Section 2.8 – Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities Recall ...
Section 2.8 – Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities Recall ...
Section 2.8 – Absolute Value Equations and Inequalities Recall ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
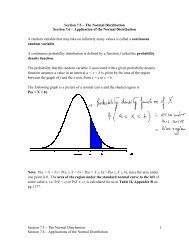
<strong>Section</strong> <strong>2.8</strong> <strong>–</strong> <strong>Absolute</strong> <strong>Value</strong> <strong>Equations</strong> <strong>and</strong> <strong>Inequalities</strong><br />
<strong>Recall</strong>: <strong>Absolute</strong> <strong>Value</strong> of a point on the number line is the distance of that point to the origin<br />
‘0’.<br />
| 4 | =<br />
| − 5 | =<br />
| 5(<br />
2<br />
− 4)<br />
| =<br />
Solving <strong>Absolute</strong> <strong>Value</strong> <strong>Equations</strong><br />
We want to solve equations of this form: x = C<br />
1) If C is positive: x = C has two solutions; x = C or x = −C<br />
2) If C is negative: x = C has no solution<br />
3) If C = 0 : x = 0 has one solution: x = 0<br />
Example 1: Solve x = 8<br />
Example 2: Solve x = −2<br />
Remember: “absolute value = negative number” has ____ solution.<br />
1
How to solve absolute value equations<br />
1. Isolate the absolute value expression on one side <strong>and</strong> a number on the other by adding or<br />
subtracting first, then multiplying or dividing. Get: Expression = Number<br />
2. If the resulting equation is absolute value equals a positive number, rewrite into the two<br />
equivalent equations. These equations do NOT have absolute value signs!<br />
3. If the resulting equation is absolute value equals 0, set the expression in the absolute<br />
value equal to 0 <strong>and</strong> solve.<br />
4. If the resulting equation is absolute value equals a negative number, there is no solution,<br />
you can stop here <strong>and</strong> state “no solution”<br />
Example 3: Solve x + 4 = 9.<br />
Example 4: Solve 2x − 4 = 8 .<br />
Example 5: Solve 4 x − 6 = 20.<br />
2
Example 6: Solve 2 2x<br />
+ 1 + 5 = 21.<br />
1<br />
Example 7: Solve 2x<br />
− 6 = 4 .<br />
4<br />
3
Example 8: Solve 20 + 2x + 4 = 15<br />
4
Solving <strong>Absolute</strong> <strong>Value</strong> <strong>Inequalities</strong><br />
If C is positive, then:<br />
a) x < C is equivalent to − C < x < C .<br />
b) x ≤ C is equivalent to − C ≤ x ≤ C .<br />
c) x > C is equivalent to x < −C<br />
or x > C .<br />
d) x ≥ C is equivalent to x ≤ −C<br />
or x ≥ C .<br />
Special Cases:<br />
If C is negative, then<br />
If C = 0, then<br />
a) The inequalities of the form x < C or x ≤ C have no solution.<br />
b) The solution of the inequalities x > C or x ≥ C is all real numbers.<br />
a) The inequalities of the form x < 0 has no solution.<br />
b) The solution of the inequality x = 0 is x = 0.<br />
c) The solution of the inequality x > 0 is all real numbers except 0.<br />
d) The solution of the inequality x ≥ 0 is all real numbers.<br />
5
How to solve absolute value inequalities:<br />
1. Rearrange the equation so that you have the form:<br />
<strong>Absolute</strong> value inequality sign number<br />
2. Write the equivalent inequality relation or relations by the rules on the last page. Note<br />
that these equivalent inequalities no longer have absolute value signs!<br />
3. Solve each inequality for x <strong>and</strong> express the answer in interval notation<br />
4. If the equation is equivalent to “x > 3 or x < -3” type inequality, use the union symbol<br />
between the two intervals in your answer.<br />
Example 9: Solve the inequality <strong>and</strong> express your answer in interval notation.<br />
a. x ≤ 5<br />
b. x < 5<br />
c. x ≥ 5<br />
d. x<br />
> 5<br />
6
Example 10: Solve the inequality <strong>and</strong> express your answer in interval notation.<br />
x + 4 <<br />
5<br />
Example 11: Solve the inequality <strong>and</strong> express your answer in interval notation.<br />
4 2x<br />
+ 1 ≤ 28<br />
7
Example 12: Solve the inequality <strong>and</strong> express your answer in interval notation.<br />
2 2x<br />
−1<br />
+ 1 > 7<br />
8
Example 13: Solve the inequality <strong>and</strong> express your answer in interval notation.<br />
2 10<br />
x<br />
− 4 ≥<br />
3 3<br />
9
Example 14: Solve the inequality <strong>and</strong> express your answer in interval notation.<br />
x + 1<br />
< 2<br />
5<br />
Example 15: Solve the inequality <strong>and</strong> express your answer in interval notation.<br />
−5 ≤ 9x + 2<br />
10
Example 16: Solve 7 + 2 + 3x ≤ 4 .<br />
11