Chapter 17 Unraveling Geologic History
Chapter 17 Unraveling Geologic History
Chapter 17 Unraveling Geologic History
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
408 CHAPTER <strong>17</strong>: UNRAVELING GEOLOGIC HISTORY<br />
10. The absolute age of an igneous rock can best be determined by<br />
(1) comparing the amount of decayed and undecayed radioactive isotopes<br />
in the rock.<br />
(2) comparing the sizes of the crystals found in the upper and lower parts<br />
of the rock.<br />
(3) examining the rock’s relative position in a rock outcrop.<br />
(4) examining the environment in which the rock is found.<br />
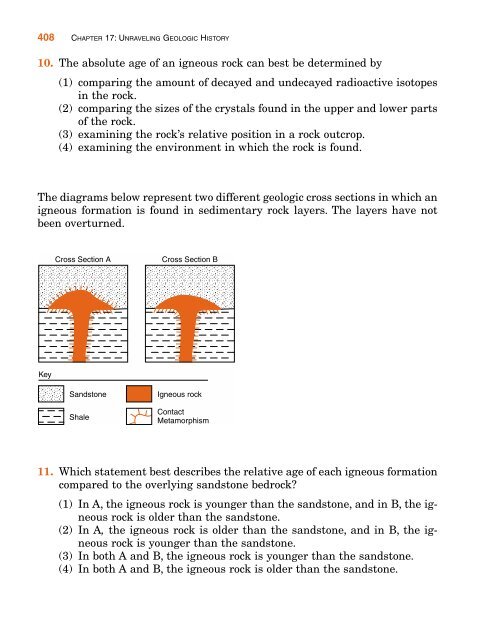
The diagrams below represent two different geologic cross sections in which an<br />
igneous formation is found in sedimentary rock layers. The layers have not<br />
been overturned.<br />
Key<br />
Cross Section A Cross Section B<br />
Sandstone<br />
Shale<br />
Igneous rock<br />
Contact<br />
Metamorphism<br />
11. Which statement best describes the relative age of each igneous formation<br />
compared to the overlying sandstone bedrock?<br />
(1) In A, the igneous rock is younger than the sandstone, and in B, the igneous<br />
rock is older than the sandstone.<br />
(2) In A, the igneous rock is older than the sandstone, and in B, the igneous<br />
rock is younger than the sandstone.<br />
(3) In both A and B, the igneous rock is younger than the sandstone.<br />
(4) In both A and B, the igneous rock is older than the sandstone.