Chapter 13 (PDF)
Chapter 13 (PDF)
Chapter 13 (PDF)
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
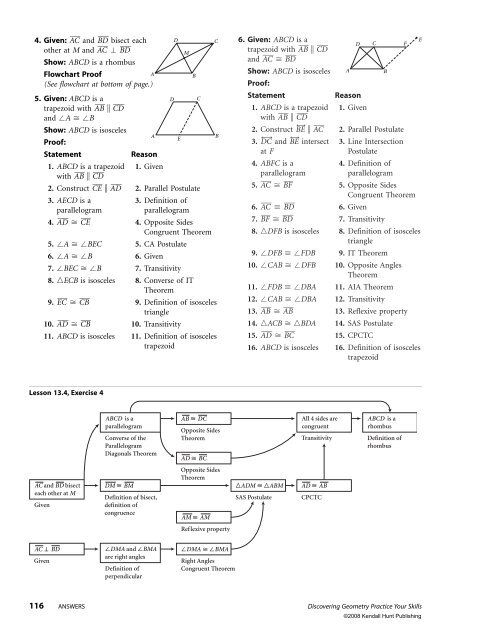
4. Given: AC and BD bisect each<br />
other at M and AC BD<br />
Show: ABCD is a rhombus<br />
Flowchart Proof<br />
A<br />
(See flowchart at bottom of page.)<br />
5. Given: ABCD is a<br />
trapezoid with AB CD <br />
and A B<br />
Show: ABCD is isosceles<br />
D C<br />
Proof:<br />
A<br />
E<br />
B<br />
Statement Reason<br />
1. ABCD is a trapezoid<br />
with AB CD <br />
1. Given<br />
2. Construct CE AD 2. Parallel Postulate<br />
3. AECD is a 3. Definition of<br />
parallelogram parallelogram<br />
4. AD CE 4. Opposite Sides<br />
Congruent Theorem<br />
5. A BEC 5. CA Postulate<br />
6. A B 6. Given<br />
7. BEC B 7. Transitivity<br />
8. ECB is isosceles 8. Converse of IT<br />
Theorem<br />
9. EC CB 9. Definition of isosceles<br />
triangle<br />
10. AD CB 10. Transitivity<br />
11. ABCD is isosceles 11. Definition of isosceles<br />
trapezoid<br />
Lesson <strong>13</strong>.4, Exercise 4<br />
AC and BD bisect<br />
each other at M<br />
Given<br />
AC BD<br />
Given<br />
ABCD is a<br />
parallelogram<br />
Converse of the<br />
Parallelogram<br />
Diagonals Theorem<br />
DM BM<br />
Definition of bisect,<br />
definition of<br />
congruence<br />
DMA and BMA<br />
are right angles<br />
Definition of<br />
perpendicular<br />
D C<br />
M<br />
B<br />
AB DC<br />
Opposite Sides<br />
Theorem<br />
AD BC<br />
Opposite Sides<br />
Theorem<br />
AM AM<br />
Reflexive property<br />
DMA BMA<br />
Right Angles<br />
Congruent Theorem<br />
6. Given: ABCD is a<br />
trapezoid with AB CD <br />
and AC BD<br />
Show: ABCD is isosceles<br />
Proof:<br />
Statement Reason<br />
1. ABCD is a trapezoid<br />
with AB CD <br />
1. Given<br />
2. Construct BE AC 2. Parallel Postulate<br />
3. DC and BE intersect 3. Line Intersection<br />
at F Postulate<br />
4. ABFC is a 4. Definition of<br />
parallelogram parallelogram<br />
5. AC BF 5. Opposite Sides<br />
Congruent Theorem<br />
6. AC BD 6. Given<br />
7. BF BD 7. Transitivity<br />
8. DFB is isosceles 8. Definition of isosceles<br />
triangle<br />
9. DFB FDB 9. IT Theorem<br />
10. CAB DFB 10. Opposite Angles<br />
Theorem<br />
11. FDB DBA 11. AIA Theorem<br />
12. CAB DBA 12. Transitivity<br />
<strong>13</strong>. AB AB <strong>13</strong>. Reflexive property<br />
14. ACB BDA 14. SAS Postulate<br />
15. AD BC 15. CPCTC<br />
16. ABCD is isosceles 16. Definition of isosceles<br />
trapezoid<br />
ADM ABM<br />
SAS Postulate<br />
All 4 sides are<br />
congruent<br />
Transitivity<br />
AD AB<br />
CPCTC<br />
D<br />
C<br />
A B<br />
ABCD is a<br />
rhombus<br />
Definition of<br />
rhombus<br />
116 ANSWERS Discovering Geometry Practice Your Skills<br />
©2008 Kendall Hunt Publishing<br />
F<br />
E