Tensile Test of Steel for Stress vs. Strain Diagram - MyWeb at WIT
Tensile Test of Steel for Stress vs. Strain Diagram - MyWeb at WIT
Tensile Test of Steel for Stress vs. Strain Diagram - MyWeb at WIT
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
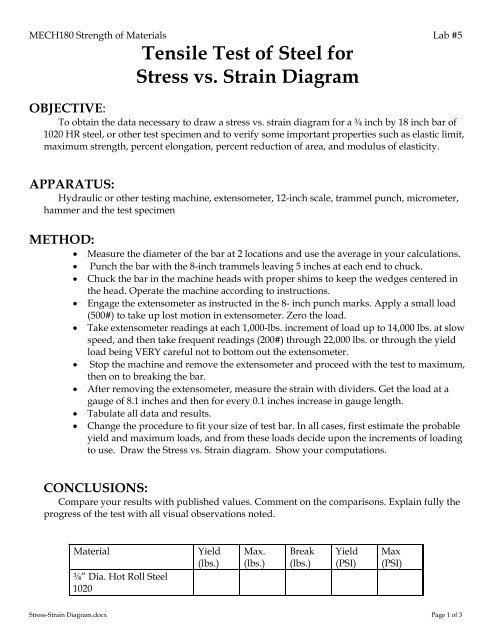
MECH180 Strength <strong>of</strong> M<strong>at</strong>erials Lab #5<br />
<strong>Tensile</strong> <strong>Test</strong> <strong>of</strong> <strong>Steel</strong> <strong>for</strong><br />
<strong>Stress</strong> <strong>vs</strong>. <strong>Strain</strong> <strong>Diagram</strong><br />
OBJECTIVE:<br />
To obtain the d<strong>at</strong>a necessary to draw a stress <strong>vs</strong>. strain diagram <strong>for</strong> a ¾ inch by 18 inch bar <strong>of</strong><br />
1020 HR steel, or other test specimen and to verify some important properties such as elastic limit,<br />
maximum strength, percent elong<strong>at</strong>ion, percent reduction <strong>of</strong> area, and modulus <strong>of</strong> elasticity.<br />
APPARATUS:<br />
Hydraulic or other testing machine, extensometer, 12-inch scale, trammel punch, micrometer,<br />
hammer and the test specimen<br />
METHOD:<br />
Measure the diameter <strong>of</strong> the bar <strong>at</strong> 2 loc<strong>at</strong>ions and use the average in your calcul<strong>at</strong>ions.<br />
Punch the bar with the 8-inch trammels leaving 5 inches <strong>at</strong> each end to chuck.<br />
Chuck the bar in the machine heads with proper shims to keep the wedges centered in<br />
the head. Oper<strong>at</strong>e the machine according to instructions.<br />
Engage the extensometer as instructed in the 8- inch punch marks. Apply a small load<br />
(500#) to take up lost motion in extensometer. Zero the load.<br />
Take extensometer readings <strong>at</strong> each 1,000-lbs. increment <strong>of</strong> load up to 14,000 lbs. <strong>at</strong> slow<br />
speed, and then take frequent readings (200#) through 22,000 lbs. or through the yield<br />
load being VERY careful not to bottom out the extensometer.<br />
Stop the machine and remove the extensometer and proceed with the test to maximum,<br />
then on to breaking the bar.<br />
After removing the extensometer, measure the strain with dividers. Get the load <strong>at</strong> a<br />
gauge <strong>of</strong> 8.1 inches and then <strong>for</strong> every 0.1 inches increase in gauge length.<br />
Tabul<strong>at</strong>e all d<strong>at</strong>a and results.<br />
Change the procedure to fit your size <strong>of</strong> test bar. In all cases, first estim<strong>at</strong>e the probable<br />
yield and maximum loads, and from these loads decide upon the increments <strong>of</strong> loading<br />
to use. Draw the <strong>Stress</strong> <strong>vs</strong>. <strong>Strain</strong> diagram. Show your comput<strong>at</strong>ions.<br />
