H1-NMR
H1-NMR
H1-NMR
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
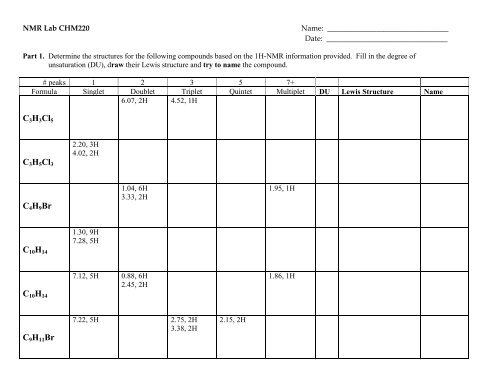
<strong>NMR</strong> Lab CHM220 Name: ________________________________<br />
Date: ________________________________<br />
Part 1. Determine the structures for the following compounds based on the 1H-<strong>NMR</strong> information provided. Fill in the degree of<br />
unsaturation (DU), draw their Lewis structure and try to name the compound.<br />
# peaks 1 2 3 5 7+<br />
Formula Singlet Doublet Triplet Quintet Multiplet DU Lewis Structure Name<br />
6.07, 2H 4.52, 1H<br />
C3H3Cl5<br />
C3H5Cl3<br />
C4H9Br<br />
C10<strong>H1</strong>4<br />
C10<strong>H1</strong>4<br />
C9<strong>H1</strong>1Br<br />
2.20, 3H<br />
4.02, 2H<br />
1.30, 9H<br />
7.28, 5H<br />
1.04, 6H<br />
3.33, 2H<br />
7.12, 5H 0.88, 6H<br />
2.45, 2H<br />
7.22, 5H 2.75, 2H<br />
3.38, 2H<br />
2.15, 2H<br />
1.95, 1H<br />
1.86, 1H
Part 2. Go to the following website http://www.nd.edu/~smithgrp/structure/workbook.html Click on Do the Problems. Answer<br />
questions 1, 3, 4, 7. DO NOT ASK Dr. Structure for help.<br />
Question Lewis Structure Compound Name<br />
1<br />
3<br />
4<br />
7
Part 3. Synthesis and Structure determination<br />
1. The product of the following reaction has a broad absorption at 3330cm -1 in its IR spectrum. Its 13 C-<strong>NMR</strong> spectrum shows<br />
absorptions at 70 (C), 34 (CH2), 30(CH3), and 15 (CH3). Suggest a structure for this compound.<br />
H2O CH 3<br />
H 3C CH<br />
CH CH 2<br />
H 2SO 4<br />
2. Compound K, molecular formula C6<strong>H1</strong>4O, readily undergoes acid-catalyzed dehydration when warmed with phosphoric acid to give<br />
compound L, molecular formula C6<strong>H1</strong>2, as the major organic product. The 1 H-<strong>NMR</strong> spectrum of compound K shows signals at δ 0.90<br />
(t, 6H), 1.12 (s, 3H), 1.38 (s, 1H), and 1.48 (q, 4H). The 13 C-<strong>NMR</strong> spectrum of compound K shows signals at δ 72.98, 33.72, 25.85,<br />
and 8.16. Deduce the structural formulas of compounds K and L.
3. The addition of HCl to but-3-en-2-one gives a product with the following 1H-<strong>NMR</strong> spectrum. Show the structure of this product,<br />
show a mechanism for its formation, and explain the regiochemistry of the reaction (see section 11.2 in your book).
4. Compound M, molecular formula C5<strong>H1</strong>0O, readily decolorizes in Br2 in CCl4 and is converted by H2/Ni into compound N, molecular<br />
formula C5<strong>H1</strong>2O. Following is the 1 H-<strong>NMR</strong> spectrum of compound M. The 13 C-<strong>NMR</strong> spectrum of compound M shows signals at δ<br />
146.2, 110.75, 71.05, and 29.38. Deduce the structural formulas of compounds M and N.
5. Following is the 1 H-<strong>NMR</strong> spectrum of compound O, molecular formula C7<strong>H1</strong>2. Compound O reacts with bromine in carbon<br />
tetrachloride to give a compound with the molecular formula C7<strong>H1</strong>2Br2. The 13 C-<strong>NMR</strong> spectrum of compound O shows signals at δ<br />
150.12, 106.43, 35.44, 28.44, and 26.36. Deduce the structural formula of compound O.
6. Treatment of compound P with BH3 followed by H2O2/NaOH gives compound Q. Following are 1 H-<strong>NMR</strong> spectra from compounds P<br />
and Q along with 13 C-<strong>NMR</strong> spectral data. From this information, deduce structural formulas for compounds P and Q.<br />
1. BH3 C7<strong>H1</strong>2 C7<strong>H1</strong>4O<br />
2. H2O2, NaOH<br />
13 C-<strong>NMR</strong><br />
(P) (Q) (P) (Q)<br />
132.38 72.71<br />
32.12 37.59<br />
29.14 28.13<br />
27.45 22.68