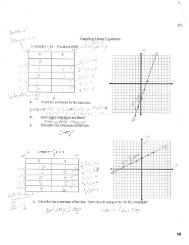
Chapter 18 Fossils and Geologic Time
Chapter 18 Fossils and Geologic Time
Chapter 18 Fossils and Geologic Time
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
420 CHAPTER <strong>18</strong>: FOSSILS AND GEOLOGIC TIME<br />
internal hard parts appeared about 545 million years ago.<br />
These organisms eventually gave rise to the complex lifeforms<br />
that exist today. The gradual change in living organisms<br />
from generation to generation is known as evolution.<br />
Although it is called a theory, organic evolution is one of the<br />
most fundamental ideas of science.<br />
The Work of Darwin<br />
Organic evolution became accepted by most scientists after<br />
Charles Darwin published On the Origin of Species by Means<br />
of Natural Selection” in <strong>18</strong>59. A species can be defined as a<br />
group of organisms so similar they can breed to produce fertile<br />
offspring. Humans are a good example of a biological<br />
species. Darwin based his book on scientific observations <strong>and</strong><br />
extensive travel. He spent many years organizing his ideas<br />
about the development of life before he published his book. In<br />
fact, Alfred Russell Wallace independently arrived at similar<br />
conclusions at about the same time.<br />
Four Principles of Evolution<br />
Organic evolution is based on four principles. First, variations<br />
exist among individuals within a species. Besides differences<br />
in size <strong>and</strong> shape, individual organisms have different abilities<br />
to find food, resist disease, <strong>and</strong> reproduce effectively. Second,<br />
organisms usually produce more offspring than the<br />
environment can support. Think of the thous<strong>and</strong>s of seeds<br />
many trees produce or the number of eggs one salmon can lay.<br />
If all these offspring survived, the world would be overrun<br />
with just trees <strong>and</strong> salmon. The third principle is the effect of<br />
competition among individuals of a given generation. Organisms<br />
die for a variety of reasons, but those best suited to their<br />
environment are most likely to survive. Fourth, the individuals<br />
best suited to the environment will live long enough to reproduce<br />
<strong>and</strong> pass their traits to following generations. This is<br />
what Darwin meant by natural selection.