Permanency Guide - Los Angeles County Department of Children ...
Permanency Guide - Los Angeles County Department of Children ...
Permanency Guide - Los Angeles County Department of Children ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
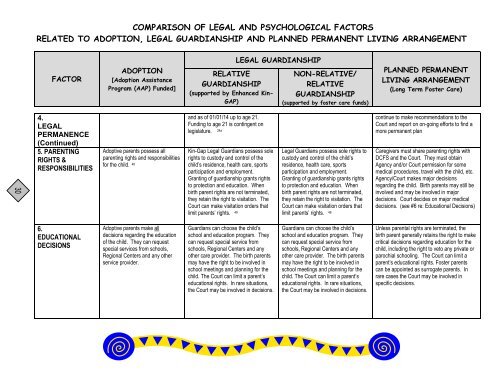
COMPARISON OF LEGAL AND PSYCHOLOGICAL FACTORS<br />
RELATED TO ADOPTION, LEGAL GUARDIANSHIP AND PLANNED PERMANENT LIVING ARRANGEMENT<br />
FACTOR<br />
4.<br />
LEGAL<br />
PERMANENCE<br />
(Continued)<br />
5. PARENTING<br />
RIGHTS &<br />
RESPONSIBILITIES<br />
6.<br />
EDUCATIONAL<br />
DECISIONS<br />
ADOPTION<br />
[Adoption Assistance<br />
Program (AAP) Funded]<br />
Adoptive parents possess all<br />
parenting rights and responsibilities<br />
for the child. 48<br />
Adoptive parents make all<br />
decisions regarding the education<br />
<strong>of</strong> the child. They can request<br />
special services from schools,<br />
Regional Centers and any other<br />
service provider.<br />
RELATIVE<br />
GUARDIANSHIP<br />
(supported by Enhanced Kin-<br />
GAP)<br />
and as <strong>of</strong> 01/01/14 up to age 21.<br />
Funding to age 21 is contingent on<br />
legislature. 24a<br />
Kin-Gap Legal Guardians possess sole<br />
rights to custody and control <strong>of</strong> the<br />
child’s residence, health care, sports<br />
participation and employment.<br />
Granting <strong>of</strong> guardianship grants rights<br />
to protection and education. When<br />
birth parent rights are not terminated,<br />
they retain the right to visitation. The<br />
Court can make visitation orders that<br />
limit parents’ rights. 49<br />
Guardians can choose the child’s<br />
school and education program. They<br />
can request special service from<br />
schools, Regional Centers and any<br />
other care provider. The birth parents<br />
may have the right to be involved in<br />
school meetings and planning for the<br />
child. The Court can limit a parent’s<br />
educational rights. In rare situations,<br />
the Court may be involved in decisions.<br />
LEGAL GUARDIANSHIP<br />
NON-RELATIVE/<br />
RELATIVE<br />
GUARDIANSHIP<br />
(supported by foster care funds)<br />
Legal Guardians possess sole rights to<br />
custody and control <strong>of</strong> the child’s<br />
residence, health care, sports<br />
participation and employment.<br />
Granting <strong>of</strong> guardianship grants rights<br />
to protection and education. When<br />
birth parent rights are not terminated,<br />
they retain the right to visitation. The<br />
Court can make visitation orders that<br />
limit parents’ rights. 49<br />
Guardians can choose the child’s<br />
school and education program. They<br />
can request special service from<br />
schools, Regional Centers and any<br />
other care provider. The birth parents<br />
may have the right to be involved in<br />
school meetings and planning for the<br />
child. The Court can limit a parent’s<br />
educational rights. In rare situations,<br />
the Court may be involved in decisions.<br />
PLANNED PERMANENT<br />
LIVING ARRANGEMENT<br />
(Long Term Foster Care)<br />
continue to make recommendations to the<br />
Court and report on on-going efforts to find a<br />
more permanent plan<br />
Caregivers must share parenting rights with<br />
DCFS and the Court. They must obtain<br />
Agency and/or Court permission for some<br />
medical procedures, travel with the child, etc.<br />
Agency/Court makes major decisions<br />
regarding the child. Birth parents may still be<br />
involved and may be involved in major<br />
decisions. Court decides on major medical<br />
decisions. (see #6 re: Educational Decisions)<br />
Unless parental rights are terminated, the<br />
birth parent generally retains the right to make<br />
critical decisions regarding education for the<br />
child, including the right to veto any private or<br />
parochial schooling. The Court can limit a<br />
parent’s educational rights. Foster parents<br />
can be appointed as surrogate parents. In<br />
rare cases the Court may be involved in<br />
specific decisions.