Chem1000A Spring 2007 Practice Assignment 6 - Answers
Chem1000A Spring 2007 Practice Assignment 6 - Answers
Chem1000A Spring 2007 Practice Assignment 6 - Answers
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
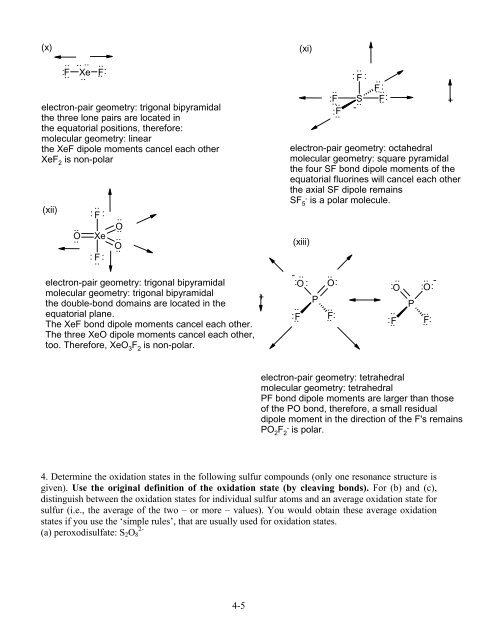
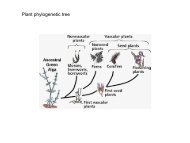
(x) (xi)<br />
..<br />
: F Xe .. F:<br />
.. .. ..<br />
.. ..<br />
electron-pair geometry: trigonal bipyramidal<br />
the three lone pairs are located in<br />
the equatorial positions, therefore:<br />
molecular geometry: linear<br />
the XeF dipole moments cancel each other<br />
XeF 2 is non-polar<br />
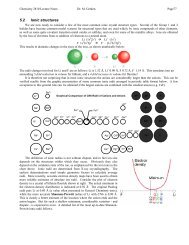
(xii)<br />
..<br />
O..<br />
..<br />
: F :<br />
Xe<br />
..<br />
F : :<br />
..<br />
O..<br />
..<br />
O..<br />
electron-pair geometry: trigonal bipyramidal<br />
molecular geometry: trigonal bipyramidal<br />
the double-bond domains are located in the<br />
equatorial plane.<br />
The XeF bond dipole moments cancel each other.<br />
The three XeO dipole moments cancel each other,<br />
too. Therefore, XeO 3 F 2 is non-polar.<br />
4-5<br />
+<br />
: ..<br />
.. F<br />
: F<br />
..<br />
..<br />
..<br />
: F : ..<br />
F..<br />
.. :<br />
S F..<br />
:<br />
..<br />
-<br />
electron-pair geometry: octahedral<br />
molecular geometry: square pyramidal<br />
the four SF bond dipole moments of the<br />
equatorial fluorines will cancel each other<br />
the axial SF dipole remains<br />
SF 5 - is a polar molecule.<br />
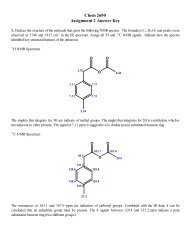
(xiii)<br />
:<br />
..<br />
.. :<br />
..<br />
O O<br />
.. F<br />
P<br />
F<br />
:<br />
..<br />
.. :<br />
..<br />
- ..<br />
: :<br />
..<br />
:<br />
..<br />
: O<br />
.. -<br />
: O:<br />
.. F<br />
P<br />
F<br />
electron-pair geometry: tetrahedral<br />
molecular geometry: tetrahedral<br />
PF bond dipole moments are larger than those<br />
of the PO bond, therefore, a small residual<br />
dipole moment in the direction of the F's remains<br />
PO 2 F 2 - is polar.<br />
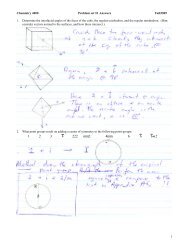
4. Determine the oxidation states in the following sulfur compounds (only one resonance structure is<br />
given). Use the original definition of the oxidation state (by cleaving bonds). For (b) and (c),<br />
distinguish between the oxidation states for individual sulfur atoms and an average oxidation state for<br />
sulfur (i.e., the average of the two – or more – values). You would obtain these average oxidation<br />
states if you use the ‘simple rules’, that are usually used for oxidation states.<br />
(a) peroxodisulfate: S2O8 2-<br />
+