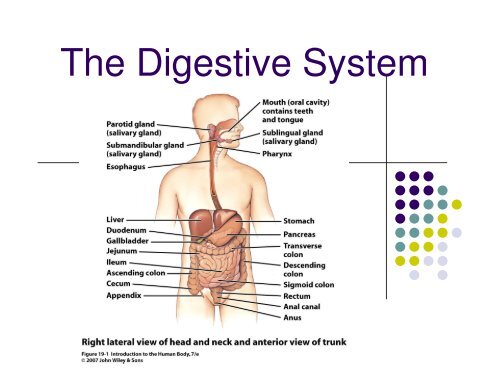
The Digestive System
The Digestive System
The Digestive System
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>The</strong> <strong>Digestive</strong> <strong>System</strong>
<strong>The</strong> function of the digestion system is to<br />
absorb substances for use by the body.<br />
Most substances that are taken into the<br />
digestive system are too large to be absorbed<br />
and must first be broken down.
Organic compounds<br />
Starches >>>>>>>>> ???<br />
Proteins>>>>>>>>>> ??<br />
Fats>>>>>>>>>>>> ??<br />
Vitamins<br />
Minerals<br />
Water
Digestion<br />
What is chemical digestion?<br />
What is mechanical digestion?
What are the two divisions of the digestive system?
What are the structures of the<br />
GI tract?
What are the four accessory<br />
organs?
A closer look at the GI tract
<strong>The</strong> GI tract is composed of four layers<br />
What layer is<br />
described?<br />
-inner most layer<br />
sometimes folds to<br />
increase surface<br />
area<br />
covered in mucus<br />
made of epithelial<br />
tissue<br />
may contain glands
What layer is described?<br />
blood vessels<br />
nervous system<br />
Transports<br />
absorbed materials
Muscularis-<br />
Made of ______ muscle<br />
Always a _____ layer and<br />
a ______ layer<br />
Sometimes a third oblique<br />
layer<br />
What is peristalsis?<br />
http://www.pennmedicin<br />
e.org/encyclopedia/em_<br />
DisplayAnimation.aspx?<br />
gcid=000097&ptid=17
Muscularis continued<br />
Thick areas of the<br />
muscularis are<br />
sphincters.<br />
Open and close<br />
portions of the GI<br />
tract.<br />
Some sphincters also<br />
contain skeletal<br />
muscle tissue
What are the GI tract<br />
sphincters?
Serosa- lubricates tube so it slides<br />
freely in body cavities
What are the major structures of<br />
the GI tract?
Oral cavity (opening to the oral<br />
cavity is the mouth)<br />
Formed by cheeks, hard & soft palate & tongue<br />
Soft palate at back includes a “hangy down” part =<br />
uvula<br />
During swallowing uvula prevents entry into nasal cavity.<br />
If a piece of food gets stuck on the uvula, the gag reflex is<br />
initiated<br />
Tongue- muscular accessory organ<br />
maneuvers food for chewing<br />
Adjusts shape for swallowing
Digestion in the oral cavity<br />
Mechanical digestion- chewing, grinding, tearing<br />
by teeth<br />
Chemical digestion-______??______ starts the<br />
break down of starch<br />
Rounds up food into a soft bolus for swallowing
Stomach<br />
Mixing chamber and holding<br />
reservoir<br />
Very elastic & muscular<br />
Only part of GI with the<br />
oblique layer of muscle<br />
Cardiac sphincter (lower<br />
esophageal) acts as the “front<br />
door” and the pyloric sphincter<br />
is the “back door”
Digestion in the stomach<br />
Chemical digestion<br />
????<br />
Mechanical digestion<br />
???
<strong>The</strong> stomach up close<br />
<strong>The</strong> wall of the<br />
stomach is folded<br />
forming gastric<br />
pits. <strong>The</strong> folds are<br />
called _________<br />
Gastric pits are<br />
lined with 4 types<br />
of cells. What are<br />
they? What does<br />
each produce?
http://www.mhhe.com/biosci/esp/2002_general/<br />
Esp/folder_structure/ab/m4/s5/abm4s5_10.ht<br />
m<br />
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6hquzCXYlN<br />
g&NR=1
What happens when food<br />
enters the stomach?<br />
Food entering the stomach or the memory<br />
of food stimulates G cells to<br />
secrete_______
2. Unfolding of rugae stimulates chief cells to<br />
secrete ________ and parietal cells to<br />
secrete_________ into the stomach.<br />
Stomach pH 2.08<br />
Low pH kills microorganism.
