comparison of gas and dust cooling rates in - Rencontres de Moriond
comparison of gas and dust cooling rates in - Rencontres de Moriond
comparison of gas and dust cooling rates in - Rencontres de Moriond
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
E. Bayet<br />
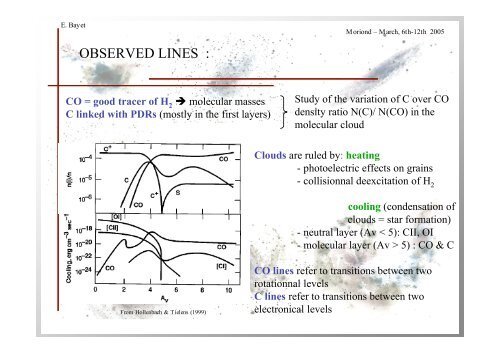
OBSERVED LINES :<br />
CO = good tracer <strong>of</strong> H 2 molecular masses<br />
C l<strong>in</strong>ked with PDRs (mostly <strong>in</strong> the first layers)<br />
From Hollenbach & Tielens (1999)<br />
<strong>Moriond</strong> – March, 6th-12th 2005<br />
Study <strong>of</strong> the variation <strong>of</strong> C over CO<br />
<strong>de</strong>nsity ratio N(C)/ N(CO) <strong>in</strong> the<br />
molecular cloud<br />
Clouds are ruled by: heat<strong>in</strong>g<br />
- photoelectric effects on gra<strong>in</strong>s<br />
- collisionnal <strong>de</strong>excitation <strong>of</strong> H 2<br />
<strong>cool<strong>in</strong>g</strong> (con<strong>de</strong>nsation <strong>of</strong><br />
clouds = star formation)<br />
- neutral layer (Av < 5): CII, OI<br />
- molecular layer (Av > 5) : CO & C<br />
CO l<strong>in</strong>es refer to transitions between two<br />
rotationnal levels<br />
C l<strong>in</strong>es refer to transitions between two<br />
electronical levels








![List of participants 27/2/09 [pdf] - Rencontres de Moriond - IN2P3](https://img.yumpu.com/17975746/1/190x135/list-of-participants-27-2-09-pdf-rencontres-de-moriond-in2p3.jpg?quality=85)






