1. Thermo-physical properties 2. Radiation properties - nptel - Indian ...
1. Thermo-physical properties 2. Radiation properties - nptel - Indian ...
1. Thermo-physical properties 2. Radiation properties - nptel - Indian ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
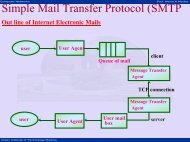
Mechanical Measurements Prof S.P.Venkatesan<br />
<strong>Indian</strong> Institute of Technology Madras<br />
Thermal conductivity may be measured by either steady state methods or<br />
unsteady (transient) methods.<br />
(i) Steady state methods<br />
o Guarded hot plate method<br />
Solid, Liquid<br />
o Radial heat flow apparatus<br />
Liquid, Gas<br />
o Thermal conductivity comparator<br />
Solid<br />
Steady state methods normally involve very large measurement times since the<br />
system should come to the steady state, possibly starting from initial room<br />
temperature of all the components that make up the apparatus. Also maintaining<br />
the steady state requires expensive controllers and uninterrupted power and<br />
water supplies.<br />
(ii) Unsteady method<br />
o Laser flash apparatus<br />
Solid<br />
Even though the unsteady methods may be expensive because of stringent<br />
instrumentation requirements the heat losses that plague the steady sate<br />
methods are not present in these. The entire measurement times may be from a<br />
few milliseconds to seconds or at the most a few minutes.<br />
Thermal conductivity is defined through Fourier law of conduction. In the case of<br />
one-dimensional heat conduction the appropriate relation that defines the thermal<br />
conductivity is