Biology 10 - General Biology Lecture 14 Circulatory System Blood ...
Biology 10 - General Biology Lecture 14 Circulatory System Blood ...
Biology 10 - General Biology Lecture 14 Circulatory System Blood ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
<strong>Biology</strong> <strong>10</strong> - <strong>General</strong> <strong>Biology</strong><br />
<strong>Lecture</strong> <strong>14</strong><br />
<strong>Circulatory</strong> <strong>System</strong><br />
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D3ZDJgFDdk0&feature=related<br />
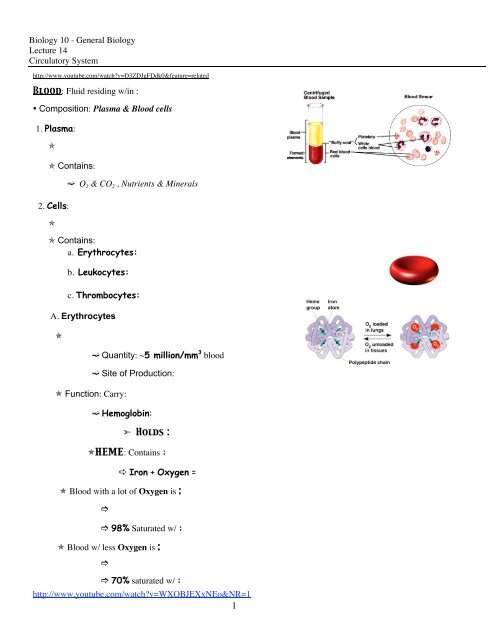
<strong>Blood</strong>: Fluid residing w/in :<br />
• Composition: Plasma & <strong>Blood</strong> cells<br />
1. Plasma:<br />
<br />
Contains:<br />
2. Cells:<br />
<br />
O 2 & CO 2 , Nutrients & Minerals<br />
Contains:<br />
a. Erythrocytes:<br />
b. Leukocytes:<br />
c. Thrombocytes:<br />
A. Erythrocytes<br />
<br />
Function: Carry:<br />
Quantity: ~5 million/mm 3 blood<br />
Site of Production:<br />
Hemoglobin:<br />
Holds :<br />
HEME: Contains :<br />
Iron + Oxygen =<br />
<strong>Blood</strong> with a lot of Oxygen is :<br />
<br />
98% Saturated w/ :<br />
<strong>Blood</strong> w/ less Oxygen is :<br />
<br />
70% saturated w/ :<br />
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WXOBJEXxNEo&NR=1<br />
1
. White <strong>Blood</strong> Cells: Leukocytes<br />
<br />
Function:<br />
5 different WBCs<br />
(Body’s internal Defense)<br />
Each has a specific function<br />
Recognizing foreign substance<br />
Initiate FIGHT<br />
Eating foreign substances<br />
Increasing blood flow to infection<br />
Remembering an infection<br />
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JnlULOjUhSQ&feature=related<br />
c. Platelets: Thrombocytes<br />
<br />
Function:<br />
Stops bleeding<br />
Transport Tubes: <strong>Blood</strong> Vessels<br />
Three Different types:<br />
1. Arteries: Carry blood :<br />
• Transport blood :<br />
• PULSE:<br />
Pressure PUSHES blood to :<br />
Correlated with each heart beat<br />
Cause: <strong>Blood</strong> pushing :<br />
Palpable<br />
• Usually transports :<br />
2
Exception: PULMONARY ARTERY<br />
2. Veins: Carry blood :<br />
• Transport blood :<br />
NO :<br />
Carries Deoxygenated blood to :<br />
• Usually transports :<br />
Exception: PULMONARY VEIN<br />
Leaves Lungs carrying Oxygenated blood<br />
• Problem: Transport LOW pressure blood<br />
“How does blood get back to the heart?”<br />
Average pressure:<br />
<strong>Blood</strong> flow:<br />
a. Veins ABOVE the heart:<br />
<strong>Blood</strong> falls back to heart<br />
b. Veins BELOW the heart:<br />
Veins below heart: <strong>Blood</strong> is pushed by:<br />
Venous Valves: Prevent :<br />
<strong>Blood</strong> can NOT fall back to heart<br />
Significance: Varicose Veins: Venous Valve incompetence<br />
3. Capillaries: Connect Arteries to veins<br />
• “Business end”; Cells
<strong>Blood</strong> Pressure: Pressure exerted by blood on :<br />
Heart: Cardiac contractions create Pressure<br />
Systole : Cardiac<br />
Diastole: Cardiac<br />
Highest pressure in vessel<br />
Heart<br />
Systolic Pressure<br />
Lowest pressure in vessel,<br />
Heart<br />
Diastolic Pressure<br />
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=luppKLO74vg&feature=related<br />
Clinically:<br />
• High <strong>Blood</strong> Pressure: Hypertension<br />
Cause: Atherosclerosis<br />
Systolic: Greater than<br />
Diastolic: Greater than<br />
Narrowing of Arteries: Due to<br />
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fUcLrdPJurU&feature=related<br />
• Risks:<br />
• Prevention:<br />
1. Heart Attacks<br />
2. Strokes<br />
3. <strong>Blood</strong> vessel damage<br />
4. Kidney failure<br />
Reduce cholesterol, saturated & trans fats<br />
Exercise at least :<br />
Study Questions:<br />
1. What is the function of the blood? What are the two main components of blood? Where are the blood cells formed?<br />
2. What is the plasma composed of?<br />
3. What are the most numerous blood cells? What is their function? What is the overall function of the Leukocytes<br />
(WBCs)? What are some of the individual functions of WBC?<br />
4. What is the primary function of thrombocytes (platelets)?<br />
5. What is the function of hemoglobin? What is the difference between oxygenated and deoxygenated blood? What<br />
mineral binds oxygen?<br />
4
6. Where does blood change from being oxygenated into being deoxygenated?<br />
7. What is thee most important difference when identifying an artery from a vein (hint: think of the flow of blood) What<br />
are the difference between arteries and veins with respect to pressure – which ones pulse?<br />
8. Do arteries ALWAYS carry oxygenated blood? Explain. Which large artery does NOT carry oxygenated blood?<br />
9. If you cut yourself & bright red blood was squirting out of the vessel; what vessels did you cut ; artery or vein?<br />
<strong>10</strong>. Which vessels allow for the exchange of materials (nutrients and gases) between the blood and the tissue?<br />
11. What is the blood pressure? What is the difference between systolic and diastolic pressure? When you feel your pulse,<br />
what are you actually feeling? What causes the blood to pulse?<br />
12. Why is the arterial blood pressurized? Are veins pressurized? Explain what the problem is for these low pressure<br />
vessels. How do the vessels solve this problem? - how does blood get back to the heart from the legs?<br />
13. What is hypertension? What are some of the problems associated with hypertension? What are some things you can<br />
do to reduce your risk of hypertension? What is the blood pressure measurement for someone that is just beginning to be<br />
hypertensive?<br />
5