Chem1000A Spring 2007 Practice Assignment 6 - Answers
Chem1000A Spring 2007 Practice Assignment 6 - Answers
Chem1000A Spring 2007 Practice Assignment 6 - Answers
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Chem1000A</strong> <strong>Spring</strong> <strong>2007</strong><br />
<strong>Practice</strong> <strong>Assignment</strong> 6 - <strong>Answers</strong><br />
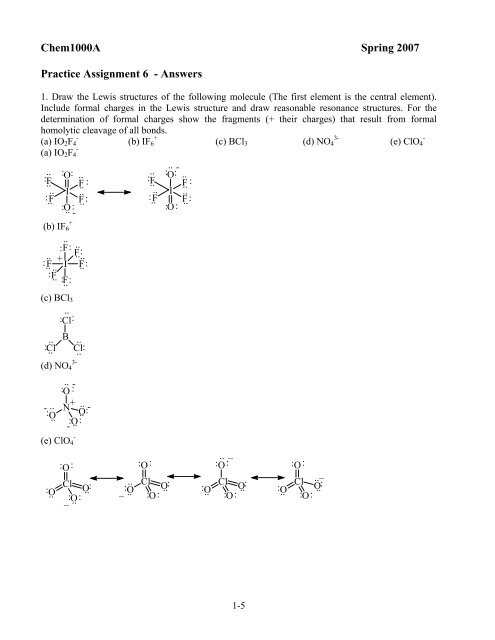
1. Draw the Lewis structures of the following molecule (The first element is the central element).<br />
Include formal charges in the Lewis structure and draw reasonable resonance structures. For the<br />
determination of formal charges show the fragments (+ their charges) that result from formal<br />
homolytic cleavage of all bonds.<br />
(a) IO2F4 -<br />
(b) IF6 +<br />
(c) BCl3 (d) NO4 3-<br />
(e) ClO4 -<br />
(a) IO2F4 -<br />
.. : O:<br />
: ..<br />
.. F F..<br />
:<br />
.. I ..<br />
: .. F F..<br />
:<br />
: O..<br />
:<br />
-<br />
(b) IF6 +<br />
..<br />
: F:<br />
..<br />
.. F..<br />
:<br />
..<br />
:<br />
+<br />
.. F..<br />
I F..<br />
:<br />
: F..<br />
: F..<br />
:<br />
(c) BCl3<br />
..<br />
: Cl:<br />
.. B ..<br />
: Cl .. Cl:<br />
..<br />
(d) NO4 3-<br />
..<br />
: O :<br />
.. N<br />
O<br />
O..<br />
.. : O:<br />
.. : -<br />
-<br />
+<br />
-<br />
:<br />
- ..<br />
(e) ClO4 -<br />
: O..<br />
: O:<br />
Cl<br />
O..<br />
:<br />
_:<br />
O..<br />
:<br />
..<br />
:<br />
.. F<br />
..<br />
: .. F<br />
: O:<br />
.. Cl<br />
: O<br />
O:<br />
_<br />
..<br />
..<br />
: O:<br />
.. -<br />
: O:<br />
..<br />
F..<br />
:<br />
I ..<br />
F..<br />
:<br />
: O:<br />
: O..<br />
.. _<br />
: O:<br />
Cl<br />
O..<br />
:<br />
: O:<br />
1-5<br />
: O:<br />
Cl ..<br />
: O<br />
O:<br />
..<br />
..<br />
: O:<br />
_
2. Looking at electronegativity differences, ∆χ, predict whether the following compounds are ionic or<br />
covalent.<br />
(a) TeF6 ∆χ = 3.98-2.10 = 1.88 covalent (polar)<br />
(b) CF4 ∆χ = 3.98-2.55 = 1.43 covalent<br />
(c) AlF3 ∆χ = 3.98-1.61 = 2.37 ionic<br />
(d) NaF ∆χ = 3.98-0.93 = 3.05 ionic<br />
(e) B2H6 ∆χ = 2.20-2.04 = 0.16 covalent<br />
3. (a) Draw Lewis structures of the following molecules. (b) Specify electron-pair geometries and<br />
molecular geometries of the following molecules according the VSEPR model. (c) Indicate the bond<br />
dipole moments and the overall molecular dipole moments (if the molecule is polar). Specify whether<br />
the molecule is polar or non-polar.<br />
(i) ClO2 -<br />
(ii) XeO4<br />
(iii) BrF4 -<br />
(iv) NO2F<br />
(v) SeF4<br />
(vi) SF3 +<br />
(vii) OH2<br />
(viii) OF2<br />
(ix) CFCl3<br />
(x) XeF2<br />
(xi) SF5 -<br />
(xii) XeO3F2<br />
(xiii) PO2F2 -<br />
(ii)<br />
(i)<br />
..<br />
: Cl<br />
: O..<br />
:<br />
-<br />
: O :<br />
Xe<br />
O O<br />
O..<br />
.. : :<br />
.. :<br />
O..<br />
:<br />
..<br />
..<br />
.. +<br />
: Cl ..<br />
Cl<br />
O :<br />
: O<br />
.. -<br />
O O<br />
..<br />
electron-pair geometry: tetrahedral (SN = 4)<br />
molecular geometry: bent(the two ClO bonds are equivalent)<br />
