gentamicin protocol - Hampshire Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
gentamicin protocol - Hampshire Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
gentamicin protocol - Hampshire Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
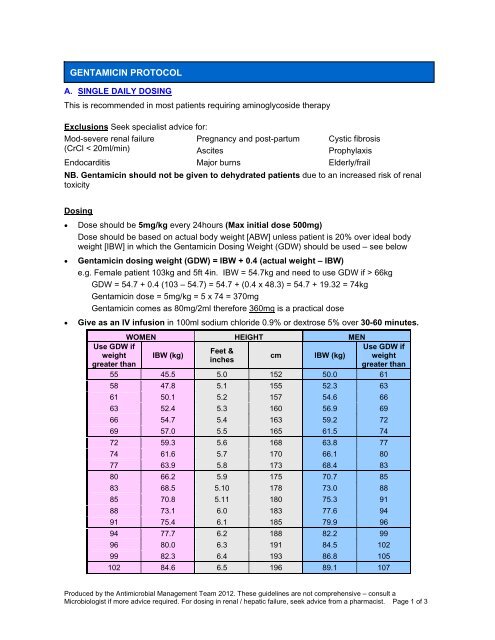
GENTAMICIN PROTOCOL<br />
A. SINGLE DAILY DOSING<br />
This is recommended in most patients requiring aminoglycoside therapy<br />
Exclusions Seek specialist advice for:<br />
Mod-severe renal failure<br />
(CrCl < 20ml/min)<br />
Endocarditis<br />
Pregnancy and post-partum<br />
Ascites<br />
Major burns<br />
Cystic fibrosis<br />
Prophylaxis<br />
Elderly/frail<br />
NB. Gentamicin should not be given to dehydrated patients due to an increased risk of renal<br />
toxicity<br />
Dosing<br />
• Dose should be 5mg/kg every 24hours (Max initial dose 500mg)<br />
Dose should be based on actual body weight [ABW] unless patient is 20% over ideal body<br />
weight [IBW] in which the Gentamicin Dosing Weight (GDW) should be used – see below<br />
• Gentamicin dosing weight (GDW) = IBW + 0.4 (actual weight – IBW)<br />
e.g. Female patient 103kg and 5ft 4in. IBW = 54.7kg and need to use GDW if > 66kg<br />
GDW = 54.7 + 0.4 (103 – 54.7) = 54.7 + (0.4 x 48.3) = 54.7 + 19.32 = 74kg<br />
Gentamicin dose = 5mg/kg = 5 x 74 = 370mg<br />
Gentamicin comes as 80mg/2ml therefore 360mg is a practical dose<br />
• Give as an IV infusion in 100ml sodium chloride 0.9% or dextrose 5% over 30-60 minutes.<br />
Use GDW if<br />
weight<br />
greater than<br />
WOMEN HEIGHT MEN<br />
IBW (kg)<br />
Feet &<br />
inches<br />
cm<br />
IBW (kg)<br />
Use GDW if<br />
weight<br />
greater than<br />
55 45.5 5.0 152 50.0 61<br />
58 47.8 5.1 155 52.3 63<br />
61 50.1 5.2 157 54.6 66<br />
63 52.4 5.3 160 56.9 69<br />
66 54.7 5.4 163 59.2 72<br />
69 57.0 5.5 165 61.5 74<br />
72 59.3 5.6 168 63.8 77<br />
74 61.6 5.7 170 66.1 80<br />
77 63.9 5.8 173 68.4 83<br />
80 66.2 5.9 175 70.7 85<br />
83 68.5 5.10 178 73.0 88<br />
85 70.8 5.11 180 75.3 91<br />
88 73.1 6.0 183 77.6 94<br />
91 75.4 6.1 185 79.9 96<br />
94 77.7 6.2 188 82.2 99<br />
96 80.0 6.3 191 84.5 102<br />
99 82.3 6.4 193 86.8 105<br />
102 84.6 6.5 196 89.1 107<br />
Produced by the Antimicrobial Management Team 2012. These guidelines are not comprehensive – consult a<br />
Microbiologist if more advice required. For dosing in renal / hepatic failure, seek advice from a pharmacist. Page 1 of 3
Monitoring<br />
1. Arrange for bloods to be taken 6–14 hours after the first dose – this is the prescriber’s<br />
responsibility<br />
2. Take 5-10mls blood in a clotted tube (yellow top)<br />
3. Record the exact sampling time and date of blood sample on request form<br />
4. Record exact time and date of last <strong>gentamicin</strong> dose administered on request form<br />
5. Use the Urban-Craig nomogram (below) to assess the Gentamicin level and establish the<br />
dosing interval<br />
6. If <strong>gentamicin</strong> level falls into the q24hr range (appropriate for 24hourly dosing) and renal function<br />
is stable, there is no need to recheck level unless Gentamicin therapy continues beyond 5 days<br />
7. Trough/pre-dose Gentamicin levels (within 2hours of the dose) should be checked twice weekly<br />
