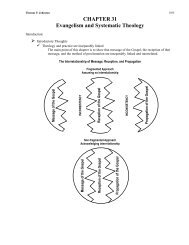
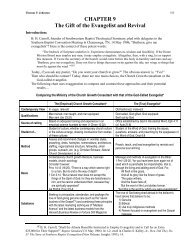
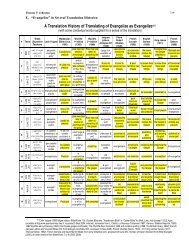
Four Categories of Evangelism Programs - Evangelism Unlimited
Four Categories of Evangelism Programs - Evangelism Unlimited
Four Categories of Evangelism Programs - Evangelism Unlimited
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Thomas P. Johnston 1019<br />
3. Paul, in the context <strong>of</strong> evangelism, even spoke <strong>of</strong> the right <strong>of</strong> the evangelist to earn his living<br />
from the Gospel, 1 Cor 9:11-14:<br />
a. While this principle is <strong>of</strong>ten applied to pastoral ministry (and not without other<br />
Scripture, 1 Tim 5:17-18), in 1 Corinthians 9 it is directed to the person who was<br />
privileged to lead the person to Christ<br />
b. There are examples <strong>of</strong> people who extended the ministry <strong>of</strong> hospitality to Paul in Acts:<br />
1) Lydia from Thyatira took in Paul and his team, Acts 16:15<br />
2) The Philippian jailer took in Paul and Silas into his house after his conversion, and<br />
fed them, Acts 16:34<br />
3) Jason took in Paul and Silas during their evangelistic ministry in Thessalonica, Acts<br />
17:6-7<br />
4. Reverse Servant <strong>Evangelism</strong> in the History <strong>of</strong> the Churches:<br />
a. The Waldenses or “Poor Men <strong>of</strong> Lyons” specifically followed the admonitions in the<br />
sending passages <strong>of</strong> Matthew, Mark, and Luke:<br />
b. As noted in Chapter 7, the Dominicans were specifically commanded to adopt the<br />
lifestyle <strong>of</strong> their “enemy” [the Albigenses and Waldenses]:<br />
1) Their method <strong>of</strong> following Matthew 10 was so effective that when the Roman<br />
Catholic Dominican order was founded, Dominic and his companions were given<br />
the mandate by Bishop Diego to “imitate” the Waldenses, by living a lifestyle <strong>of</strong><br />
“voluntary poverty,” begging for their food—which, by the way, the Waldenses did<br />
not do!<br />
2) Herein, by the way, we have an example <strong>of</strong> imitating a method without the message<br />
Some Servant Resources:<br />
A. Servant <strong>Evangelism</strong> (Sjogren, 1993)<br />
History:<br />
Steve Sjogren, Conspiracy <strong>of</strong> Kindness (Ann Harbor, MI: Servant, 1993)<br />
Steve Sjogren, Dave Ping, and Doug Pollock, Irresistible <strong>Evangelism</strong> (Group, 2003)<br />
Theology: The difference between Sjogren and Atkinson/Roesel<br />
Methodology—individual service<br />
B. Ministry <strong>Evangelism</strong> (Atkinson and Roesel, 1995)<br />
History: Donald A. Atkinson and Charles L. Roesel, Meeting Needs—Sharing Christ (Nashville:<br />
Lifeway, 1995).<br />
Theology: The difference between Sjogren and Atkinson/Roesel<br />
Methodology—social service<br />
C. Servanthood <strong>Evangelism</strong> (Reid and Wheeler, 1997):<br />
Definition: Alvin Reid and David Wheeler, “Intentionally Sharing Christ by Modeling Biblical<br />
Servanthood”<br />
Methodology—individual service<br />
D. Operation Angel Food (2005):<br />
Definition: Low cost food is provided to needy families once-a-month. The families must come to<br />
church to receive the food, and initial contacts are made through church members.<br />
Involved churches can share the Gospel either in the church or at the homes <strong>of</strong> those who receive the<br />
food.<br />
E. AERDO—or the Association <strong>of</strong> Evangelical Relief and Development Organizations all promote and<br />
raise funds among Evangelicals assuming the premises <strong>of</strong> Servant <strong>Evangelism</strong>, which were earlier