Vascular Rings and Slings - December 2005
Vascular Rings and Slings - December 2005
Vascular Rings and Slings - December 2005
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
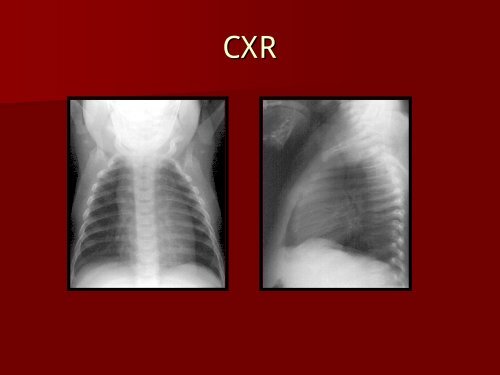
CXR
Diagnosis: Diagnosis<br />
<strong>Vascular</strong> Ring- Ring probable double aortic arch
<strong>Vascular</strong> <strong>Rings</strong> & <strong>Slings</strong><br />
Morning Report<br />
<strong>December</strong> 13, <strong>2005</strong>
Introduction<br />
“<strong>Vascular</strong> <strong>Vascular</strong> ring” ring refers to a variety of<br />
congenital vascular anomalies that encircle<br />
<strong>and</strong> compress the esophagus <strong>and</strong> trachea<br />
Complete or “true true ring” ring vs. Incomplete<br />
Abnormalities of the aortic arch <strong>and</strong> its<br />
branching arteries make up most of the<br />
“vascular vascular rings” rings (exception- (exception pulmonary artery sling)
In the embryonic aortic arch,<br />
the ventral <strong>and</strong> dorsal aorta<br />
are connected by six primitive<br />
aortic arches<br />
Regressions or persistence of<br />
the primitive arches cause the<br />
different vascular ring<br />
anomalies<br />
A “left left” or “right right” aortic arch is<br />
defined by the mainstem mainstem<br />
bronchus bronchus that is crossed by the<br />
aorta arch (not to the side of the<br />
midline the aorta descends)<br />
Embryology<br />
www.childsdoc.org/spring98/vascular
Clinical Presentations<br />
Respiratory Symptoms<br />
(Most Common)<br />
Inspiratory stridor<br />
“noisy noisy breathing” breathing or<br />
wheezing<br />
Chronic cough<br />
Recurrent respiratory<br />
infections<br />
Hoarse cry<br />
ALTE/apnea (infants)<br />
Feeding Symptoms<br />
(More common in older pts)<br />
Gagging or choking w/<br />
food<br />
Recurrent emesis<br />
Dysphagia (typically in older<br />
children/ especially with solid<br />
foods)<br />
Dysphagia<br />
Failure to thrive (food<br />
avoidance)<br />
Symptoms are often made worse w/ feeding <strong>and</strong> during intercurrent illness
Often Normal<br />
Physical Exam<br />
Poor weight gain (if severe compression)<br />
Pulmonary exam may reveal wheezing, stridor, stridor,<br />
dyspnea, dyspnea,<br />
retractions<br />
Abnormal positioning may be observed<br />
– Lie w/ neck extended, back arched when supine to<br />
minimize tracheal narrowing
Complete<br />
Complete<br />
(encircle <strong>and</strong> compress the<br />
esophagus <strong>and</strong> trachea)<br />
– Double aortic arch<br />
– Right aortic arch w/<br />
aberrant left<br />
subclavian (<strong>and</strong> left<br />
ligamentum arteriosum)<br />
arteriosum<br />
These two anomalies<br />
make up >95% of all<br />
complete vascular rings<br />
<strong>Vascular</strong> <strong>Rings</strong><br />
Incomplete<br />
Incomplete<br />
(compress but do not encircle<br />
the esophagus <strong>and</strong> trachea)<br />
– Aberrant right<br />
subclavian artery<br />
– Anomalous innominate<br />
artery<br />
– Pulmonary vascular<br />
sling<br />
– Right aortic arch w/<br />
mirror image<br />
branching
Park: Pediatric Cardiology for Practitioners, 4th ed., Copyright © 2002 Mosby, Inc
Normal Aortic Arch Anatomy<br />
(aka innominate<br />
artery)<br />
www.pediatriconcall.com/fordoctor/Diseases<strong>and</strong>condition/Difficultydia.asp
Double Aortic Arch<br />
Most common vascular<br />
ring (40%)<br />
Persistence of both right<br />
<strong>and</strong> left branchial arches<br />
Infants present early in<br />
life w/ respiratory distress<br />
(stridor stridor) ) <strong>and</strong> feeding<br />
problems<br />
Right-arch Right arch dominant is<br />
most common (75%)<br />
Usually an isolated<br />
anomaly<br />
www.childsdoc.org/spring98/vascular
Right Aortic Arch w/ Aberrant Left<br />
Second most common vascular<br />
ring (30%)<br />
The ring is formed by the right<br />
aortic arch w/ left sided<br />
ligamentum arteriosum<br />
attached to an aberrant LSA<br />
Present later in life (3-9mo) (3 9mo)<br />
b/c the ring is “looser looser”<br />
compared to double aortic arch<br />
Not often associated w/<br />
congenital heart defects<br />
(except w/ “mirror mirror image<br />
