Drug-Induced Immune-Mediated Thrombocytopenia ... - Hem-aids.ru
Drug-Induced Immune-Mediated Thrombocytopenia ... - Hem-aids.ru
Drug-Induced Immune-Mediated Thrombocytopenia ... - Hem-aids.ru
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
PERSPECTIVE<br />
<strong>D<strong>ru</strong>g</strong>-<strong>Induced</strong> <strong>Immune</strong>-<strong>Mediated</strong> <strong>Thrombocytopenia</strong> — From Purpura to Thrombosis<br />
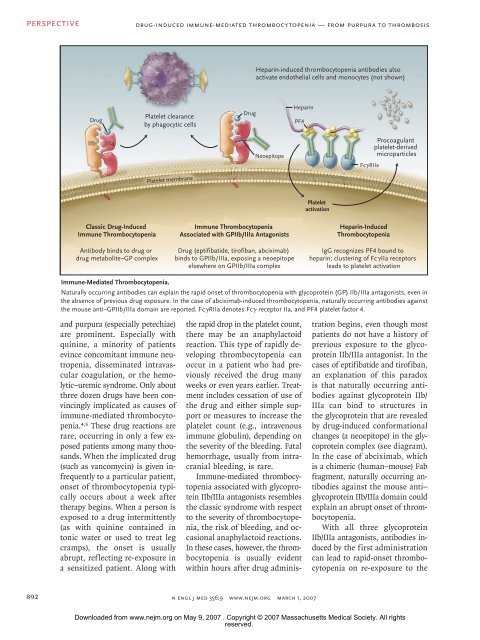
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia antibodies also<br />
activate endothelial cells and monocytes (not shown)<br />
<strong>D<strong>ru</strong>g</strong><br />
Platelet clearance<br />
by phagocytic cells<br />
<strong>D<strong>ru</strong>g</strong><br />
Heparin<br />
PF4<br />
IIb<br />
IIIa<br />
Neoepitope<br />
FcγRIIa<br />
Procoagulant<br />
platelet-derived<br />
microparticles<br />
Platelet membrane<br />
Platelet<br />
activation<br />
Classic <strong>D<strong>ru</strong>g</strong>-<strong>Induced</strong><br />
<strong>Immune</strong> <strong>Thrombocytopenia</strong><br />
Antibody binds to d<strong>ru</strong>g or<br />
d<strong>ru</strong>g metabolite–GP complex<br />
<strong>Immune</strong> <strong>Thrombocytopenia</strong><br />
Associated with GPIIb/IIIa Antagonists<br />
<strong>D<strong>ru</strong>g</strong> (eptifibatide, tirofiban, abciximab)<br />
binds to GPIIb/IIIa, exposing a neoepitope<br />
elsewhere on GPIIb/IIIa complex<br />
Heparin-<strong>Induced</strong><br />
<strong>Thrombocytopenia</strong><br />
IgG recognizes PF4 bound to<br />
heparin; clustering of FcγIIa receptors<br />
leads to platelet activation<br />
<strong>Immune</strong>-<strong>Mediated</strong> <strong>Thrombocytopenia</strong>.<br />
COLOR FIGURE<br />
Naturally occurring antibodies can explain the rapid onset of thrombocytopenia with glycoprotein (GP) IIb/IIIa antagonists, even in<br />
the absence of previous d<strong>ru</strong>g exposure. In the case of abciximab-induced thrombocytopenia, naturally occurring Draft 7 antibodies 2/06/07 against<br />
Author Warketin<br />
the mouse anti–GPIIb/IIIa domain are reported. FcγRIIa denotes Fcγ receptor IIa, and PF4 platelet factor 4.<br />
Fig # 2<br />
Title<br />
and purpura (especially petechiae)<br />
are prominent. Especially with<br />
quinine, a minority of patients<br />
evince concomitant immune neutropenia,<br />
disseminated intravascular<br />
coagulation, or the hemolytic–uremic<br />
syndrome. Only about<br />
three dozen d<strong>ru</strong>gs have been convincingly<br />
implicated as causes of<br />
immune-mediated thrombocytopenia.<br />
4,5 These d<strong>ru</strong>g reactions are<br />
rare, occurring in only a few exposed<br />
patients among many thousands.<br />
When the implicated d<strong>ru</strong>g<br />
(such as vancomycin) is given infrequently<br />
to a particular patient,<br />
onset of thrombocytopenia typically<br />
occurs about a week after<br />
therapy begins. When a person is<br />
exposed to a d<strong>ru</strong>g intermittently<br />
(as with quinine contained in<br />
tonic water or used to treat leg<br />
cramps), the onset is usually<br />
ab<strong>ru</strong>pt, reflecting re-exposure in<br />
a sensitized patient. Along with<br />
the rapid drop in the platelet count,<br />
there may be an anaphylactoid<br />
reaction. This type of rapidly developing<br />
thrombocytopenia can<br />
occur in a patient who had previously<br />
received the d<strong>ru</strong>g many<br />
weeks or even years earlier. Treatment<br />
includes cessation of use of<br />
the d<strong>ru</strong>g and either simple support<br />
or measures to increase the<br />
platelet count (e.g., intravenous<br />
immune globulin), depending on<br />
the severity of the bleeding. Fatal<br />
hemorrhage, usually from intracranial<br />
bleeding, is rare.<br />
<strong>Immune</strong>-mediated thrombocytopenia<br />
associated with glycoprotein<br />
IIb/IIIa antagonists resembles<br />
the classic syndrome with respect<br />
to the severity of thrombocytopenia,<br />
the risk of bleeding, and occasional<br />
anaphylactoid reactions.<br />
In these cases, however, the thrombocytopenia<br />
is usually evident<br />
within hours after d<strong>ru</strong>g adminis-<br />
<strong>D<strong>ru</strong>g</strong>-<strong>Induced</strong> <strong>Immune</strong> <strong>Thrombocytopenia</strong><br />
tration begins, ME even CH though most<br />
patients do DE Schwartz<br />
not have a history of<br />
Artist KMK<br />
previous exposure AUTHOR to PLEASE the NOTE: glycoprotein<br />
IIb/IIIa antagonist. In the<br />
Please check carefully<br />
Figure has been redrawn and type has been reset<br />
Issue date<br />
cases of eptifibatide 3/1/07 and tirofiban,<br />
an explanation of this paradox<br />
is that naturally occurring antibodies<br />
against glycoprotein IIb/<br />
IIIa can bind to st<strong>ru</strong>ctures in<br />
the glycoprotein that are revealed<br />
by d<strong>ru</strong>g-induced conformational<br />
changes (a neoepitope) in the glycoprotein<br />
complex (see diagram).<br />
In the case of abciximab, which<br />
is a chimeric (human–mouse) Fab<br />
fragment, naturally occurring antibodies<br />
against the mouse anti–<br />
glycoprotein IIb/IIIa domain could<br />
explain an ab<strong>ru</strong>pt onset of thrombocytopenia.<br />
With all three glycoprotein<br />
IIb/IIIa antagonists, antibodies induced<br />
by the first administration<br />
can lead to rapid-onset thrombocytopenia<br />
on re-exposure to the<br />
892<br />
n engl j med 356;9 www.nejm.org march 1, 2007<br />
Downloaded from www.nejm.org on May 9, 2007 . Copyright © 2007 Massachusetts Medical Society. All rights<br />
reserved.