Radiative Transfer in Protoplanetary Disks
Radiative Transfer in Protoplanetary Disks
Radiative Transfer in Protoplanetary Disks
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
IR excesses, we can measure a truly <strong>in</strong>dependent gas depletion timescale and exam<strong>in</strong>e the possibility of gas rich,<br />
dust poor systems. These objects are (<strong>in</strong>itially) only observed <strong>in</strong> [CII]158µm and [OI]63µm and account for<br />
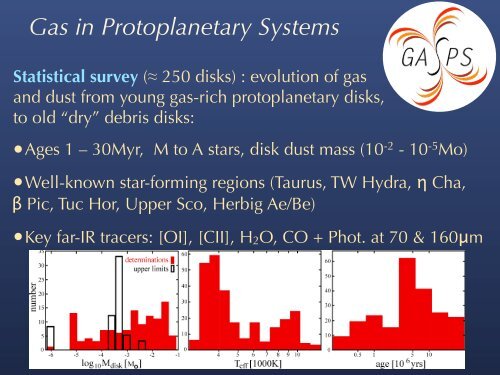
Gas <strong>in</strong> <strong>Protoplanetary</strong> Systems<br />
14% of the Phase I time. A significant fraction of the targets are multiple stars (25%, separations 5-1000 AU),<br />
enabl<strong>in</strong>g the survey to be used to study the effect of companions on gas disks. These have not been excluded<br />
to avoid selection bias. F<strong>in</strong>ally the target list has a wide range of X-ray lum<strong>in</strong>osity (10 28 − 10 31 erg s −1 ) and<br />
Hα l<strong>in</strong>e strength (W (Hα) =1− 150 ˚A). This allows multivariate analysis of l<strong>in</strong>e strengths and ratios, which<br />
is only possible with such a large and unbiased sample, and <strong>in</strong>creases the legacy value. An estimate of the<br />
Statistical survey (≈ 250 disks) : evolution of gas<br />
required number of targets is given by the number of b<strong>in</strong>s of primary parameters (mass, spectral type and age):<br />
Ntargets = Nmass.Nsp.t.Nage.N, whereN is the number <strong>in</strong> each b<strong>in</strong>. To <strong>in</strong>vestigate effects of other parameters<br />
and dust from young gas-rich protoplanetary disks,<br />
and give a statistically-robust result, we have set Nb = 10. A m<strong>in</strong>imum of 3 logarithmically-spaced b<strong>in</strong>s of<br />
each parameter means we need ∼270 targets. Figure 4 shows the distribution over the primary parameters, and<br />
Table 4 summarises the sample clusters.<br />
to old “dry” debris disks:<br />
Table 4. Target clusters<br />
•Ages 1 – 30Myr, M to A stars, disk dust mass (10-2 - 10-5 Distance Age Total Number Mo)<br />
Group (pc) (Myr) number Phase I<br />
Taurus 140 0.3 − 4 109 48<br />
Upper Sco 145 5 48 2<br />
η Cha 112 5 − 9 17 1<br />
TW Hya 50 8 − 10 13 0<br />
β Pic 30 10 − 20 19 0<br />
Tuc Hor 46 30 18 0<br />
Ae/Be stars 50 − 200 0.5 − 30 50 26<br />
•Well-known star-form<strong>in</strong>g regions (Taurus, TW Hydra, η Cha,<br />
β Pic, Tuc Hor, Upper Sco, Herbig Ae/Be)<br />
•Key far-IR tracers: [OI], [CII], H2O, CO + Phot. at 70 & 160μm