Lec14
Lec14
Lec14
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
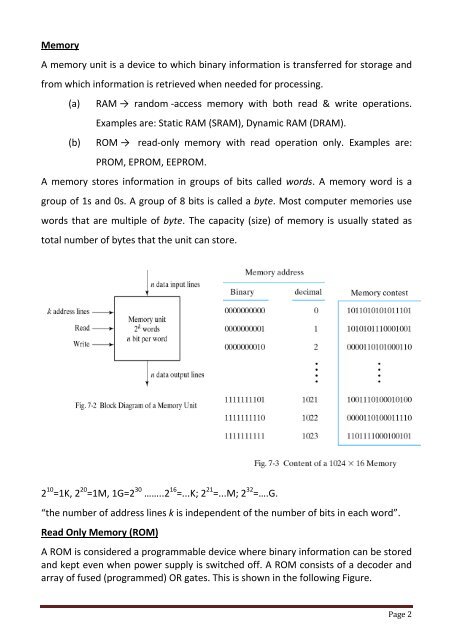
Memory<br />
A memory unit is a device to which binary information is transferred for storage and<br />
from which information is retrieved when needed for processing.<br />
(a) RAM → random -access memory with both read & write operations.<br />
Examples are: Static RAM (SRAM), Dynamic RAM (DRAM).<br />
(b) ROM → read-only memory with read operation only. Examples are:<br />
PROM, EPROM, EEPROM.<br />
A memory stores information in groups of bits called words. A memory word is a<br />
group of 1s and 0s. A group of 8 bits is called a byte. Most computer memories use<br />
words that are multiple of byte. The capacity (size) of memory is usually stated as<br />
total number of bytes that the unit can store.<br />
2 10 =1K, 2 20 =1M, 1G=2 30 ……..2 16 =...K; 2 21 =...M; 2 32 =….G.<br />
“the number of address lines k is independent of the number of bits in each word”.<br />
Read Only Memory (ROM)<br />
A ROM is considered a programmable device where binary information can be stored<br />
and kept even when power supply is switched off. A ROM consists of a decoder and<br />
array of fused (programmed) OR gates. This is shown in the following Figure.<br />
Page 2