polar molecule: molecular dipole moment is pointing towards the side of the oxygens, away from Cl<br />
electron-pair geometry: tetrahedral<br />
(SN =4)<br />
molecular geometry: tetrahedral<br />
bond dipole moments cancel each other,<br />
therefore, no mol. dipole moment<br />
XeO 4 is non-polar<br />
(iii)<br />
..<br />
.. - .. F..<br />
: ..<br />
: F..<br />
.. Br .. F<br />
F<br />
.. :<br />
: ..<br />
electron-pair geometry: octahedra (SN = 6)<br />
molecular geometry: square planar<br />
(lone pairs on opposite sides of the plane)<br />
bond dipole moments cancel each other,<br />
therefore, no molecular dipole moment<br />
BrF 4 - is non-polar<br />
2-5
(iv)<br />
..<br />
: .. F<br />
.. : :<br />
..<br />
O:<br />
N<br />
O<br />
-<br />
S<br />
F<br />
..<br />
F<br />
F..<br />
:<br />
.. : :<br />
: ..<br />
.. +<br />
..<br />
O<br />
..<br />
F F : :<br />
.. : :<br />
.. ..<br />
..<br />
: .. F<br />
.. -<br />
: O:<br />
N<br />
O..<br />
:<br />
electron-pair geometry: trigonal planar<br />
(both NO bonds are equivalent due to resonance)<br />
molecular geometry: trigonal planar<br />
The bond dipole moment of NF is significantly<br />
larger than that of the NO bonds, hence,<br />
the NF dipole is only partially compensated by the<br />
NO dipoles. The resulting molecular dipole moment<br />
points in the direction of the fluorine.<br />
NOF 2 is polar.<br />
(vi)<br />
electron-pair geometry: tetrahedral<br />
molecular geometry: trigonal pyramidal<br />
The SF bond dipole moments point have all<br />
a component pointing down.<br />
SF 3 + is polar.<br />
(viii)<br />
electron-pair geometry: tetrahedral<br />
molecular geometry: bent<br />
The OF bond dipole moments point towards F.<br />
F 2 O is polar.<br />
+<br />
+<br />
F<br />
N<br />
3-5<br />
O<br />
O<br />
+<br />
(v)<br />
.. ..<br />
O<br />
H H<br />
Cl<br />
Cl<br />
.. : :<br />
: ..<br />
..<br />
..<br />
: F :<br />
..<br />
Cl .. :<br />
..<br />
: F :<br />
F<br />
Se<br />
F<br />
.. F:<br />
:<br />
..<br />
.. :<br />
: ..<br />
.. :<br />
+<br />
electron-pair geometry: trigonal bipyramidal<br />
(lone pair goes into the equatorial position)<br />
molecular geometry: see saw<br />
the axial SeF dipoles will cancel each other.<br />
The equatorial SeF dipoles will add up to a<br />
molecular dipole moment, pointing to the side<br />
of the two equatorial fluorines.<br />
SeF 4 is polar.<br />
(vii)<br />
electron-pair geometry: tetrahedral<br />
molecular geometry: bent<br />
The OH bond dipole moments point towards O.<br />
H 2 O is polar.<br />
(ix)<br />
electron-pair geometry: tetrahedral<br />
molecular geometry: tetrahedral<br />
The CCl bond dipole moments are smaller than<br />
that of the CF bond. Hence, the overall molecular<br />
dipole moment points in the direction of F.<br />
CFCl 3 is polar.<br />
+<br />
+
(x) (xi)<br />
..<br />
: F Xe .. F:<br />
.. .. ..<br />
.. ..<br />
electron-pair geometry: trigonal bipyramidal<br />
the three lone pairs are located in<br />
the equatorial positions, therefore:<br />
molecular geometry: linear<br />
