
Kuperberg, G.R., Sitnikova, T., Caplan, D., Holcomb, P.J., 2003.<br />
Electrophysiological distinctions in processing conceptual<br />
relationships within simple <strong>sentence</strong>s. Brain Res. 17,<br />
117–129.<br />
Kuperberg, G.R., Kreher, D., Blais, K., Caplan, D., Holcomb, P., 2005.<br />
Semantic influences on syntactic processing: evidence from<br />
event-related potentials. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 29.<br />
Kutas, M., Federmeier, K.D., 2000. Electrophysiology reveals<br />
semantic memory use in language comprehension. Trends<br />
Cogn. Sci. 4, 463–470.<br />
Kutas, M., Hillyard, S.A., 1980. Reading senseless <strong>sentence</strong>s:<br />
brain potentials reflect semantic incongruity. Science 207,<br />
203–205.<br />
Kutas, M., Hillyard, S.A., 1983. Event-related brain potentials to<br />
B R A I N R E S E A R C H 1 1 4 6 ( 2 0 0 7 ) 5 0 – 5 8<br />
grammatical errors and semantic anomalies. Mem. Cogn. 11,<br />
539–550.<br />
Kutas, M., Van Petten, C., 1994. Psycholinguistics electrified.<br />
Event-related brain potential investigations. In: Gernsbacher,<br />
M.A. (Ed.), Handbook of Psycholinguistics. Academic Press, San<br />
Diego, pp. 83–143.<br />
Lau, E., Stroud, C., Plesch, S., Philips, C., 2006. <strong>The</strong> role of structural<br />
prediction in rapid syntactic analysis. Brain Lang. 98, 74–88.<br />
Li, X., Shu, H., Liu, Y.Y., Li, P., in press. Mental representation of<br />
verb <strong>meaning</strong>s: behavioral and electrophysiological evidence.<br />
J. Cogn. Neurosci.<br />
MacDonald, M.C., Just, M.A., Carpenter, P.A., 1992. Working<br />
memory constraints on the processing of syntactic ambiguity.<br />
Cognit. Psychol. 24, 56–98.<br />
MacDonald, M.C., Pearlmutter, N.J., Seidenberg, M.S., 1994a.<br />
Lexical nature of syntactic ambiguity resolution. Psychol. Rev.<br />
101, 676–703.<br />
MacDonald, M.C., Pearlmutter, N.J., Seidenberg, M.S., 1994b.<br />
Syntactic ambiguity resolution as lexical ambiguity resolution.<br />
In: Clifton Jr., C., Frazier, L., Rayner, K. (Ed.), Perspectives on<br />
Sentence Processing. Lawrence Erlbaum, Hillsdale,<br />
NJ, pp. 123–154.<br />
Marslen-Wilson, W.D., Tyler, L.K., 1980. <strong>The</strong> temporal structure of<br />
spoken language understanding. Cognition 8, 1–71.<br />
McClelland, R.J., St.John, M., Taraban, R., 1989. An interaction<br />
model of context effects in letter perception: Part 1. An account<br />
of basic findings. Lang. Cogn. Processes 4, 287–336.<br />
Mitchell, D.C., 1994. Sentence parsing. In: Gernsbacher, M.A. (Ed.),<br />
Handbook of Psycholinguistics. Academic Press, San Diego,<br />
pp. 375–409.<br />
Mueller, J.L., Hahne, A., Fujii, Y., Friederici, A.D., 2005. Native and<br />
nonnative speakers’ processing of a miniature version of<br />
Japanese as revealed by ERPs. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 17,<br />
1229–1244.<br />
Münte, T.F., Heinze, H.J., Mangun, G.R., 1993. Dissociation of brain<br />
activity related to syntactic and semantic aspects of language.<br />
J. Cogn. Neurosci. 5, 335–344.<br />
Münte, T.F., Szentkuti, A., Wieringa, B.M., Matzke, M., Johannes, S.,<br />
1997. Human brain potentials to reading syntactic errors in<br />
<strong>sentence</strong>s of different complexity. Neurosci. Lett. 235,<br />
105–108.<br />
Neville, H., Nicol, J.L., Barss, A., Forster, K.I., Garrett, M.F., 1991.<br />
Syntactically based <strong>sentence</strong> processing classes—Evidence<br />
from event-related brain potentials. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 3,<br />
151–165.<br />
Osterhout, L., Holcomb, P.J., 1993. Event-related potentials and<br />
syntactic anomaly—Evidence of anomaly detection during<br />
the perception of continuous speech. Lang. Cogn. Proc. 8,<br />
413–437.<br />
Osterhout, L., Mobley, L.A., 1995. Event-related brain potentials<br />
elicited by failure to agree. J. Mem. Lang. 34, 739–773.<br />
Osterhout, L., Nicol, J., 1999. On the distinctiveness, independence,<br />
and time course of the brain responses to syntactic and<br />
semantic anomalies. Lang. Cogn. Proc. 14, 283–317.<br />
Penke, M., Weyerts, H., Gross, M., Zander, E., Münte, T.F., Clahsen,<br />
H., 1997. How the brain processes complex words: an<br />
event-related potential study of German verb inflections. Brain<br />
Res. 6, 37–52.<br />
Rossi, S., Gugler, M.F., Hahne, A., Friederici, A.D., 2005. When word<br />
category in<strong>form</strong>ation encounters morphosyntax: an ERP study.<br />
Neurosci. Lett. 384, 228–233.<br />
Rösler, F., Pütz, P., Friederici, A.D., Hahne, A., 1993. Event-related<br />
brain potentials while encountering semantic and syntactic<br />
constraint violations. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 5, 345–362.<br />
Schlesewsky, M., Bornkessel, I., 2004. On incremental<br />
interpretation: degrees of <strong>meaning</strong> accessed during <strong>sentence</strong><br />
comprehension. Lingua 114, 1213–1234.<br />
Silva-Pereyra, J., Carreiras, M., 2006. An ERP study of PHI-features<br />
in Spanish. J. Cogn. Neurosci. 130.<br />
57