Automatic Vertebra Detection in X-Ray Images - Faculdade de ...
Automatic Vertebra Detection in X-Ray Images - Faculdade de ...
Automatic Vertebra Detection in X-Ray Images - Faculdade de ...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
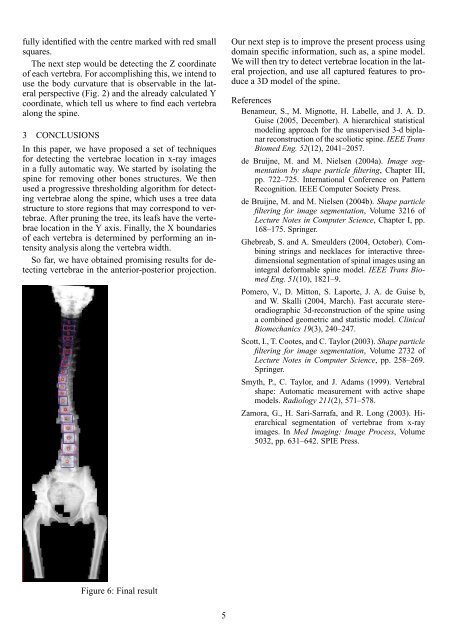
fully i<strong>de</strong>ntified with the centre marked with red small<br />
squares.<br />
The next step would be <strong>de</strong>tect<strong>in</strong>g the Z coord<strong>in</strong>ate<br />
of each vertebra. For accomplish<strong>in</strong>g this, we <strong>in</strong>tend to<br />
use the body curvature that is observable <strong>in</strong> the lateral<br />
perspective (Fig. 2) and the already calculated Y<br />
coord<strong>in</strong>ate, which tell us where to f<strong>in</strong>d each vertebra<br />
along the sp<strong>in</strong>e.<br />
3 CONCLUSIONS<br />
In this paper, we have proposed a set of techniques<br />
for <strong>de</strong>tect<strong>in</strong>g the vertebrae location <strong>in</strong> x-ray images<br />
<strong>in</strong> a fully automatic way. We started by isolat<strong>in</strong>g the<br />
sp<strong>in</strong>e for remov<strong>in</strong>g other bones structures. We then<br />
used a progressive threshold<strong>in</strong>g algorithm for <strong>de</strong>tect<strong>in</strong>g<br />
vertebrae along the sp<strong>in</strong>e, which uses a tree data<br />
structure to store regions that may correspond to vertebrae.<br />
After prun<strong>in</strong>g the tree, its leafs have the vertebrae<br />
location <strong>in</strong> the Y axis. F<strong>in</strong>ally, the X boundaries<br />
of each vertebra is <strong>de</strong>term<strong>in</strong>ed by perform<strong>in</strong>g an <strong>in</strong>tensity<br />
analysis along the vertebra width.<br />
So far, we have obta<strong>in</strong>ed promis<strong>in</strong>g results for <strong>de</strong>tect<strong>in</strong>g<br />
vertebrae <strong>in</strong> the anterior-posterior projection.<br />
Our next step is to improve the present process us<strong>in</strong>g<br />
doma<strong>in</strong> specific <strong>in</strong>formation, such as, a sp<strong>in</strong>e mo<strong>de</strong>l.<br />
We will then try to <strong>de</strong>tect vertebrae location <strong>in</strong> the lateral<br />
projection, and use all captured features to produce<br />
a 3D mo<strong>de</strong>l of the sp<strong>in</strong>e.<br />
References<br />
Benameur, S., M. Mignotte, H. Labelle, and J. A. D.<br />
Guise (2005, December). A hierarchical statistical<br />
mo<strong>de</strong>l<strong>in</strong>g approach for the unsupervised 3-d biplanar<br />
reconstruction of the scoliotic sp<strong>in</strong>e. IEEE Trans<br />
Biomed Eng. 52(12), 2041–2057.<br />
<strong>de</strong> Bruijne, M. and M. Nielsen (2004a). Image segmentation<br />
by shape particle filter<strong>in</strong>g, Chapter III,<br />
pp. 722–725. International Conference on Pattern<br />
Recognition. IEEE Computer Society Press.<br />
<strong>de</strong> Bruijne, M. and M. Nielsen (2004b). Shape particle<br />
filter<strong>in</strong>g for image segmentation, Volume 3216 of<br />
Lecture Notes <strong>in</strong> Computer Science, Chapter I, pp.<br />
168–175. Spr<strong>in</strong>ger.<br />
Ghebreab, S. and A. Smeul<strong>de</strong>rs (2004, October). Comb<strong>in</strong><strong>in</strong>g<br />
str<strong>in</strong>gs and necklaces for <strong>in</strong>teractive threedimensional<br />
segmentation of sp<strong>in</strong>al images us<strong>in</strong>g an<br />
<strong>in</strong>tegral <strong>de</strong>formable sp<strong>in</strong>e mo<strong>de</strong>l. IEEE Trans Biomed<br />
Eng. 51(10), 1821–9.<br />
Pomero, V., D. Mitton, S. Laporte, J. A. <strong>de</strong> Guise b,<br />
and W. Skalli (2004, March). Fast accurate stereoradiographic<br />
3d-reconstruction of the sp<strong>in</strong>e us<strong>in</strong>g<br />
a comb<strong>in</strong>ed geometric and statistic mo<strong>de</strong>l. Cl<strong>in</strong>ical<br />
Biomechanics 19(3), 240–247.<br />
Scott, I., T. Cootes, and C. Taylor (2003). Shape particle<br />
filter<strong>in</strong>g for image segmentation, Volume 2732 of<br />
Lecture Notes <strong>in</strong> Computer Science, pp. 258–269.<br />
Spr<strong>in</strong>ger.<br />
Smyth, P., C. Taylor, and J. Adams (1999). <strong>Vertebra</strong>l<br />
shape: <strong>Automatic</strong> measurement with active shape<br />
mo<strong>de</strong>ls. Radiology 211(2), 571–578.<br />
Zamora, G., H. Sari-Sarrafa, and R. Long (2003). Hierarchical<br />
segmentation of vertebrae from x-ray<br />
images. In Med Imag<strong>in</strong>g: Image Process, Volume<br />
5032, pp. 631–642. SPIE Press.<br />
Figure 6: F<strong>in</strong>al result<br />
5