CONCLUSIONS:<br />
Compare your results with published values. Comment on the comparisons. Explain fully the<br />
progress <strong>of</strong> the test with all visual observ<strong>at</strong>ions noted.<br />
M<strong>at</strong>erial Yield<br />
(lbs.)<br />
¾” Dia. Hot Roll <strong>Steel</strong><br />
1020<br />
Max.<br />
(lbs.)<br />
Break<br />
(lbs.)<br />
Yield<br />
(PSI)<br />
Max<br />
(PSI)<br />
<strong>Stress</strong>-<strong>Strain</strong> <strong>Diagram</strong>.docx Page 1 <strong>of</strong> 3
MECH180 Strength <strong>of</strong> M<strong>at</strong>erials Lab #5<br />
DATA:<br />
M<strong>at</strong>erial________ Initial diameter________ Initial Gage Length_________<br />
Rdng Load Elong<strong>at</strong>ion Rdng Load Elong<strong>at</strong>ion Rdng Load Elong<strong>at</strong>ion<br />
1 41 81<br />
2 42 82<br />
3 43 83<br />
4 44 84<br />
5 45 85<br />
6 46 86<br />
7 47 86<br />
8 48 88<br />
9 49 89<br />
10 50 90<br />
11 51 91<br />
12 52 92<br />
13 53 93<br />
14 54 94<br />
15 55 95<br />
16 56 96<br />
17 57 97<br />
18 58 98<br />
19 59 99<br />
20 60 100<br />
21 61 101<br />
22 62 102<br />
23 63 103<br />
24 64 104<br />
25 65 105<br />
26 66 106<br />
27 67 107<br />
28 68 108<br />
29 69 109<br />
30 70 110<br />
31 71 111<br />
32 72 112<br />
33 73 113<br />
34 74 114<br />
35 75 115<br />
36 76 116<br />
37 77 117<br />
38 78 118<br />
39 79 119<br />
40 80 120<br />
RESULTS:<br />
<strong>Stress</strong>-<strong>Strain</strong> <strong>Diagram</strong>.docx Page 2 <strong>of</strong> 3
MECH180 Strength <strong>of</strong> M<strong>at</strong>erials Lab #5<br />
Proportional Limit__________ Modulus <strong>of</strong> Elasticity__________<br />
Yield <strong>Stress</strong>__________ Modulus <strong>of</strong> Resilience__________<br />
Ultim<strong>at</strong>e <strong>Tensile</strong> <strong>Stress</strong>__________ Modulus <strong>of</strong> Toughness__________<br />
Rdng <strong>Stress</strong> <strong>Strain</strong> Rdng <strong>Stress</strong> <strong>Strain</strong> Rdng <strong>Stress</strong> <strong>Strain</strong><br />
1 41 81<br />
2 42 82<br />
3 43 83<br />
4 44 84<br />
5 45 85<br />
6 46 86<br />
7 47 86<br />
8 48 88<br />
9 49 89<br />
10 50 90<br />
11 51 91<br />
12 52 92<br />
13 53 93<br />
14 54 94<br />
15 55 95<br />
16 56 96<br />
17 57 97<br />
18 58 98<br />
19 59 99<br />
20 60 100<br />
21 61 101<br />
22 62 102<br />
23 63 103<br />
24 64 104<br />
25 65 105<br />
26 66 106<br />
27 67 107<br />
28 68 108<br />
29 69 109<br />
30 70 110<br />
31 71 111<br />
32 72 112<br />
33 73 113<br />
34 74 114<br />
35 75 115<br />
36 76 116<br />
37 77 117<br />
38 78 118<br />
39 79 119<br />
40 80 120<br />
<strong>Stress</strong>-<strong>Strain</strong> <strong>Diagram</strong>.docx Page 3 <strong>of</strong> 3