branching” branching type)<br />
Subclavian Artery<br />
www.childsdoc.org/spring98/vascular
Right Aortic Arch Anomalies<br />
Complete Ring Incomplete Ring<br />
www.childsdoc.org/spring98/vascular
Incomplete <strong>Vascular</strong> <strong>Rings</strong><br />
Anomalous Innominate Artery<br />
– The innominate arises from the left side of the aortic arch <strong>and</strong><br />
compresses the trachea<br />
– Asymptomatic or causes mild respiratory symptoms<br />
– Barium Esophagram is normal; Bronchoscopy can be diagnostic<br />
– Commonly associated with other cardiac defects<br />
Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery<br />
– RSA arises from the descending aorta <strong>and</strong> courses behind the<br />
esophagus<br />
– Usually asymptomatic<br />
– Mild feeding problems may occur/swallowing dysfunction<br />
– Usually an isolated anomaly
Anomalous Left Pulmonary Artery<br />
“Pulmonary Pulmonary <strong>Vascular</strong> Sling” Sling<br />
– Left PA arises from the RPA<br />
<strong>and</strong> courses behind the<br />
trachea <strong>and</strong> in front of the<br />
esophagus to enter the hilum<br />
of the left lung<br />
– Respiratory AND feeding<br />
problems may occur-<br />
symptoms may be severe<br />
– Esophagram shows anterior anterior<br />
compression only<br />
– Bronchoscopy is required to<br />
r/o associated tracheal<br />
stenosis w/ complete tracheal<br />
rings<br />
“ring ring-sling sling complex” complex (50%) www.childsdoc.org/spring98/vascular
Diagnosis<br />
CXR (AP <strong>and</strong> lateral)<br />
– Tracheal narrowing <strong>and</strong>/or displacement (lateral)<br />
– Aortic arch location<br />
– Tracheal Position: abnormal deviation to the left<br />
(due to the aorta coursing over the right mainstem bronchus) OR<br />
Midline position with double aortic arch<br />
– Atelectasis, Atelectasis,<br />
hyperinflation, or pneumonia may be present<br />
(especially in pulmonary artery slings)<br />
Barium Esophagram<br />
Barium<br />
– Most important <strong>and</strong> reliable diagnostic tool<br />
Except in anomalous innominate artery<br />
– Posterior (<strong>and</strong> anterior) compression of esophagus on lateral<br />
Except in pulmonary artery sling sling anterior compression only
CXR<br />
www.uhrad.com/ pedsarc/peds056a.jpg
Tracheal Deviation<br />
www.pediatriconcall.com/fordoctor/Diseases<strong>and</strong>condition/Difficultydia.asp
Barium Esophagram
Other Imaging… Imaging<br />
ECHO<br />
– Recommended to exclude other cardiac defects <strong>and</strong> visualizes the<br />
vascular ring<br />
– Very useful in diagnosing pulmonary artery sling<br />
CT/MRI<br />
– Identify vascular structures <strong>and</strong> anatomy of tracheobronchial tree<br />
Angiography<br />
– Considered “gold gold st<strong>and</strong>ard”, st<strong>and</strong>ard , but rarely needed for diagnosis<br />
Bronchoscopy<br />
– Use as a diagnostic tool is controversial<br />
– Recommended for diagnosis of a vascular sling to r/o concomitant<br />
tracheal rings (<strong>and</strong> useful for aberrant innominate artery)
Management<br />
Asymptomatic patients need no surgical treatment, even<br />
when anomalies are found incidentally<br />
Medical management is recommended for infants with<br />
mild symptoms<br />
– Careful feeding w/ soft foods<br />
– Aggressive treatment of pulmonary infections<br />
Respiratory distress, h/o recurrent pulmonary infections,<br />
apneic spells, FTT are indications for surgical<br />
intervention
Surgical Management<br />
Double Aortic Arch<br />
– Division of the smaller of the two arches (usually the left arch) arch<br />
Right Aortic Arch w/ Aberrant LSA<br />
– Division of the ligamentum arteriosum<br />
Anomalous Innominate Artery<br />
– Surgical suturing of the artery to the sternum (if >75% tracheal<br />
narrowing)- narrowing) rarely indicated<br />
Aberrant right Subclavian Artery<br />
– Surgical interruption of the artery (rarely indicated)<br />
Anomalous Left Pulmonary Artery (Pulmonary <strong>Vascular</strong><br />
Sling)<br />
– Surgical division <strong>and</strong> reimplantation of the LPA
Complications<br />
Surgical Mortality rate is generally low (