Verslag – Rapport – Bericht – Report - GSKE - FMRE
Verslag – Rapport – Bericht – Report - GSKE - FMRE
Verslag – Rapport – Bericht – Report - GSKE - FMRE
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
was reported in detail in the 2011 report. Here we report on an international follow-up study and on the<br />
exploration of the effect of the repeat expansion on gene expression.<br />
In 2006, we identified GRN null mutations as a major gene for FTLD explaining 26 % of familial FTLD in<br />
Belgium (Cruts et al., 2006). Now, we published a paper describing the generation and detailed genetic,<br />
clinical, behavioral and immunohistochemical characterization of GRN knock-out mize.<br />
C9orf72<br />
We assessed the geographical distribution of C9orf72 G 4 C 2 repeat expansions in a collection of 1,205<br />
European FTLD patients, ascertained by the European Early-Onset Dementia (EOD) consortium. Next,<br />
we performed a meta-analysis of these data and that of other European studies, together 2,668 patients<br />
from 15 Western European countries. The frequency of C9orf72 repeat expansions in Western Europe<br />
was 9.98%, with 18.52% in familial, and 6.26% in sporadic FTLD patients. Outliers were Finland and<br />
Sweden with overall frequencies of respectively 29.33% and 20.73%, but also Spain with 25.49%. In<br />
contrast, prevalence in Germany was limited to 4.82% (van der Zee and Gijselinck et al., 2012).<br />
Intermediate repeat sizes (7 to 24 repeat units) are strongly correlated with a haplotype conferring<br />
significant risk especially for developing ALS and FTLD-TDP (van Es et al., 2009; Laaksovirta et al.,<br />
2010; Shatunov et al., 2010; Van Deerlin et al., 2010). We studied the role of intermediate repeat sizes<br />
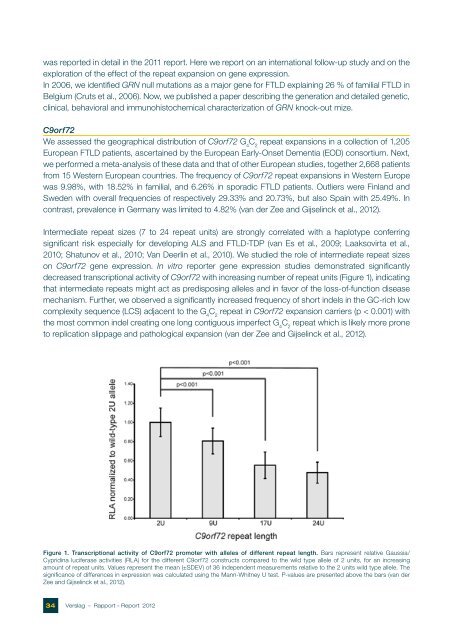
on C9orf72 gene expression. In vitro reporter gene expression studies demonstrated significantly<br />
decreased transcriptional activity of C9orf72 with increasing number of repeat units (Figure 1), indicating<br />
that intermediate repeats might act as predisposing alleles and in favor of the loss-of-function disease<br />
mechanism. Further, we observed a significantly increased frequency of short indels in the GC-rich low<br />
complexity sequence (LCS) adjacent to the G 4 C 2 repeat in C9orf72 expansion carriers (p < 0.001) with<br />
the most common indel creating one long contiguous imperfect G 4 C 2 repeat which is likely more prone<br />
to replication slippage and pathological expansion (van der Zee and Gijselinck et al., 2012).<br />
Figure 1. Transcriptional acti vi ty of C9orf72 promoter with alleles of different repeat length. Bars represent relative Gaussia/<br />
Cypridina luciferase ac ti vities (RLA) for the different C9orf72 constructs compared to the wild type allele of 2 units, for an increasing<br />
amount of repeat units. Values represent the mean (±SDEV) of 36 independent measure ments relative to the 2 units wild type allele. The<br />
significance of differences in expression was calculated using the Mann-Whitney U test. P-values are presented above the bars (van der<br />
Zee and Gijselinck et al., 2012).<br />
34<br />
<strong>Verslag</strong> <strong>–</strong> <strong>Rapport</strong> <strong>–</strong> <strong>Report</strong> 2012