Worksheet 4.8 Properties of Trigonometric Functions
Worksheet 4.8 Properties of Trigonometric Functions
Worksheet 4.8 Properties of Trigonometric Functions
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Example 2 : Show that 2 cos 2 2x − cos 2 x − sin 2 x = cos 4x.<br />
2 cos 2 2x − cos 2 x − sin 2 x = 2 cos 2 2x − (cos 2 x + sin 2 x)<br />
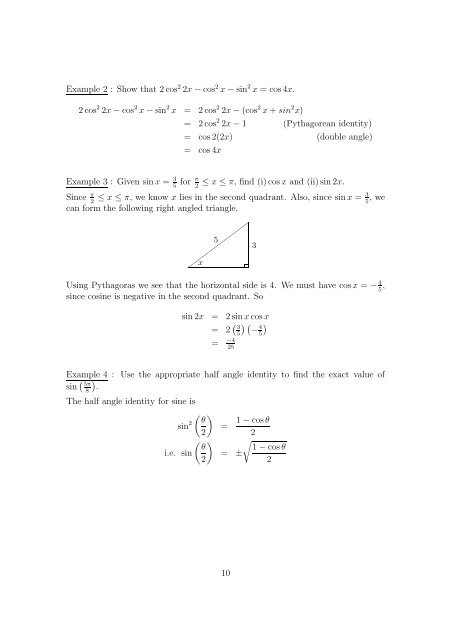
Example 3 : Given sin x = 3<br />
5<br />
Since π<br />
= 2 cos 2 2x − 1 (Pythagorean identity)<br />
= cos 2(2x) (double angle)<br />
= cos 4x<br />
for π<br />
2<br />
≤ x ≤ π, find (i) cos x and (ii) sin 2x.<br />
3<br />
≤ x ≤ π, we know x lies in the second quadrant. Also, since sin x = , we<br />
2 5<br />
can form the following right angled triangle.<br />
5<br />
✚ ✚✚✚✚✚✚✚<br />
x<br />
Using Pythagoras we see that the horizontal side is 4. We must have cos x = − 4<br />
5 ,<br />
since cosine is negative in the second quadrant. So<br />
sin 2x = 2 sin x cos x<br />
= 2 <br />
3 4 − 5 5<br />
= −4<br />
25<br />
Example 4 : Use the appropriate half angle identity to find the exact value <strong>of</strong><br />
sin <br />
5π . 8<br />
The half angle identity for sine is<br />
sin 2<br />
<br />
θ<br />
=<br />
2<br />
1 − cos θ<br />
2<br />
<br />
θ<br />
1 − cos θ<br />
i.e. sin = ±<br />
2<br />
2<br />
10<br />
3