the XeF dipole moments cancel each other<br />
XeF 2 is non-polar<br />
(xii)<br />
..<br />
O..<br />
..<br />
: F :<br />
Xe<br />
..<br />
F : :<br />
..<br />
O..<br />
..<br />
O..<br />
electron-pair geometry: trigonal bipyramidal<br />
molecular geometry: trigonal bipyramidal<br />
the double-bond domains are located in the<br />
equatorial plane.<br />
The XeF bond dipole moments cancel each other.<br />
The three XeO dipole moments cancel each other,<br />
too. Therefore, XeO 3 F 2 is non-polar.<br />
4-5<br />
+<br />
: ..<br />
.. F<br />
: F<br />
..<br />
..<br />
..<br />
: F : ..<br />
F..<br />
.. :<br />
S F..<br />
:<br />
..<br />
-<br />
electron-pair geometry: octahedral<br />
molecular geometry: square pyramidal<br />
the four SF bond dipole moments of the<br />
equatorial fluorines will cancel each other<br />
the axial SF dipole remains<br />
SF 5 - is a polar molecule.<br />
(xiii)<br />
:<br />
..<br />
.. :<br />
..<br />
O O<br />
.. F<br />
P<br />
F<br />
:<br />
..<br />
.. :<br />
..<br />
- ..<br />
: :<br />
..<br />
:<br />
..<br />
: O<br />
.. -<br />
: O:<br />
.. F<br />
P<br />
F<br />
electron-pair geometry: tetrahedral<br />
molecular geometry: tetrahedral<br />
PF bond dipole moments are larger than those<br />
of the PO bond, therefore, a small residual<br />
dipole moment in the direction of the F's remains<br />
PO 2 F 2 - is polar.<br />
4. Determine the oxidation states in the following sulfur compounds (only one resonance structure is<br />
given). Use the original definition of the oxidation state (by cleaving bonds). For (b) and (c),<br />
distinguish between the oxidation states for individual sulfur atoms and an average oxidation state for<br />
sulfur (i.e., the average of the two – or more – values). You would obtain these average oxidation<br />
states if you use the ‘simple rules’, that are usually used for oxidation states.<br />
(a) peroxodisulfate: S2O8 2-<br />
+
-II<br />
..<br />
O..<br />
-II<br />
: O:<br />
S<br />
.. -I<br />
O.. -I ..<br />
O.. -II<br />
: O:<br />
-II ..<br />
S O..<br />
+VI : O..<br />
:<br />
-<br />
-II<br />
(b) S2F4<br />
..<br />
F<br />
: S S F<br />
: F F<br />
: O..<br />
:<br />
-<br />
-II<br />
+VI<br />
..<br />
-I..<br />
+I +III:<br />
:<br />
.. -I<br />
.. :<br />
.. : : .. :<br />
-I -I<br />
(c) disulfite S2O5 2-<br />
-II -II<br />
O:<br />
O :<br />
-II<br />
: :<br />
..<br />
O..<br />
S S:<br />
+III<br />
+V<br />
O: .. : : O..<br />
:<br />
- -<br />
-II -II<br />
(d) dithionate S2O6 2-<br />
-II -II<br />
..<br />
-IIO..<br />
: O:<br />
: O :<br />
+V +V..<br />
S S O..<br />
-II<br />
O: .. : : O..<br />
:<br />
- -<br />
-II -II<br />
5. Determine oxidation states for all elements in the following compounds:<br />
(a) H-O-O-F H +I -O -I -O +I -F -I<br />
(b) H3C-O-O-F H +I 3C -II -O -I -O +I -F -I<br />
(c) glycol, H2C(OH)CH(OH)CH2(OH):<br />
H<br />
H<br />
H<br />
H<br />
H<br />
(d) ClO3 -<br />
..<br />
O.. ..<br />
.. H<br />
O<br />
.. H<br />
O..<br />
H<br />
H +I 2C -I (O -II H +I )C 0 H +I (O -II H +I )C -I H +I 2(O -II H +I )<br />
Cl +V O -II 3 -<br />
5-5