3. Why doesn’t the stomach store active<br />
pepsin?<br />
Mucus cells continually secrete mucus to<br />
protect stomach from the HCl and the<br />
pepsin.
4. Gastrin regulates the<br />
release of gherlin<br />
High amounts of<br />
gherlin=?????<br />
Low amounts of<br />
gherlin=?????
Does any absorption occur in the<br />
stomach?<br />
alcohol and aspirin are absorbed from the<br />
stomach into the blood stream.
Small Intestine<br />
22-28 feet<br />
long<br />
3 parts:<br />
duodenum<br />
(10%)<br />
jejunum<br />
(80%)<br />
ileum (10%)
duodenum<br />
Most chemical digestion<br />
takes place in the<br />
duodenum. Proteins,<br />
carbohydrates, nucleic<br />
acids and lipids are all<br />
digested here.
What happen when chyme/food<br />
enters the duodenum?<br />
1. Cells lining the duodenum<br />
secrete ________<br />
2. Pancreas secretes….????<br />
All of these enzymes break<br />
down protein
Pancreas also secretes<br />
Lipase<br />
Nuclease<br />
Amylase<br />
Sodium bicarbonate<br />
What is the function<br />
of each?
Liver and gall bladder<br />
secrete bile into<br />
duodenum via the bile<br />
duct. What is the<br />
function of bile? Liver<br />
makes and secretes<br />
bile. Gall bladder only<br />
stores bile
Liver functions- give thanks to your<br />
liver. It is the hardest working organ in<br />
your body!<br />
Make bile to emulsify fats<br />
Stores iron and other minerals and vitamins<br />
Hepatic portal system sends materials absorbed from<br />
the small intestine to liver where it is filtered of waste.<br />
Stores glucose as glycogen<br />
Makes cholesterol<br />
Packages proteins and lipids for proper transport to<br />
other parts of the body<br />
Removes drugs and hormones<br />
Removes bilirubin
What is bilirubin?<br />
Bilirubin is a waste product derived<br />
from dead red blood cells.<br />
RBCs live for 120 days<br />
<strong>The</strong> liver filters the dead cells from<br />
the blood producing bilirubin.<br />
Bilirubin is mixed with bile where it is<br />
excreted into the small intestine and<br />
removed as a waste.<br />
Bilirubin gives bile and feces its<br />
characteristic brownish color.<br />
If bilirubin is not removed from the<br />
blood, it collects in the body. Makes<br />
eyes and skin appear yellow or<br />
jaundice.
jejunum<br />
Most absorption of<br />
takes place in the<br />
jejunum.<br />
Small amount of<br />
digestion takes place<br />
in jejunum
<strong>The</strong> jejunum is lined with villi and microvilli<br />
Increase surface area for<br />
maximum absorption<br />
Site of diffusion of materials<br />
out of the GI tract.
What is the function of villi and<br />
microvilli?<br />
Amino acids,<br />
monosaccharides<br />
and short fatty<br />
acids (good for<br />
you!) are absorbed<br />
into the blood<br />
stream of the villi<br />
and shipped to the<br />
liver via the hepatic<br />
vein
Longer fatty acids (not so<br />
good for you) are absorbed<br />
into villi then reassembled<br />
into triglycerides<br />
surrounded by cholesterol<br />
and protein to from a<br />
chylomicron.<br />
Chylomicron is absorbed<br />
into the lymph system and<br />
then dumped into the<br />
circulatory system via the<br />
left subclavian artery
Ileum<br />
Lined with Peyer’s patches (lymph tissue)<br />
Transition to the large intestine.
Large Intestine<br />
Cecum, colon, rectum, anus<br />
Cecum- appendix attaches to cecum.<br />
Colon- ascending, transverse, descending &<br />
sigmoid<br />
Rectum- feces storage<br />
Anus- opening for waste
Figure 19.15a
What happens to the remaining material<br />
when it enters the large intestine?<br />
In the colon…<br />
Water and salt is absorbed. Improper regulation<br />
of water absorption causes diarrhea and<br />
constipation<br />
Millions of bacteria feed on the undigested<br />
material<br />
Bacteria produce some B-vitamins & Vit. K which is then<br />
absorbed.<br />
Bacteria produce gases
By the time material reached the rectum, it is<br />
all waste called feces.<br />
Defecation is the removal of feces through<br />
the anus.