if Gentamicin continues beyond 5days and renal function is stable. Trough levels should be<br />
less than 1mg/L before redosing.<br />
8. If the renal function is unstable or the patient requires a dosing interval greater than 24hourly,<br />
discuss frequency of monitoring with a Pharmacist or Microbiologist<br />
9. Monitor serum creatinine at least twice a week or daily if renal function is unstable.<br />
10. Additive toxicity is likely with concomitant nephrotoxic agents e.g. IV Furosemide, Amphotericin<br />
B, Ciclosporin, Cisplatin, Colistin, Methotrexate, radio-contrast media, glycopeptide antibiotics,<br />
Tacrolimus, ACE inhibitors<br />
URBAN-CRAIG NOMOGRAM FOR 5MG/KG GENTAMICIN DOSING ONLY<br />
Produced by the Antimicrobial Management Team 2012. These guidelines are not comprehensive – consult a<br />
Microbiologist if more advice required. For dosing in renal / hepatic failure, seek advice from a pharmacist. Page 2 of 3
Trouble-shooting<br />
• If first level is missed and if renal function is stable and within normal range (i.e. eGFR ><br />
50ml/min and urine output is normal): give 2 nd dose after 24hours and take Gentamicin level 6–<br />
14 hours after 2 nd dose. Seek advice if the level has not been taken after this time.<br />
• If first level is missed and renal function is deranged or urine output has dropped, DO NOT<br />
redose until Gentamicin level < 1mg/L<br />
• If renal function improves during Gentamicin treatment, recheck 6-14hour post-dose level to<br />
ensure dosing interval has not changed<br />
B. MULTIPLE DAILY DOSING<br />
This regimen is recommended for Gram positive Endocarditis<br />
• In these cases, the dose recommended is 1mg/Kg (Ideal Body Weight) 12hourly.<br />
• Give as an intravenous infusion in 100ml glucose 5% or sodium chloride 0.9%, over 30-60<br />
minutes<br />
Monitoring<br />
1. Arrange for bloods to be taken 1hour pre and 1hour post the third dose after start of<br />
therapy or change in dosing – this is the prescriber’s responsibility<br />
2. Take 5-10mls blood in a clotted tube (yellow top)<br />
3. Record the exact sampling time and date of blood sample on request form and medical<br />
notes<br />
4. Record exact time and date of last <strong>gentamicin</strong> dose administered on request form and<br />
medical notes<br />
5. Pre-dose (trough) levels should be less than 1mg/L<br />
6. Peak (post-dose) levels should be between 3-5mg/L<br />
7. If <strong>gentamicin</strong> levels fall within range and renal function is stable, recheck pre-dose levels<br />
weekly (levels should be less than 1mg/l).<br />
8. If the renal function is unstable or the patient requires a dosing interval greater than 12hourly,<br />
discuss frequency of monitoring with a Pharmacist or Microbiologist<br />
9. Monitor serum creatinine at least twice a week or daily if renal function is unstable.<br />
10. Additive toxicity is likely with concomitant nephrotoxic agents e.g. IV Furosemide, Amphotericin<br />
B, Ciclosporin, Cisplatin, Colistin, Methotrexate, radio-contrast media, glycopeptide antibiotics,<br />
Tacrolimus, ACE inhibitors<br />
Produced by the Antimicrobial Management Team 2012. These guidelines are not comprehensive – consult a<br />
Microbiologist if more advice required. For dosing in renal / hepatic failure, seek advice from a pharmacist. Page 3 of 3