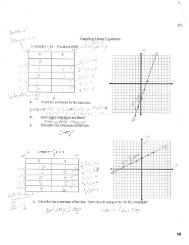
Chapter 28 Stars and the Universe
Chapter 28 Stars and the Universe
Chapter 28 Stars and the Universe
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>the</strong>ory proposes that at <strong>the</strong> time of its origin, <strong>the</strong> universe<br />
was a concentration of matter so dense that <strong>the</strong> laws of nature<br />
as we know <strong>the</strong>m today did not apply. This matter exp<strong>and</strong>ed<br />
explosively, forming <strong>the</strong> universe. Even <strong>the</strong> most<br />
extreme conditions that exist within <strong>the</strong> largest stars could<br />
not compare with <strong>the</strong> beginning of <strong>the</strong> universe.<br />
Experiments <strong>and</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>the</strong>ories of physics show that <strong>the</strong><br />
greatest possible velocity for matter or energy is <strong>the</strong> speed of<br />
light: about 300 million meters per second. Like <strong>the</strong> temperature<br />
of absolute zero (0 K), this is one of <strong>the</strong> absolute limits<br />
known to science. Astronomers reason that <strong>the</strong> universe is<br />
exp<strong>and</strong>ing at this rate.<br />
By working backward, astronomers estimate that <strong>the</strong> universe<br />
began in <strong>the</strong> big bang 14 billion years ago. Exp<strong>and</strong>ing<br />
outward in all directions, <strong>the</strong> universe today could be as much<br />
as <strong>28</strong> billion light years across. This is so gigantic that it is<br />
nearly impossible for humans to comprehend how large this is.<br />
Earth, <strong>the</strong> solar system, <strong>and</strong> even <strong>the</strong> huge Milky Way Galaxy<br />
are incredibly small compared with <strong>the</strong> size of <strong>the</strong> universe.<br />
ACTIVITY <strong>28</strong>-6 A MODEL OF THE BIG BANG<br />
WHAT IS THE FUTURE OF THE UNIVERSE? 729<br />
Inflate a round balloon into a small ball. Draw several small dots<br />
on <strong>the</strong> balloon’s surface. Notice that as <strong>the</strong> balloon is inflated<br />
more, <strong>the</strong> dots always move apart. If observers were located anywhere<br />
on <strong>the</strong> surface of <strong>the</strong> balloon or even inside <strong>the</strong> balloon, as<br />
<strong>the</strong> balloon is inflated, <strong>the</strong>y would see <strong>the</strong> dots moving away in<br />
all directions. No matter what location is chosen, it would appear<br />
that <strong>the</strong> observer is at <strong>the</strong> center of <strong>the</strong> expansion. Therefore, <strong>the</strong>re<br />
is no way that astronomers can find <strong>the</strong> center of <strong>the</strong> universe.<br />
WHAT IS THE FUTURE OF THE UNIVERSE?<br />
From an astronomical point of view, Earth is in a reasonably<br />
unchanging state. Earth’s orbit around <strong>the</strong> sun is stable <strong>and</strong><br />
scientists expect <strong>the</strong> sun to continue its energy production on