Autoignition Temperatures for Mixtures of Flammable Liquids with ...
Autoignition Temperatures for Mixtures of Flammable Liquids with ...
Autoignition Temperatures for Mixtures of Flammable Liquids with ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
hydrocarbons, ketones, esters and amines. The<br />
following conclusions can be drawn from this table:<br />
1. The temperature <strong>of</strong> autoignition drops, as expected,<br />
substantially <strong>with</strong> increasing pressure.<br />
2. The order <strong>of</strong> the compounds <strong>with</strong> respect to the<br />
AIT at higher pressures is different from the one at<br />
atmospheric pressure.<br />
Semen<strong>of</strong>f plots<br />
According to Semen<strong>of</strong>f's theory <strong>of</strong> thermal explosion<br />
/1/, the relation between the pressure pZ <strong>of</strong> a<br />
fuel/air-mixture and its autoignition temperature TZ is<br />
described by the relation:<br />
where EA Sem ( + 1)<br />
n EA<br />
pZ<br />
= k ⋅Tz<br />
⋅ exp( )<br />
RTZ<br />
is an apparent activation energy <strong>of</strong> the<br />
reaction and n is the overall reaction order (usually<br />
assumed to be 2).<br />
in bar/K²<br />
p /T<br />
Z 2<br />
Z<br />
1E-4<br />
1E-5<br />
1E-6<br />
n-Heptane<br />
Benzene<br />
Ethanol<br />
Propionic acid<br />
Methyl propionate<br />
Butyl acetate<br />
2<br />
Sem<br />
200 250 300 350 400 450 500 550<br />
Temperature in ° C<br />
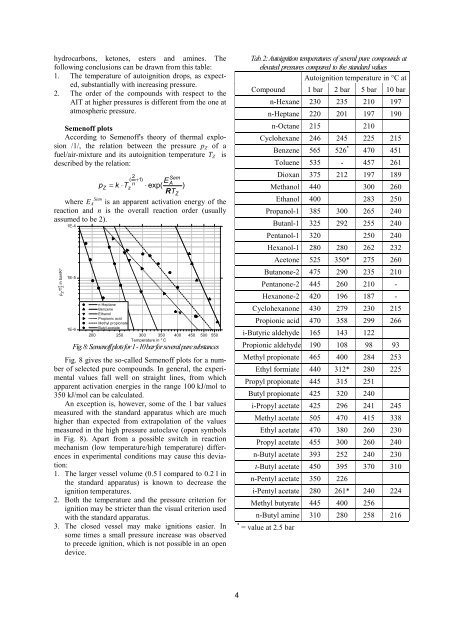
Fig. 8: Semen<strong>of</strong>f plots <strong>for</strong> 1 - 10 bar <strong>for</strong> several pure substances<br />
Fig. 8 gives the so-called Semen<strong>of</strong>f plots <strong>for</strong> a number<br />
<strong>of</strong> selected pure compounds. In general, the experimental<br />
values fall well on straight lines, from which<br />
apparent activation energies in the range 100 kJ/mol to<br />
350 kJ/mol can be calculated.<br />
An exception is, however, some <strong>of</strong> the 1 bar values<br />
measured <strong>with</strong> the standard apparatus which are much<br />
higher than expected from extrapolation <strong>of</strong> the values<br />
measured in the high pressure autoclave (open symbols<br />
in Fig. 8). Apart from a possible switch in reaction<br />
mechanism (low temperature/high temperature) differences<br />
in experimental conditions may cause this deviation:<br />
1. The larger vessel volume (0.5 l compared to 0.2 l in<br />
the standard apparatus) is known to decrease the<br />
ignition temperatures.<br />
2. Both the temperature and the pressure criterion <strong>for</strong><br />
ignition may be stricter than the visual criterion used<br />
<strong>with</strong> the standard apparatus.<br />
3. The closed vessel may make ignitions easier. In<br />
some times a small pressure increase was observed<br />
to precede ignition, which is not possible in an open<br />
device.<br />
4<br />
Tab. 2: <strong>Autoignition</strong> temperatures <strong>of</strong> several pure compounds at<br />
elevated pressures compared to the standard values<br />
<strong>Autoignition</strong> temperature in °C at<br />
Compound 1 bar 2 bar 5 bar 10 bar<br />
n-Hexane 230 235 210 197<br />
n-Heptane 220 201 197 190<br />
n-Octane 215 210<br />
Cyclohexane 246 245 225 215<br />
Benzene 565 526 *<br />
470 451<br />
Toluene 535 - 457 261<br />
Dioxan 375 212 197 189<br />
Methanol 440 300 260<br />
Ethanol 400 283 250<br />
Propanol-1 385 300 265 240<br />
Butanl-1 325 292 255 240<br />
Pentanol-1 320 250 240<br />
Hexanol-1 280 280 262 232<br />
Acetone 525 350* 275 260<br />
Butanone-2 475 290 235 210<br />
Pentanone-2 445 260 210 -<br />
Hexanone-2 420 196 187 -<br />
Cyclohexanone 430 279 230 215<br />
Propionic acid 470 358 299 266<br />
i-Butyric aldehyde 165 143 122<br />
Propionic aldehyde 190 108 98 93<br />
Methyl propionate 465 400 284 253<br />
Ethyl <strong>for</strong>miate 440 312* 280 225<br />
Propyl propionate 445 315 251<br />
Butyl propionate 425 320 240<br />
i-Propyl acetate 425 296 241 245<br />
Methyl acetate 505 470 415 338<br />
Ethyl acetate 470 380 260 230<br />
Propyl acetate 455 300 260 240<br />
n-Butyl acetate 393 252 240 230<br />
t-Butyl acetate 450 395 370 310<br />
n-Pentyl acetate 350 226<br />
i-Pentyl acetate 280 261* 240 224<br />
Methyl butyrate 445 400 256<br />
n-Butyl amine 310 280 258 216<br />
* = value at 2.5 bar